Research Projects
Pamoramic vision data analysis, processing and VR interaction, Key Program,
National Natural Science Foundation,
PI: Song-Hai Zhang, Project Number: 6213000127, 2022-2026.
Deep learning algorithm and framework for computational visual media,
Key International Joint Research Program, National Natural Science Foundation,
PI: Shi-Min Hu, Project number: 62220106003, 2023-2027.
Narrative Visual Content Creation and Immersive Interaction of Panoramic Video,
International Cooperation and Exchange Programs (NSFC-ISF), National Natural Science Foundation,
PI: Song-Hai Zhang, Project number: 62361146854, 2024-2026.
Deep Learning Framework and Large Model Application Verification for Complex
Heterogeneous Computing Systems, Majar Program, National Natural Science Foundation,
PI: Shi-Min Hu, Project number: 62495060, 2025-2029.
2025
Fast Galerkin Multigrid Method for Unstructured Meshes
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2025, Vol.44, No.6, Article No.179, 1 - 16.

Jia-Ming Lu, Tailing Yuan, Zhe-Han Mo, Shi-Min Hu
This research presents an efficient multigrid solver for deformable body simulations
on unstructured tetrahedral meshes. The method combines the Full Approximation Scheme
with Galerkin formulation and introduces a matrix-free vertex block Jacobi smoother
that eliminates the computational burden of dense coarse matrices. The approach
supports both piecewise constant and linear Galerkin formulations and achieves up to
6.9x speedup over traditional methods. Comprehensive GPU optimization techniques address
parallel architecture challenges through Morton sorting, grid reduction, and spatial hashing.
Extensive experiments demonstrate robust convergence across varying mesh resolutions,
material stiffness values, extreme deformations, and complex collision scenarios, enabling
practical simulation of million-vertex meshes at interactive frame rates.
RBench-V: A Primary Assessment for Visual Reasoning Models with Multimodal Outputs
NeurIPS 2025 Datasets and Benchmarks Track, 2025.

Meng-Hao Guo, Xuanyu Chu, Qianrui Yang, Zhe-Han Mo, Yiqing Shen, Pei-lin Li, Xinjie Lin, Jinnian Zhang, Xin-Sheng Chen, Yi Zhang, Kiyohiro Nakayama, Zhengyang Geng, Houwen Peng, Han Hu, Shi-Min Hu
The rapid advancement of native multi-modal models and omni-models, exemplified by GPT-4o,
Gemini and o3 with their capability to process and generate content across modalities such
as text and images, marks a significant milestone in the evolution of intelligence.
Systematic evaluation of their multi-modal output capabilities in visual thinking process
(a.k.a., multi-modal chain of thought, M-CoT) becomes critically important. However,
existing benchmarks for evaluating multi-modal models primarily focus on assessing
multi-modal inputs and text-only reasoning process while neglecting the importance of
reasoning through multi-modal outputs. In this paper, we present a benchmark, dubbed as
RBench-V, designed to assess models¡¯ vision-indispensable reasoning. To conduct RBench-V,
we carefully hand-pick 803 questions covering math, physics, counting and games. Unlike
problems in previous benchmarks, which typically specify certain input modalities,
RBench-V presents problems centered on multi-modal outputs, which require image
manipulation, such as generating novel images and constructing auxiliary lines to
support reasoning process. We evaluate numerous open- and closed-source models on RBench-V,
including o3, Gemini 2.5 pro, Qwen2.5-VL, etc. Even the best-performing model, o3, achieves
only 25.8% accuracy on RBench-V, far below the human score of 82.3%, which shows
current models struggle to leverage multi-modal reasoning. Data and code are available
at https://evalmodels.github.io/rbenchv.
One Model to Rig Them All: Diverse Skeleton Rigging with UniRig
Simulation
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2025, Vol.44, No.4, Article No.123, 1 - 19.

Jia-Peng Zhang, Cheng-Feng Pu, Meng-Hao Guo, Yan-Pei Cao, Shi-Min Hu
The rapid evolution of 3D content creation, encompassing both AI-powered
methods and traditional workflows, is driving an unprecedented demand
for automated rigging solutions that can keep pace with the increasing
complexity and diversity of 3D models. We introduce UniRig, a novel, unified
framework for automatic skeletal rigging that leverages the power of large
autoregressive models and a bone-point cross-attention mechanism to generate
both high-quality skeletons and skinning weights. Unlike previous
methods that struggle with complex or non-standard topologies, UniRig
accurately predicts topologically valid skeleton structures thanks to a new
Skeleton Tree Tokenization method that efficiently encodes hierarchical
relationships within the skeleton. To train and evaluate UniRig, we present
Rig-XL, a new large-scale dataset of over 14,000 rigged 3D models spanning
a wide range of categories. UniRig significantly outperforms state-of-the-art
academic and commercial methods, achieving a 215% improvement in rigging
accuracy and a 194% improvement in motion accuracy on challenging
datasets. Our method works seamlessly across diverse object categories,
from detailed anime characters to complex organic and inorganic structures,
demonstrating its versatility and robustness. By automating the tedious
and time-consuming rigging process, UniRig has the potential to speed up
animation pipelines with unprecedented ease and efficiency. Project Page:
https://zjp-shadow.github.io/works/UniRig/
RBench: Graduate-level Multi-disciplinary Benchmarks for LLM & MLLM Complex Reasoning Evaluation
Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Vancouver, Canada. PMLR 267, 2025.

Meng-Hao Guo, Jiajun Xu, Yi Zhang, Jiaxi Song, Haoyang Peng, Yi-Xuan Deng,
Xinzhi Dong, Kiyohiro Nakayama, Zhengyang Geng, Chen Wang, Bolin Ni, Guo-Wei Yang,
Yongming Rao, Houwen Peng, Han Hu, Gordon Wetzstein, Shi-min Hu
Reasoning stands as a cornerstone of intelligence, enabling the synthesis of
existing knowledge to solve complex problems. Despite remarkable progress,
existing reasoning benchmarks often fail to rigorously evaluate the nuanced
reasoning capabilities required for complex, real-world problemsolving,
particularly in multi-disciplinary and multimodal contexts. In this paper,
we introduce a graduate-level, multi-disciplinary, EnglishChinese benchmark,
dubbed as Reasoning Bench (RBench), for assessing the reasoning capability
of both language and multimodal models. RBench spans 1,094 questions across
108 subjects for language model evaluation and 665 questions across 83 subjects
for multimodal model testing. These questions are meticulously curated to
ensure rigorous difficulty calibration, subject balance, and cross-linguistic
alignment, enabling the assessment to be an Olympiad-level multidisciplinary
benchmark. We evaluate many models such as o1, GPT-4o, DeepSeek-R1, etc.
Experimental results indicate that advanced models perform poorly on complex
reasoning, especially multimodal reasoning. Even the top-performing model
OpenAI o1 achieves only 53.2% accuracy on our multimodal evaluation. Data and
code are made publicly available athttps://evalmodels.github.io/rbench/
Reliable Iterative Dynamics: A Versatile Method for Fast and Robust
Simulation
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2025, Vol.44, No.3, Article No.29, 1 - 18.

Jia-Ming Lu, Shi-Min Hu
Simulating stiff materials has long posed formidable challenges for traditional
physics-based solvers. Explicit time integration schemes demand
prohibitively small time steps, while implicit methods necessitate an excessive
number of iterations to converge, often yielding visually objectionable
transient configurations in the early iterations, severely limiting their
real-time applicability. Position-based dynamics techniques can efficiently
simulate stiff constraints but are inherently restricted to constraint-based
formulations, curtailing their versatility.We present "Reliable Iterative Dynamics"
(RID), a novel iterative solver that introduces a dual descent framework
with theoretical guarantees for visual reliability at each iteration,
while maintaining fast and stable convergence even for extremely stiff systems.
Our core innovation is an iterativemethod that circumvents the need
for numerous iterations or small time steps to handle stiff materials robustly.
Experimental evaluations demonstrate our method¡¯s ability to handle
a wide range of materials, from soft to infinitely rigid, while producing
visually reliable results even with large time steps and minimal iterations.
The versatile formulation allows seamless integration with diverse simulation
paradigms like the finite element method, material point method,
smoothed particle hydrodynamics, and incremental potential contact for
applications ranging from elastic body simulations to fluids and collision
handling.
Adaptive Parameter Selection for Tuning Vision-Language Models
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025, 4280-4290.

Yi Zhang, Yi-Xuan Deng, Meng-Hao Guo, Shi-Min Hu
Vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP have been widely used in various specific tasks.
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, such as prompt and adapter tuning,
have become key techniques for adapting these models to specific domains.
However, existing approaches rely on prior knowledgeto manually identify the locations
requiring fine-tuning.Adaptively selecting which parameters in VLMs should be tuned remains
unexplored. In this paper, we propose CLIP with Adaptive Selective Tuning (CLIP-AST),
which can be used to automatically select critical parameters in VLMs for fine-tuning
for specific tasks.It opportunely leveragesthe adaptive learning rate in the optimizer
and improves model performance without extra parameter overhead. We conduct extensive
experiments on 13 benchmarks, such as ImageNet, Food101, Flowers102, etc,with different
settings, including few-shot learning, base-to-novel class generalization, and
out-of-distribution. The results show that CLIP-AST consistently outperforms the original
CLIP model as well as its variantsand achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in all
cases. For example, with the 16-shot learning, CLIP-AST surpasses GraphAdapter and PromptSRC
by 3.56% and 2.20% in average accuracy on 11 datasets, respectively. Code will be
publicly available.
Splatter-360: Generalizable 360? Gaussian Splatting for Wide-baseline
Panoramic Images
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025, 21590-21598.

Zheng Chen, Chenming Wu, Zhelun Shen, Chen Zhao, Weicai Ye, Haocheng Feng, Errui Ding, Song-Hai Zhang
Vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP have been widely used in various specific tasks.
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, such as prompt and adapter tuning,
have become key techniques for adapting these models to specific domains.
However, existing approaches rely on prior knowledgeto manually identify the locations
requiring fine-tuning.Adaptively selecting which parameters in VLMs should be tuned remains
unexplored. In this paper, we propose CLIP with Adaptive Selective Tuning (CLIP-AST),
which can be used to automatically select critical parameters in VLMs for fine-tuning
for specific tasks.It opportunely leveragesthe adaptive learning rate in the optimizer
and improves model performance without extra parameter overhead. We conduct extensive
experiments on 13 benchmarks, such as ImageNet, Food101, Flowers102, etc,with different
settings, including few-shot learning, base-to-novel class generalization, and
out-of-distribution. The results show that CLIP-AST consistently outperforms the original
CLIP model as well as its variantsand achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in all
cases. For example, with the 16-shot learning, CLIP-AST surpasses GraphAdapter and PromptSRC
by 3.56% and 2.20% in average accuracy on 11 datasets, respectively. Code will be
publicly available.
MeGA: Hybrid Mesh-Gaussian Head Avatar for High-Fidelity Rendering and Head Editing
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025, 26274-26284.


Cong Wang, Di Kang, Heyi Sun, Shenhan Qian, Zixuan Wang, Linchao Bao, Song-Hai Zhang
Creating high-fidelity head avatars from multi-view videos is essential for many AR/VR applications.
However, current methods often struggle to achieve high-quality renderings across all head components
(e.g., skin vs. hair) due to the limitations of using one single representation for elements with
varying characteristics. In this paper, we introduce a Hybrid Mesh-Gaussian Head Avatar (MeGA)
that models different head components with more suitable representations. Specifically,
we employ an enhanced FLAME mesh for the facial representation and predict a UV displacement
map to provide per-vertex offsets for improved personalized geometric details.
To achieve photorealistic rendering, we use deferred neural rendering to obtain facial
colors and decompose neural textures into three meaningful parts. For hair modeling,
we first build a static canonical hair using 3D Gaussian Splatting. A rigid transformation
and an MLP-based deformation field are further applied to handle complex dynamic expressions.
Combined with our occlusion-aware blending, MeGA generates higher-fidelity renderings for
the whole head and naturally supports diverse downstream tasks. Experiments on the NeRSemble
dataset validate the effectiveness of our designs, outperforming previous state-of-the-art
methods and enabling versatile editing capabilities, including hairstyle alteration and texture editing.
Implicit Bonded Discrete Element Method with Manifold Optimization
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2025, Vol.44, No.1, Article No.9, 1 - 17.

Jia-Ming Lu, Geng-Chen Cao, Chenfeng Li, Shi-Min Hu
This paper proposes a novel simulation approach that combines implicit integration with the
Bonded Discrete Element Method (BDEM) to achieve faster, more stable and more accurate
fracture simulation. The new method leverages the eiciency of implicit schemes in dynamic
simulation and the versatility of BDEM in fracture modelling. Speciically, an
optimization-based integrator for BDEM is introduced and combined with a manifold optimization
approach to accelerate the solution process of the quaternion-constrained system. Our
comparative experiments indicate that our method ofers better scale consistency and more
realistic collision efects than FEM and MPM fragmentation approaches. Additionally, our method
achieves a computational speedup of 2.1 ~ 9.8 times over explicit BDEM methods.
Diffusion models for 3D generation: A survey
Computational Visual Media, 2025, Vol. 11, No.1, 1-28.

Chen Wang, Hao-Yang Peng, Ying-Tian Liu, Jiatao Gu, Shi-Min Hu
Denoising diffusion models have demonstrated tremendous success in modeling data
distributions and synthesizing high-quality samples. In the 2D image domain,
they have become the state-of-the-art and are capable of generating
photo-realistic images with high controllability. More recently, researchers
have begun to explore how to utilize diffusion models to generate 3D data,
as doing so has more potential in real-world applications. This requires careful
design choices in two key ways: identifying a suitable 3D representation and
determining how to apply the diffusion process. In this survey, we provide the
first comprehensive review of diffusion models for manipulating 3D content,
including 3D generation, reconstruction, and 3D-aware image synthesis.
We classify existing methods into three major categories: 2D space diffusion with
pretrained models, 2D space diffusion without pretrained models, and 3D space
diffusion. We also summarize popular datasets used for 3D generation with diffusion
models. Along with this survey, we maintain a repository
https://github.com/cwchenwang/awesome-3d-diffusion
to track the latest relevant papers and codebases. Finally, we pose current
challenges for diffusion models for 3D generation, and suggest future research directions.
2024
Tuning Vision-Language Models With Multiple Prototypes Clustering
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, Vol. 46, No. 12, 11186-11199.

Meng-Hao Guo, Yi Zhang, Tai-Jiang Mu, Sharon X. Huang, Shi-Min Hu
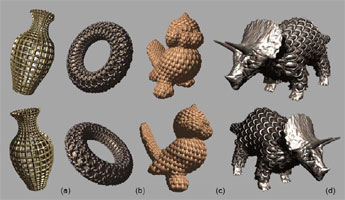
Attention mechanisms, especially self-attention, have played an increasingly important role
in deep feature representation for visual tasks. Self-attention updates the feature at each
position by computing a weighted sum of features using pair-wise affinities across all positions
to capture the long-range dependency within a single sample. However, self-attention has
quadratic complexity and ignores potential correlation between different samples.
This article proposes a novel attention mechanism which we call external attention ,
based on two external, small, learnable, shared memories, which can be implemented easily
by simply using two cascaded linear layers and two normalization layers; it conveniently
replaces self-attention in existing popular architectures. External attention has linear
complexity and implicitly considers the correlations between all data samples. We further
incorporate the multi-head mechanism into external attention to provide an all-MLP architecture,
external attention MLP (EAMLP), for image classification. Extensive experiments on
image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, image
generation, and point cloud analysis reveal that our method provides results comparable or
superior to the self-attention mechanism and some of its variants, with much lower
computational and memory costs.
DIScene: Object Decoupling and Interaction Modeling for Complex Scene Generation
ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Conference Papers, 2024, Article No.101, 1-12.

Xiao-Lei Li, Haodong Li, Hao-Xiang Chen, Tai-Jiang Mu, and Shi-Min Hu
This paper reconsiders how to distill knowledge from pretrained 2D diffusion
models to guide 3D asset generation, in particular to generate complex 3D scenes:
it should accept varied inputs, i.e., texts or images, to allow for flexible
expression of requirement; objects in the scene should be style-consistent
and decoupled with clearly modeled interactions, benefiting downstream tasks.
We propose DIScene, a novel method for this task. It represents the entire 3D
scene with a learnable structured scene graph: each node explicitly models an
object with its appearance, textual description, transformation, geometry as
a mesh attached with surface-aligned Gaussians; the graph's edges model object
interactions. With this new representation, objects are optimized in the
canonical space and interactions between objects are optimized by object-aware
rendering to avoid wrong back-propagation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the
significant utility and superiority of our approach and that DIScene can greatly
facilitate 3D content creation tasks.
FragmentDiff: A Diffusion Model for Fractured Object Assembly
ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Conference Papers, 2024, Article No. 58, Pages 1 - 12.

Qun-Ce Xu, Hao-Xiang Chen, Jiacheng Hua, Xiaohua Zhan, Yong-Liang Yang, Tai-Jiang Mu
Fractured object reassembly is a challenging problem in computer vision and graphics
with applications in industrial manufacturing and archaeology. Traditional methods
based on shape descriptors and geometric registration often struggle with ambiguous
features, resulting in lower accuracy. Recent data-driven methods are inherently affected
by the representation and learning ability of the trained models. To address this,
we propose a novel approach inspired by diffusion models and transformers. Our method
applies diffusion denoising via a transformer to predict the pose parameter of each fragment,
taking advantage of their global feature correlation and pose prior learning abilities.
We evaluate our approach on a fractured object dataset and demonstrate superior performance
compared to state-of-the-art methods. Our method offers a promising solution for accurate
and robust fractured object reassembly, advancing the field in complex shape analysis and
assembly tasks.
EVSplitting: An Efficient and Visually Consistent Splitting Algorithm for 3D Gaussian Splatting
ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2024 Conference Papers, 2024, Article No. 35, Pages 1 - 11.

Qi-Yuan Feng, Geng-Chen Cao, Hao-Xiang Chen, Qun-Ce Xu, Tai-Jiang Mu, Ralph Martin, Shi-Min Hu
This paper presents EVSplitting, an efficient and visually consistent splitting algorithm for
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). It is designed to make operating 3DGS as easy and effective as
other 3D explicit representations, readily for industrial productions. The challenges of above
target are: 1) The huge number and complex attributes of 3DGS make it tough to explicitly
operate on 3DGS in a real-time and learning-free manner; 2) The visual effect of 3DGS is
very difficult to maintain during explicit operations and 3) The anisotropism of Gaussian
always leads to blurs and artifacts. As far as we know, no prior work can address these
challenges well. In this work, we introduce a direct and efficient 3DGS splitting algorithm
to solve them. Specifically, we formulate the 3DGS splitting as two minimization problems
that aim to ensure visual consistency and reduce Gaussian overflow across boundary (splitting
plane), respectively. Firstly, we impose conservations on the zero-, first- and second-order
moments of the weighted Gaussian distribution to guarantee visual consistency. Secondly, we
reduce the boundary overflow with a special constraint on the aforementioned conservations.
With these conservations and constraints, we derive a closed-form solution for the 3DGS splitting
problem. This yields an easy-to-implement, plug-and-play, efficient and fundamental tool,
benefiting various downstream applications of 3DGS.
CharacterGen: Efficient 3D Character Generation from Single Images with Multi-View Pose Canonicalization
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2024, Vol. 43, No. 4, article number: 84, 1-13, ACM SIGGRAPH.

Hao-Yang Peng, Jia-Peng Zhang, Meng-Hao Guo, Yan-Pei Cao, Shi-Min Hu
In the field of digital content creation, generating high-quality 3D characters
from single images is challenging, especially given the complexities of various
body poses and the issues of self-occlusion and pose ambiguity. In this paper,
we present CharacterGen, a framework developed to efficiently generate 3D characters.
CharacterGen introduces a streamlined generation pipeline along with an
image-conditioned multi-view diffusion model. This model effectively
calibrates input poses to a canonical form while retaining key attributes of
the input image, thereby addressing the challenges posed by diverse poses.
A transformer-based, generalizable sparse-view reconstruction model is the
other core component of our approach, facilitating the creation of detailed 3D
models from multi-view images. We also adopt a texture-back-projection strategy
to produce high-quality texture maps. Additionally, we have curated a dataset of
anime characters, rendered in multiple poses and views, to train and evaluate our
model. Our approach has been thoroughly evaluated through quantitative and
qualitative experiments, showing its proficiency in generating 3D characters
with high-quality shapes and textures, ready for downstream applications such
as rigging and animation.
LC-NeRF: Local Controllable Face Generation in Neural Radiance Field
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2024, Vol. 30, No. 8, 5437-5448.

Wen-Yang Zhou, Lu Yuan, Shu-Yu Chen, Lin Gao, Shi-Min Hu
3D face generation has achieved high visual quality and 3D consistency thanks
to the development of neural radiance fields (NeRF). However, these methods model
the whole face as a neural radiance field, which limits the controllability of the
local regions. In other words, previous methods struggle to independently control
local regions, such as the mouth, nose, and hair. To improve local controllability in
NeRF-based face generation, we propose LC-NeRF, which is composed of a Local Region
Generators Module (LRGM) and a Spatial-Aware Fusion Module (SAFM) , allowing for
geometry and texture control of local facial regions. The LRGM models different
facial regions as independent neural radiance fields and the SAFM is responsible
for merging multiple independent neural radiance fields into a complete representation.
Finally, LC-NeRF enables the modification of the latent code associated with each
individual generator, thereby allowing precise control over the corresponding
local region. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations show that our method provides
better local controllability than state-of-the-art 3D-aware face generation methods.
A perception study reveals that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods
in terms of image quality, face consistency, and editing effects. Furthermore, our method
exhibits favorable performance in downstream tasks, including real image editing
and text-driven facial image editing.
SceneDirector: Interactive Scene Synthesis by Simultaneously Editing Multiple Objects in Real-Time
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2024, Vol. 30, No. 8, 4558-4569,.

Shao-Kui Zhang, Hou Tam, Yike Li, Ke-Xin Ren, Hongbo Fu, Song-Hai Zhang
3D face generation has achieved high visual quality and 3D consistency thanks
to the development of neural radiance fields (NeRF). However, these methods model
the whole face as a neural radiance field, which limits the controllability of the
local regions. In other words, previous methods struggle to independently control
local regions, such as the mouth, nose, and hair. To improve local controllability in
NeRF-based face generation, we propose LC-NeRF, which is composed of a Local Region
Generators Module (LRGM) and a Spatial-Aware Fusion Module (SAFM) , allowing for
geometry and texture control of local facial regions. The LRGM models different
facial regions as independent neural radiance fields and the SAFM is responsible
for merging multiple independent neural radiance fields into a complete representation.
Finally, LC-NeRF enables the modification of the latent code associated with each
individual generator, thereby allowing precise control over the corresponding
local region. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations show that our method provides
better local controllability than state-of-the-art 3D-aware face generation methods.
A perception study reveals that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods
in terms of image quality, face consistency, and editing effects. Furthermore, our method
exhibits favorable performance in downstream tasks, including real image editing
and text-driven facial image editing.
Mesh Neural Networks Based on Dual Graph Pyramids
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2024, Vol. 30, No. 7, 4211-4224.

Xiang-Li Li, Zheng-Ning Liu, Tuo Chen, Tai-Jiang Mu, Ralph R. Martin, Shi-Min Hu
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have been widely used for mesh processing in recent years.
However, current DNNs can not process arbitrary meshes efficiently. On the one hand,
most DNNs expect 2-manifold, watertight meshes, but many meshes, whether manually
designed or automatically generated, may have gaps, non-manifold geometry, or other
defects. On the other hand, the irregular structure of meshes also brings challenges
to building hierarchical structures and aggregating local geometric information,
which is critical to conduct DNNs. In this paper, we present DGNet, an efficient,
effective and generic deep neural mesh processing network based on dual graph pyramids;
it can handle arbitrary meshes. First, we construct dual graph pyramids for meshes to
guide feature propagation between hierarchical levels for both downsampling and
upsampling. Second, we propose a novel convolution to aggregate local features on
the proposed hierarchical graphs. By utilizing both geodesic neighbors and
euclidean neighbors, the network enables feature aggregation both within local
surface patches and between isolated mesh components. Experimental results demonstrate
that DGNet can be applied to both shape analysis and large-scale scene understanding.
Furthermore, it achieves superior performance on various benchmarks, including
ShapeNetCore, HumanBody, ScanNet and Matterport3D. Code and models will be available
at https://github.com/li-xl/DGNet .
Theoretically Achieving Continuous Representation of Oriented Bounding Boxes
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024, 16912-16922.

Zi-Kai Xiao, Guo-Ye Yang, Xue Yang, Tai-Jiang Mu, Junchi Yan, Shi-Min Hu
Considerable efforts have been devoted to Oriented Ob-ject Detection (OOD).
However, one lasting issue regarding the discontinuity in Oriented Bounding Box (OBB)
rep-resentation remains unresolved, which is an inherent bot-tleneck for extant OOD
methods. This paper endeavors to completely solve this issue in a theoretically
guaranteed manner and puts an end to the ad-hoc efforts in this di-rection. Prior
studies typically can only address one of the two cases of discontinuity: rotation
and aspect ratio, and often inadvertently introduce decoding discontinuity, e.g.
Decoding Incompleteness (DI) and Decoding Ambi-guity (DA) as discussed in literature.
Specifically, we pro-pose a novel representation method called Continuous OBB (COBB),
which can be readily integrated into existing de-tectors e.g. Faster-RCNN as a
plugin. It can theoreti-cally ensure continuity in bounding box regression which
to our best knowledge, has not been achieved in literature for rectangle-based
object representation. For fairness and transparency of experiments, we have developed
a modu-larized benchmark based on the open-source deep learning framework Jittor's
detection toolbox JDetfor OOD evaluation. On the popular DOTA dataset, by integrating
Faster-RCNN as the same baseline model, our new method out-performs the peer method
Gliding Vertex by 1.13% mAP 50 (relative improvement 1.54%), and 2.46% mAP 75
(relative improvement 5.91%), without any tricks.
Wonder3D: Single Image to 3D Using Cross-Domain Diffusion
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024, 9970-9980.

Xiaoxiao Long, Yuan-Chen Guo, Cheng Lin, Yuan Liu, Zhiyang Dou, Lingjie Liu, Yuexin Ma, Song-Hai Zhang, Marc Habermann,
Christian Theobalt, Wenping Wang
In this work, we introduce Wonder3D, a novel method for efficiently generating high-fidelity textured
meshes from single-view images. Recent methods based on Score Distillation Sampling (SDS)
have shown the potential to recover 3D geometry from 2D diffusion priors, but they typically
suffer from time-consuming per-shape optimization and inconsistent geometry. In contrast,
certain works di-rectly produce 3D information via fast network inferences, but their results
are often of low quality and lack geometric details. To holistically improve the quality,
consistency, and efficiency of single-view reconstruction tasks, we pro-pose a cross-domain
diffusion model that generates multi-view normal maps and the corresponding color images.
To ensure the consistency of generation, we employ a multi-view cross-domain attention
mechanism that facilitates information exchange across views and modalities. Lastly, we
introduce a geometry-aware normal fusion algorithm that extracts high-quality surfaces
from the multi-view 2D representations in only 2 ~ 3 minutes. Our extensive evaluations
demonstrate that our method achieves high-quality reconstruction results, robust generalization,
and good efficiency compared to prior works.
BiRD: Using Bidirectional Rotation Gain Differences to Redirect Users during Back-and-forth Head Turns in Walking
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 30, No. 4, 1916-1926.

Sen-Zhe Xu, Fiona Xiao Yu Chen, Ran Gong, Fang-Lue Zhang, Song-Hai Zhang
Redirected walking (RDW) facilitates user navigation within expansive
virtual spaces despite the constraints of limited physical spaces. It employs
discrepancies between human visual-proprioceptive sensations, known as gains,
to enable the remapping of virtual and physical environments. In this paper,
we explore how to apply rotation gain while the user is walking. We propose
to apply a rotation gain to let the user rotate by a different angle when
reciprocating from a previous head rotation, to achieve the aim of steering
the user to a desired direction. To apply the gains imperceptibly based on
such a Bidirectional Rotation gain Difference (BiRD), we conduct both
measurement and verification experiments on the detection thresholds of
the rotation gain for reciprocating head rotations during walking. Unlike
previous rotation gains which are measured when users are turning around
in place (standing or sitting), BiRD is measured during users' walking.
Our study offers a critical assessment of the acceptable range of rotational
mapping differences for different rotational orientations across the user's
walking experience, contributing to an effective tool for redirecting users
in virtual environments.
Spatial Contraction Based on Velocity Variation for Natural Walking in Virtual Reality
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 30, No. 5, 2444-2453.

Sen-Zhe Xu, Kui Huang, Cheng-Wei Fan, Song-Hai Zhang
Virtual Reality (VR) offers an immersive 3D digital environment,
but enabling natural walking sensations without the constraints of physical space
remains a technological challenge. Previous VR locomotion methods, including
game controller, teleportation, treadmills, walking-in-place, and redirected
walking (RDW), have made strides towards overcoming this challenge. However,
these methods also face limitations such as possible unnaturalness,
additional hardware requirements, or motion sickness risks. This paper
introduces ¡°Spatial Contraction (SC)¡±, an innovative VR locomotion method
inspired by the phenomenon of Lorentz contraction in Special Relativity.
Similar to the Lorentz contraction, our SC contracts the virtual space
along the user's velocity direction in response to velocity variation.
The virtual space contracts more when the user's speed is high, whereas
minimal or no contraction happens at low speeds. We provide a virtual space
transformation method for spatial contraction and optimize the user experience
in smoothness and stability. Through SC, VR users can effectively traverse a
longer virtual distance with a shorter physical walking. Different from locomotion
gains, the spatial contraction effect is observable by the user and aligns
with their intentions, so there is no inconsistency between the user's
proprioception and visual perception. SC is a general locomotion method
that has no special requirements for VR scenes. The experimental results
of our live user studies in various virtual scenarios demonstrate that SC
has a significant effect in reducing both the number of resets and the physical
walking distance users need to cover. Furthermore, experiments have also
demonstrated that SC has the potential for integration with existing
locomotion techniques such as RDW.
Multi-User Redirected Walking in Separate Physical Spaces for Online VR Scenarios
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 30, No. 4, 1916-1926.

Sen-Zhe Xu, Jia-Hong Liu, Miao Wang, Fang-Lue Zhang, Song-Hai Zhang
With the recent rise of Metaverse, online multiplayer VR applications are becoming
increasingly prevalent worldwide. However, as multiple users are located in different
physical environments, different reset frequencies and timings can lead to serious
fairness issues for online collaborative/competitive VR applications. We propose a
novel multi-user RDW method that is able to significantly reduce
the overall reset number and give users a better immersive experience by providing
a fair exploration. Our key idea is to first find out the ¡±bottleneck¡± user that
may cause all users to be reset and estimate the time to reset given the users¡¯
next targets, and then redirect all the users to favorable poses during that maximized
bottleneck time to ensure the subsequent resets can be postponed as much as possible.
More particularly, we develop methods to estimate the time of possibly encountering
obstacles and the reachable area for a specific pose to enable the prediction of the
next reset caused by any user. Our experiments and user study found that our method
outperforms existing RDW methods in online VR applications.
Other publications in 2024
1. Tai-Jiang Mu, Ming-Yuan Shen, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu,
Learning Virtual View Selection for 3D Scene Semantic Segmentation,
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2024, Vol. 33, 4159-4172.

2. Guo-Ye Yang, George Kiyohiro Nakayama, Zi-Kai Xiao, Tai-Jiang Mu, Xiaolei Huang, Shi-Min Hu,
Semantic-Aware Transformation-Invariant RoI Align,
AAAI 2024: 6486-6493.

3. Yi Zhang, Meng-Hao Guo, Miao Wang, Shi-Min Hu,
Exploring Regional Clues in CLIP for Zero-Shot Semantic Segmentation,
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024, 3270-3280.

4. Xin Yu, Yuan-Chen Guo, Yangguang Li, Ding Liang, Song-Hai Zhang, Xiaojuan Qi,
Text-to-3D with Classifier Score Distillation,
ICLR 2024: 6486-6493.

2023
Visual attention network
Computational Visual Media, 2023, Vol. 9, No. 4, 733-752.

Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng & Shi-Min Hu
While originally designed for natural language processing tasks, the self-attention
mechanism has recently taken various computer vision areas by storm. However,
the 2D nature of images brings three challenges for applying self-attention
in computer vision: (1) treating images as 1D sequences neglects their 2D structures;
(2) the quadratic complexity is too expensive for high-resolution images;
(3) it only captures spatial adaptability but ignores channel adaptability.
In this paper, we propose a novel linear attention named large kernel attention (LKA) to
enable self-adaptive and long-range correlations in self-attention while avoiding
its shortcomings. Furthermore, we present a neural network based on LKA, namely
Visual Attention Network (VAN). While extremely simple, VAN achieves comparable results
with similar size convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs)
in various tasks, including image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation,
panoptic segmentation, pose estimation, etc. For example, VAN-B6 achieves 87.8% accuracy
on ImageNet benchmark, and sets new state-of-the-art performance (58.2 PQ) for panoptic
segmentation. Besides, VAN-B2 surpasses Swin-T 4 mIoU (50.1 vs. 46.1) for semantic
segmentation on ADE20K benchmark, 2.6 AP (48.8 vs. 46.2) for object detection on COCO dataset.
It provides a novel method and a simple yet strong baseline for the community.
The code is available at https://github.com/Visual-Attention-Network.
StructNeRF: Neural Radiance Fields for Indoor Scenes With Structural Hints
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, Vol. 45, No. 12, 15694-15705.

Zheng Chen, Chen Wang, Yuan-Chen Guo, Song-Hai Zhang
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) achieve photo-realistic view synthesis with densely
captured input images. However, the geometry of NeRF is extremely under-constrained
given sparse views, resulting in significant degradation of novel view synthesis quality.
Inspired by self-supervised depth estimation methods, we propose StructNeRF, a
solution to novel view synthesis for indoor scenes with sparse inputs. StructNeRF
leverages the structural hints naturally embedded in multi-view inputs to handle the
unconstrained geometry issue in NeRF. Specifically, it tackles the texture and
non-texture regions respectively: a patch-based multi-view consistent photometric
loss is proposed to constrain the geometry of textured regions; for non-textured
ones, we explicitly restrict them to be 3D consistent planes. Through the dense
self-supervised depth constraints, our method improves both the geometry and the view
synthesis performance of NeRF without any additional training on external data.
Extensive experiments on several real-world datasets demonstrate that StructNeRF
shows superior or comparable performance compared to state-of-the-art methods
(e.g. NeRF, DSNeRF, RegNeRF, Dense Depth Priors, MonoSDF, etc.) for indoor scenes
with sparse inputs both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Recursive-NeRF: An Efficient and Dynamically Growing NeRF
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2023, Vol. 29, No. 12, 5124-5136.

Guo-Wei Yang, Wen-Yang Zhou, Hao-Yang Peng, Dun Liang, Tai-Jiang Mu, Shi-Min Hu
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) achieve photo-realistic view synthesis with densely
captured input images. However, the geometry of NeRF is extremely under-constrained
given sparse views, resulting in significant degradation of novel view synthesis quality.
Inspired by self-supervised depth estimation methods, we propose StructNeRF, a
solution to novel view synthesis for indoor scenes with sparse inputs. StructNeRF
leverages the structural hints naturally embedded in multi-view inputs to handle the
unconstrained geometry issue in NeRF. Specifically, it tackles the texture and
non-texture regions respectively: a patch-based multi-view consistent photometric
loss is proposed to constrain the geometry of textured regions; for non-textured
ones, we explicitly restrict them to be 3D consistent planes. Through the dense
self-supervised depth constraints, our method improves both the geometry and the view
synthesis performance of NeRF without any additional training on external data.
Extensive experiments on several real-world datasets demonstrate that StructNeRF
shows superior or comparable performance compared to state-of-the-art methods
(e.g. NeRF, DSNeRF, RegNeRF, Dense Depth Priors, MonoSDF, etc.) for indoor scenes
with sparse inputs both quantitatively and qualitatively.
DiffFacto: Controllable Part-Based 3D Point Cloud Generation with Cross Diffusion
IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, 14211-14221.

George Kiyohiro Nakayama; Mikaela Angelina Uy; Jiahui Huang; Shi-Min Hu; Ke Li; Leonidas Guibas
While the community of 3D point cloud generation has witnessed a big growth in recent
years, there still lacks an effective way to enable intuitive user control in the
generation process, hence limiting the general utility of such methods. Since an
intuitive way of decomposing a shape is through its parts, we propose to tackle
the task of controllable part-based point cloud generation. We introduce DiffFacto,
a novel probabilistic generative model that learns the distribution of shapes
with part-level control. We propose a factorization that models independent part
style and part configuration distributions, and present a novel cross diffusion
network that enables us to generate coherent and plausible shapes under our
proposed factorization. Experiments show that our method is able to generate
novel shapes with multiple axes of control. It achieves state-of-the-art
part-level generation quality and generates plausible and coherent shape while
enabling various downstream editing applications such as shape interpolation,
mixing, and transformation editing. Please visit our project webpage at https://difffacto.github.io/
Beyond Self-Attention: External Attention Using Two Linear Layers for Visual Tasks
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, Vol. 45, No. 5, 5436-5447.

Meng-Hao Guo, Zheng-Ning Liu, Tai-Jiang Mu, Shi-Min Hu
Attention mechanisms, especially self-attention, have played an increasingly important role
in deep feature representation for visual tasks. Self-attention updates the feature at each
position by computing a weighted sum of features using pair-wise affinities across all positions
to capture the long-range dependency within a single sample. However, self-attention has
quadratic complexity and ignores potential correlation between different samples.
This article proposes a novel attention mechanism which we call external attention ,
based on two external, small, learnable, shared memories, which can be implemented easily
by simply using two cascaded linear layers and two normalization layers; it conveniently
replaces self-attention in existing popular architectures. External attention has linear
complexity and implicitly considers the correlations between all data samples. We further
incorporate the multi-head mechanism into external attention to provide an all-MLP architecture,
external attention MLP (EAMLP), for image classification. Extensive experiments on
image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, image
generation, and point cloud analysis reveal that our method provides results comparable or
superior to the self-attention mechanism and some of its variants, with much lower
computational and memory costs.
Adaptive Optimization Algorithm for Resetting Techniques in Obstacle-Ridden Environments
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2023, Vol. 29, No. 4, 1977-1991.

Song-Hai Zhang, Chia-Hao Chen, Fu Zheng, Yong-Liang Yang, Shi-Min Hu
Redirected Walking (RDW) algorithms aim to impose several types of gains on users
immersed in Virtual Reality and distort their walking paths in the real world,
thus enabling them to explore a larger space. Since collision with physical boundaries
is inevitable, a reset strategy needs to be provided to allow users to reset when they
hit the boundary. However, most reset strategies are based on simple heuristics by
choosing a seemingly suitable solution, which may not perform well in practice.
In this article, we propose a novel optimization-based reset algorithm adaptive to
different RDW algorithms. Inspired by the approach of finite element analysis, our
algorithm splits the boundary of the physical world by a set of endpoints. Each
endpoint is assigned a reset vector to represent the optimized reset direction when
hitting the boundary. The reset vectors on the edge will be determined by the
interpolation between two neighbouring endpoints. We conduct simulation-based experiments
for three RDW algorithms with commonly used reset algorithms to compare with. The
results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly reduces the number of resets.
Real-Time Globally Consistent 3D Reconstruction With Semantic Priors
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2023, Vol. 29, No. 4, 1977-1991.

Shi-Sheng Huang, Haoxiang Chen, Jiahui Huang, Hongbo Fu, Shi-Min Hu
Maintaining global consistency continues to be critical for online 3D indoor
scene reconstruction. However, it is still challenging to generate satisfactory
3D reconstruction in terms of global consistency for previous approaches using
purely geometric analysis, even with bundle adjustment or loop closure techniques.
In this article, we propose a novel real-time 3D reconstruction approach which
effectively integrates both semantic and geometric cues. The key challenge is
how to map this indicative information, i.e., semantic priors, into a metric
space as measurable information, thus enabling more accurate semantic fusion
leveraging both the geometric and semantic cues. To this end, we introduce a
semantic space with a continuous metric function measuring the distance between
discrete semantic observations. Within the semantic space, we present an accurate
frame-to-model semantic tracker for camera pose estimation, and semantic pose
graph equipped with semantic links between submaps for globally consistent 3D
scene reconstruction. With extensive evaluation on public synthetic and real-world
3D indoor scene RGB-D datasets, we show that our approach outperforms the previous
approaches for 3D scene reconstruction both quantitatively and qualitatively,
especially in terms of global consistency.
Multiway Non-Rigid Point Cloud Registration via Learned Functional Map Synchronization
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, Vol. 45, No. 2, 2038 - 2053.

Jiahui Huang, Tolga Birdal, Zan Gojcic, Leonidas J. Guibas, Shi-Min Hu
We present SyNoRiM, a novel way to jointly register multiple non-rigid shapes by synchronizing
the maps that relate learned functions defined on the point clouds. Even though the ability
to process non-rigid shapes is critical in various applications ranging from computer
animation to 3D digitization, the literature still lacks a robust and flexible framework to
match and align a collection of real, noisy scans observed under occlusions. Given a set
of such point clouds, our method first computes the pairwise correspondences parameterized via
functional maps. We simultaneously learn potentially non-orthogonal basis functions to effectively
regularize the deformations, while handling the occlusions in an elegant way.
To maximally benefit from the multi-way information provided by the inferred pairwise
deformation fields, we synchronize the pairwise functional maps into a cycle-consistent whole
thanks to our novel and principled optimization formulation. We demonstrate via extensive
experiments that our method achieves a state-of-the-art performance in registration accuracy,
while being flexible and efficient as we handle both non-rigid and multi-body cases in a unified
framework and avoid the costly optimization over point-wise permutations by the use
of basis function maps.
2022
A Neural Galerkin Solver for Accurate Surface Reconstruction
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2022, Vol. 41, No. 6, article no. 229.

Jiahui Huang, Hao-Xiang Chen, Shi-Min Hu
We present SyNoRiM, a novel way to jointly register multiple non-rigid shapes by
synchronizing the maps that relate learned functions defined on the point clouds.
Even though the ability to process non-rigid shapes is critical in various applications
ranging from computer animation to 3D digitization, the literature still lacks a robust and flexible framework to match and align a collection of real, noisy scans observed under occlusions. Given a set of such point clouds, our method first computes the pairwise correspondences parameterized via functional maps. We simultaneously learn potentially non-orthogonal basis functions to effectively regularize the deformations, while handling the occlusions in an elegant way. To maximally benefit from the multi-way information provided by the inferred pairwise deformation fields, we synchronize the pairwise functional maps into a cycle-consistent whole thanks to our novel and principled optimization formulation. We demonstrate via extensive experiments that our method achieves a state-of-the-art performance in registration accuracy, while being flexible and efficient as we handle both non-rigid and multi-body cases in a unified framework and avoid the costly optimization over point-wise permutations by the use of basis function maps.
Context-Consistent Generation of Indoor Virtual Environments based on Geometry Constraints
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2022, Vol. 28, No. 12, 3986-3999.

Yu He, Yingtian Liu, Yihan Jin, Song-Hai Zhang, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu
In this paper, we propose a system that can automatically generate immersive
and interactive virtual reality (VR) scenes by taking real-world geometric
constraints into account. Our system can not only help users avoid real-world
obstacles in virtual reality experiences, but also provide context-consistent
contents to preserve their sense of presence. To do so, our system first
identifies the positions and bounding boxes of scene objects as well as a set
of interactive planes from 3D scans. Then context-compatible virtual objects
that have similar geometric properties to the real ones can be automatically
selected and placed into the virtual scene, based on learned object association
relations and layout patterns from large amounts of indoor scene configurations.
We regard virtual object replacement as a combinatorial optimization problem,
considering both geometric and contextual consistency constraints. Quantitative
and qualitative results show that our system can generate plausible interactive
virtual scenes that highly resemble real environments, and have the ability to
keep the sense of presence for users in their VR experiences.
SegNeXt: rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation
The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2022, article No. 84, 1140-1156.

Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Qibin Hou, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu
We present SegNeXt, a simple convolutional network architecture for semantic segmentation.
Recent transformer-based models have dominated the field of semantic segmentation due
to the efficiency of self-attention in encoding spatial information. In this paper, we
show that convolutional attention is a more Efficient and effective way to encode contextual
information than the self-attention mechanism in transformers. By re-examining the
characteristics owned by successful segmentation models, we discover several key components
leading to the performance improvement of segmentation models. This motivates us to design
a novel convolutional attention network that uses cheap convolutional operations. Without
bells and whistles, our SegNeXt significantly improves the performance of previous
state-of-the-art methods on popular benchmarks, including ADE20K, Cityscapes, COCO-Stuff,
Pascal VOC, Pascal Context, and iSAID. Notably, SegNeXt outperforms EfficientNet-L2 w/ NAS-FPN
and achieves 90.6% mIoU on the Pascal VOC 2012 test leaderboard using only 1/10 parameters
of it. On average, SegNeXt achieves about 2.0% mIoU improvements compared to
the state-of-the-art methods on the ADE20K datasets with the same or fewer computations.
NeRF-SR: High Quality Neural Radiance Fields using Supersampling
Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2022, 6445-6454.

Chen Wang, Xian Wu, Yuan-Chen Guo, Song-Hai Zhang, Yu-Wing Tai, Shi-Min Hu
We present NeRF-SR, a solution for high-resolution (HR) novel view synthesis with mostly
low-resolution (LR) inputs. Our method is built upon Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) that
predicts per-point density and color with a multi-layer perceptron. While producing
images at arbitrary scales, NeRF struggles with resolutions that go beyond observed images.
Our key insight is that NeRF benefits from 3D consistency, which means an observed pixel
absorbs information from nearby views. We first exploit it by a super-sampling strategy
that shoots multiple rays at each image pixel, which further enforces multi-view constraint
at a sub-pixel level. Then, we show that NeRF-SR can further boost the performance of
super-sampling by a refinement network that leverages the estimated depth at hand to
hallucinate details from related patches on only one HR reference image. Experiment
results demonstrate that NeRF-SR generates high-quality results for novel view synthesis
at HR on both synthetic and real-world datasets without any external information. Project
page: https://cwchenwang.github.io/NeRF-SR
Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey
Computational Visual Media, 2022, Vol. 8, No. 3, 331-368.

Meng-Hao Guo, Tian-Xing Xu, Jiang-Jiang Liu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Peng-Tao Jiang, Tai-Jiang Mu, Song-Hai Zhang, Ralph R. Martin, Ming-Ming Cheng & Shi-Min Hu
Humans can naturally and effectively find salient regions in complex scenes.
Motivated by this observation, attention mechanisms were introduced into computer
vision with the aim of imitating this aspect of the human visual system. Such an
attention mechanism can be regarded as a dynamic weight adjustment process based
on features of the input image. Attention mechanisms have achieved great success
in many visual tasks, including image classification, object detection, semantic
segmentation, video understanding, image generation, 3D vision, multimodal tasks,
and self-supervised learning. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of
various attention mechanisms in computer vision and categorize them according to
approach, such as channel attention, spatial attention, temporal attention, and
branch attention; a related repository
https://github.com/MenghaoGuo/Awesome-Vision-Attentions is dedicated to collecting
related work. We also suggest future directions for attention mechanism research.
Fast 3D Indoor Scene Synthesis by Learning Spatial Relation Priors of Objects
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2022, Vol. 28, No. 9, 3082-3092.

Song-Hai Zhang, Shao-Kui Zhang, Wei-Yu Xie, Cheng-Yang Luo, Yongliang Yang, Hongbo Fu
We present a framework for fast synthesizing indoor scenes, given a room geometry
and a list of objects with learnt priors.Unlike existing data-driven solutions,
which often learn priors by co-occurrence analysis and statistical model fitting,
our methodmeasures the strengths of spatial relations by tests for complete
spatial randomness (CSR), and learns discrete priors based onsamples with the
ability to accurately represent exact layout patterns. With the learnt priors,
our method achieves both acceleration andplausibility by partitioning the input
objects into disjoint groups, followed by layout optimization using position-based
dynamics (PBD)based on the Hausdorff metric. Experiments show that our framework
is capable of measuring more reasonable relations amongobjects and simultaneously
generating varied arrangements in seconds compared with the state-of-the-art works.
Subdivision-Based Mesh Convolution Networks
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2022, Vol. 41, No. 3, article no. 25.

Shi-Min Hu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Meng-Hao Guo, Jun-Xiong Cai, Jiahui Huang, Tai-Jiang Tai, Ralph R. Martin
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have made great breakthroughs in
2D computer vision. However, their irregular structure makes it hard to
harness the potential of CNNs directly on meshes. A subdivision surface
provides a hierarchical multi-resolution structure, in which each face in a
closed 2-manifold triangle mesh is exactly adjacent to three faces. Motivated
by these two observations, this paper presents SubdivNet, an innovative and
versatile CNN framework for 3D triangle meshes with Loop subdivision
sequence connectivity. Making an analogy between mesh faces and pixels
in a 2D image allows us to present a mesh convolution operator to aggregate
local features from nearby faces. By exploiting face neighborhoods,
this convolution can support standard 2D convolutional network concepts,
e.g. variable kernel size, stride, and dilation. Based on the multi-resolution
hierarchy, we make use of pooling layers which uniformly merge four faces
into one and an upsampling method which splits one face into four. Thereby,
many popular 2D CNN architectures can be easily adapted to process 3D
meshes. Meshes with arbitrary connectivity can be remeshed to have Loop
subdivision sequence connectivity via self-parameterization, making SubdivNet
a general approach. Extensive evaluation and various applications
demonstrate SubdivNet¡¯s effectiveness and efficiency.
2021
Fast and accurate spherical harmonics products
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2021, Vol. 40, No. 6. article no. 280.

Hanggao Xin, Zhiqian Zhou, Di An, Ling-Qi Yan, Kun Xu, Shi-Min Hu, Shing-Tung Yau
Spherical Harmonics (SH) have been proven as a powerful tool for rendering,
especially in real-time applications such as Precomputed Radiance Transfer (PRT).
Spherical harmonics are orthonormal basis functions and are efficient in computing
dot products. However, computations of triple product and multiple product
operations are often the bottlenecks that prevent moderately high-frequency
use of spherical harmonics. Specifically state-of-the-art methods for accurate
SH triple products of order n have a time complexity of O(n5), which is a heavy
burden for most real-time applications. Even worse, a brute-force way to compute
k-multiple products would take O(n2k) time. In this paper, we propose a fast and
accurate method for spherical harmonics triple products with the time complexity
of only O(n3), and further extend it for computing k-multiple products with the
time complexity of O(kn3 + k2n2 log(kn)). Our key insight is to conduct the
triple and multiple products in the Fourier space, in which the multiplications
can be performed much more efficiently. To our knowledge, our method is theoretically
the fastest for accurate spherical harmonics triple and multiple products.
And in practice, we demonstrate the efficiency of our method in rendering
applications including mid-frequency relighting and shadow fields.
DI-Fusion: Online Implicit 3D Reconstruction with Deep Priors
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021, 8932-8941.

Jiahui Huang, Shi-Sheng Huang, Haoxuan Song, Shi-Min Hu
Previous online 3D dense reconstruction methods struggle to achieve
the balance between memory storage and surface quality,
largely due to the usage of stagnant underlying
geometry representation, such as TSDF (truncated signed
distance functions) or surfels, without any knowledge of the
scene priors. In this paper, we present DI-Fusion (Deep
Implicit Fusion), based on a novel 3D representation, i.e.
Probabilistic Local Implicit Voxels (PLIVoxs), for online
3D reconstruction with a commodity RGB-D camera. Our
PLIVox encodes scene priors considering both the local
geometry and uncertainty parameterized by a deep neural network.
With such deep priors, we are able to perform online implicit 3D
reconstruction achieving state-ofthe-art camera trajectory estimation accuracy and mapping
quality, while achieving better storage efficiency compared
with previous online 3D reconstruction approaches. Our
implementation is available at https://www.github.
com/huangjh-pub/di-fusion.
MultiBodySync: Multi-Body Segmentation and Motion Estimation via 3D Scan Synchronization
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021, 7108-7118.

Jiahui Huang, He Wang, Tolga Birdal, Minhyuk Sung, Federica Arrigoni, Shi-Min Hu, Leonidas Guibas
We present MultiBodySync, a novel, end-to-end trainable multi-body motion segmentation
and rigid registration framework for multiple input 3D point clouds. The
two non-trivial challenges posed by this multi-scan multibody setting that we
investigate are: (i) guaranteeing correspondence and segmentation consistency
across multiple input point clouds capturing different spatial arrangements
of bodies or body parts; and (ii) obtaining robust motion-based rigid body
segmentation applicable to
novel object categories. We propose an approach to address these issues that
incorporates spectral synchronization into an iterative deep declarative network,
so as to simultaneously recover consistent correspondences as well
as motion segmentation. At the same time, by explicitly
disentangling the correspondence and motion segmentation estimation modules,
we achieve strong generalizability across different object categories.
Our extensive evaluations demonstrate that our method is effective on various
datasets ranging from rigid parts in articulated objects to
individually moving objects in a 3D scene, be it single-view
or full point clouds. Code at https://github.com/
huangjh-pub/multibody-sync.
Sketch2Model: View-Aware 3D Modeling from Single Free-Hand Sketches
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021, 6012-6021.

Song-Hai Zhang, Yuan-Chen Guo, Qing-Wen Gu
We investigate the problem of generating 3D meshes
from single free-hand sketches, aiming at fast 3D modeling
for novice users. It can be regarded as a single-view
reconstruction problem, but with unique challenges, brought
by the variation and conciseness of sketches. Ambiguities in
poorly-drawn sketches could make it hard to determine how
the sketched object is posed. In this paper, we address the
importance of viewpoint specification for overcoming such
ambiguities, and propose a novel view-aware generation
approach. By explicitly conditioning the generation process on a given
viewpoint, our method can generate plausible shapes automatically with predicted viewpoints, or with
specified viewpoints to help users better express their intentions.
Extensive evaluations on various datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our view-aware design in solving
sketch ambiguities and improving reconstruction quality.
ChoreoMaster: Choreography-Oriented Music-Driven Dance Synthesis
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2021, Vol. 40, No.4, artice no. 145, pages 1-13.

Kang Chen, Zhipeng Tan, Jin Lei, Song-Hai Zhang, Yuan-Chen Guo, Weidong Zhang, Shi-Min Hu
Despite strong demand in the game and film industry, automatically synthesizing
high-quality dance motions remains a challenging task. In this paper,
we present ChoreoMaster, a production-ready music-driven dance motion
synthesis system. Given a piece of music, ChoreoMaster can automatically
generate a high-quality dance motion sequence to accompany the input
music in terms of style, rhythm and structure. To achieve this goal, we
introduce a novel choreography-oriented choreomusical embedding framework,
which successfully constructs a unified choreomusical embedding space
for both style and rhythm relationships between music and dance phrases.
The learned choreomusical embedding is then incorporated into a novel
choreography-oriented graph-based motion synthesis framework, which
can robustly and efficiently generate high-quality dance motions following
various choreographic rules. Moreover, as a production-ready system,
ChoreoMaster is sufficiently controllable and comprehensive for users to
produce desired results. Experimental results demonstrate that dance motions
generated by ChoreoMaster are accepted by professional artists.
MoCap-Solver: A Neural Solver for Optical Motion Capture Data
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2021, Vol. 40, No.4, artice no. 84, pages 1-11.

Kang Chen, Yupan Wang, Song-Hai Zhang, Sen-Zhe Xu, Weidong Zhang, Shi-Min Hu
In a conventional optical motion capture (MoCap) workflow, two processes
are needed to turn captured raw marker sequences into correct skeletal
animation sequences. Firstly, various tracking errors present in the
markers must be fixed (cleaning or refining). Secondly, an agent skeletal mesh
must be prepared for the actor/actress, and used to determine skeleton
information from the markers (re-targeting or solving). The whole process,
normally referred to as solving MoCap data, is extremely time-consuming,
labor-intensive, and usually the most costly part of animation production.
Hence, there is a great demand for automated tools in industry. In this
work, we present MoCap-Solver, a production-ready neural solver for optical
MoCap data. It can directly produce skeleton sequences and clean marker
sequences from raw MoCap markers, without any tedious manual operations.
To achieve this goal, our key idea is to make use of neural encoders
concerning three key intrinsic components: the template skeleton, marker
configuration and motion, and to learn to predict these latent vectors from
imperfect marker sequences containing noise and errors. By decoding these
components from latent vectors, sequences of clean markers and skeletons
can be directly recovered. Moreover, we also provide a novel normalization
strategy based on learning a pose-dependent marker reliability function,
which greatly improves system robustness. Experimental results demonstrate
that our algorithm consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art on
both synthetic and real-world datasets
MageAdd: Real-Time Interaction Simulation for Scene Synthesis
Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, October 2021, 965-973.

 (click for project webpage in Github)
(click for project webpage in Github)
Shao-Kui Zhang, Yi-Xiao Li, Yu He, Yong-Liang Yang, Song-Hai Zhang
While recent researches on computational 3D scene synthesis have achieved
impressive results, automatically synthesized scenes do not guarantee satisfaction
of end users. On the other hand, manual scene modelling can always ensure high
quality, but requires a cumbersome trial-and-error process. In this paper,
we bridge the above gap by presenting a data-driven 3D scene synthesis framework
that can intelligently infer objects to the scene by incorporating and simulating
user preferences with minimum input. While the cursor is moved and clicked in
the scene, our framework automatically selects and transforms suitable objects
into scenes in real time. This is based on priors learnt from the dataset for
placing different types of objects, and updated according to the current scene
context. Through extensive experiments we demonstrate that our framework outperforms
the state-of-the-art on result aesthetics, and enables effective and efficient user
interactions.
Supervoxel Convolution for Online 3D Semantic Segmentation
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2021, Vol. 40, No. 3, article No. 34, pages 1-15.

Shi-Sheng Huang, Ze-Yu Ma, Tai-Jiang Ma, Hongbo FU, Shi-Min Hu
Online 3D semantic segmentation, which aims to perform real-time 3D scene
reconstruction along with semantic segmentation, is an important but challenging topic.
A key challenge is to strike a balance between efficiency and
segmentation accuracy. There are very few deep learning based solutions
to this problem, since the commonly used deep representations based on
volumetric-grids or points do not provide efficient 3D representation and
organization structure for online segmentation. Observing that on-surface
supervoxels, i.e., clusters of on-surface voxels, provide a compact representation of 3D
surfaces and brings efficient connectivity structure via supervoxel
clustering, we explore a supervoxel-based deep learning solution for this task.
To this end, we contribute a novel convolution operation (SVConv) directly
on supervoxels. SVConv can efficiently fuse the multi-view 2D features and
3D features projected on supervoxels during the online 3D reconstruction,
and leads to an effective supervoxel-based convolutional neural network,
termed as Supervoxel-CNN, enabling 2D-3D joint learning for 3D semantic
prediction. With the Supervoxel-CNN, we propose a clustering-then-prediction
online 3D semantic segmentation approach. The extensive evaluations on
the public 3D indoor scene datasets show that our approach significantly
outperforms the existing online semantic segmentation systems in terms of
efficiency or accuracy.
PCT: Point cloud transformer
Computational Visual Media, 2021, Vol. 7, No. 2, 187-199.

Meng-Hao Guo, Jun-Xiong Cai, Zheng-Ning Liu, Tai-Jiang Mu, Ralph R. Martin & Shi-Min Hu
The irregular domain and lack of ordering make it challenging to design deep neural networks for point
cloud processing. This paper presents a novel framework named Point Cloud Transformer (PCT) for point
cloud learning. PCT is based on Transformer, which achieves huge success in natural language processing
and displays great potential in image processing. It is inherently permutation invariant for processing
a sequence of points, making it well-suited for point cloud learning. To better capture local
context within the point cloud, we enhance input embedding with the support of farthest point sampling
and nearest neighbor search. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the PCT achieves the state-of-the-art
performance on shape classification, part segmentation, semantic segmentation, and normal estimation tasks.
Prominent Structures for Video Analysis and Editing
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2021, Vol. 27, No. 7, 3305-3317.

Miao Wang, Xiao-Nan Fang, Guo-Wei Yang, Ariel Shamir, Shi-Min Hu
We present prominent structures in video, a representation of visually strong,
spatially sparse and temporally stable structural units, for use in video analysis and editing.
With a novel quality measurement of prominent structures in video, we develop a general framework
for prominent structure computation, and an ef?cient hierarchical structure alignment algorithm
between a pair of videos. The prominent structural unit map is proposed to encode both binary
prominence guidances and numerical strength and geometry details for each video frame.
Even though the detailed appearance of videos could be visually different, the proposed
alignment algorithm can ?nd candidate matched prominent structure sub-volumes. Prominent
structures in video support a wide range of video analysis and editing applications
including graphic match-cut between successive videos, instant cut editing,
finding transition portals from a video collection,
structure-aware video re-ranking, visualizing human action differences, etc.
High-quality Textured 3D Shape Reconstruction with Cascaded Fully Convolutional Networks
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2021, Vol. 27, No.1, 83-97.

Zheng-Ning Liu, Yan-Pei Cao, Zheng-Fei Kuang, Leif Kobbelt, Shi-Min Hu
We present a learning-based approach to reconstructing high-resolution three-dimensional (3D)
shapes with detailed geometry and high-?delity textures. Albeit extensively studied,
algorithms for 3D reconstruction from multi-view depth-and-color (RGB-D) scans are
still prone to measurement noise and occlusions; limited scanning or capturing angles
also often lead to incomplete reconstructions. Propelled by recent advances in 3D deep
learning techniques, in this paper, we introduce a novel computation and memory efficient cascaded
3D convolutional network architecture, which learns to reconstruct implicit surface representations
as well as the corresponding color information from noisy and imperfect RGB-D maps. The proposed 3D
neural network performs reconstruction in a progressive and coarse-to-?ne manner, achieving
unprecedented output resolution and ?delity. Meanwhile, an algorithm for end-to-end training
of the proposed cascaded structure is developed. We further introduce Human10, a newly created
dataset containing both detailed and textured full body reconstructions as well as corresponding
raw RGB-D scans of 10 subjects. Qualitative and quantitative experimental results on both
synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that the presented approach outperforms existing
state-of-the-art work regarding visual quality and accuracy of reconstructed models.
Other publications in 2021
1. Haoxuan Song, Jiahui Huang, Yan-Pei Cao, Tai-Jiang Mu,
HDR-Net-Fusion: Real-time 3D dynamic scene reconstruction with a hierarchical deep reinforcement network,
Computational Visual Media, 2021, Vol. 7, No. 4, 419-435.

2. Xian Wu, Chen Li, Shi-Min Hu, Yu-Wing Tai,
Hierarchical Generation of Human Pose With Part-Based Layer Representation,
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, Vol. 30, 7856-7866.

3. Meng-Hao Guo, Zheng-Ning Liu, Tai-Jiang Mu, Dun Liang, Ralph R. Martin, Shi-Min Hu,
Can attention enable MLPs to catch up with CNNs?
Computational Visual Media, 2021, Vol. 7, No. 3, 283-288.

4. Shaokui Zhang, Wei-Yu Xie, Song-Hai Zhang,
Geometry-Based Layout Generation with Hyper-Relations AMONG Objects,
Graphical Models, 2021, Vol. 116, article no. 101104.

5. Hanchao Liu, Tai-Jiang Mu, Xiaolei Huang,
Detecting human - object interaction with multi-level pairwise feature network,
Computational Visual Media, 2021, Vol. 7, No. 2, 229-239.

6. Wen-Yang Zhou, Guo-Wei Yang, Shi-Min Hu,
Jittor-GAN: A fast-training generative adversarial network model zoo based on Jittor,
Computational Visual Media, 2021, Vol. 7, No. 1, 153-157.

7. Jiahui Huang, Sheng Yang, Zishuo Zhao, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu,
ClusterSLAM: A SLAM backend for simultaneous rigid body clustering and motion estimation,
Computational Visual Media, 2021, Vol. 7, No. 1, 87-101 (Extended version of ICCV 2019 paper).

8. Junxiong Cai, Tai-Jiang Mu, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu,
LinkNet: 2D-3D linked multi-modal network for online semantic segmentation of RGB-D videos,
Computer & Graphics, 2021, Vol. 98, 37-47.

2020
Jittor: a novel deep learning framework with meta-operators and unified graph execution
Science China Information Science, 2020, Vol. 63, Article No. 222103, 1-21.

 (click for project webpage in Github)
(click for project webpage in Github)
Shi-Min Hu, Dun Liang, Guo-Ye Yang, Guo-Wei Yang & Wen-Yang Zhou
This paper introduces Jittor, a fully just-in-time (JIT) compiled deep learning framework.
With JIT compilation, we can achieve higher performance while making systems highly customizable.
Jittor provides classes of Numpy-like operators, which we call meta-operators.
A deep learning model built upon these meta-operators is compiled into high-performance
CPU or GPU code in real-time. To manage metaoperators, Jittor uses a highly optimized
way of executing computation graphs, which we call unified graph execution. This approach
is as easy to use as dynamic graph execution yet has the efficiency of static graph execution.
It also provides other improvements, including operator fusion, cross iteration fusion,
and unified memory.
A Moving Least Square Reproducing Kernel Particle Method for Unified Multiphase Continuum Simulation
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2020, Vol. 39, No.6, Article No. 150, ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2020.

Xiao-Song Chen, Chen-Feng Li, Geng-Chen Cao, Yun-Tao Jiang and Shi-Min Hu
In physically based-based animation, pure particle methods are popular due to
their simple data structure, easy implementation, and convenient parallelization.
As a pure particle-based method and using Galerkin discretization,
the Moving Least Square Reproducing Kernel Method(MLSRK) was developed in engineering computation as a general numerical tool for solving PDEs.
The basic idea of Moving Least Square(MLS) has also been used in computer graphics to estimatede formation gradient for deformable solids.
Based on the seprevious studies, we propose a multiphase MLSRK framework that animates complex and coupled fluids and solids in a unified manner.
Specifically, we use the Cauchy momentum equation and phase field model to uniformly capture the momentum balance and phase
evolution/interaction in a multiphase system, and systematically formulate the MLSRK discretization to support general multiphase constitutive
models. A series of animation examples are presented to demonstrate the performance of our new multiphase MLSRK framework,including hyperelastic,
elastoplastic, viscous, fracturing and multiphase coupling behaviours etc.
HeteroFusion: Dense Scene Reconstruction Integrating Multi-sensors
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2020, Vol. 26, No. 11, 3217-3230.

Sheng Yang, Beichen Li, Minghua Liu, Yu-Kun Lai, Leif Kobbelt, Shi-Min Hu
We present a novel approach to integrate data from multiple sensor types for dense 3D reconstruction of
indoor scenes in realtime. Existing algorithms are mainly based on a single RGBD camera and thus require
continuous scanning of areas with sufficient geometric features. Otherwise, tracking may fail due to
unreliable frame registration. Inspired by the fact that the fusion of multiple sensors can combine
their strengths towards a more robust and accurate self-localization, we incorporate multiple types
of sensors which are prevalent in modern robot systems, including a 2D range sensor, an inertial
measurement unit (IMU), and wheel encoders. We fuse their measurements to reinforce the tracking
process and to eventually obtain better 3D reconstructions. Specifically, we develop a 2D truncated
signed distance field (TSDF) volume representation for the integration and ray-casting of laser frames,
leading to a unified cost function in the pose estimation stage. For validation of the estimated poses
in the loop-closure optimization process, we train a classifier for the features extracted from
heterogeneous sensors during the registration progress. To evaluate our method on challenging use
case scenarios, we assembled a scanning platform prototype to acquire real-world scans.
We further simulated synthetic scans based on high-fidelity synthetic scenes for quantitative evaluation.
Extensive experimental evaluation on these two types of scans demonstrate that our system is
capable of robustly acquiring dense 3D reconstructions and outperforms state-of-the-art RGBD and LiDAR systems.
Noise-Resilient Reconstruction of Panoramas and 3D Scenes Using Robot-Mounted Unsynchronized Commodity RGB-D Cameras
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2020, Vol. 39, No.5, Article 152.

Sheng Yang, Beichen Li, Yan-Pei Cao, Hongbo Fu, Yu-Kun Lai, Leif Kobbelt and Shi-Min Hu
We present prominent structures in video, a representation of visually strong,
spatially sparse and temporally stable structural units, for use in video analysis and editing.
With a novel quality measurement of prominent structures in video, we develop a general framework
for prominent structure computation, and an ef?cient hierarchical structure alignment algorithm
between a pair of videos. The prominent structural unit map is proposed to encode both binary
prominence guidances and numerical strength and geometry details for each video frame.
Even though the detailed appearance of videos could be visually different, the proposed
alignment algorithm can ?nd candidate matched prominent structure sub-volumes. Prominent
structures in video support a wide range of video analysis and editing applications
including graphic match-cut between successive videos, instant cut editing,
finding transition portals from a video collection,
structure-aware video re-ranking, visualizing human action differences, etc.
Semantic Labeling and Instance Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds using Patch Context Analysis and Multiscale Processing
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2020, Vol. 26, No. 07, 2485-2498.

Shi-Min Hu, Jun-Xiong Cai, Yu-Kun Lai
We present a novel algorithm for semantic segmentation and labeling of 3D point clouds of indoor scenes,
where objects in point clouds can have significant variations and complex configurations.
Effective segmentation methods decomposing point clouds into semantically meaningful pieces are highly
desirable for object recognition, scene understanding, scene modeling, etc.
However, existing segmentation methods based on low-level geometry tend to either under-segment
or over-segment point clouds. Our method takes a fundamentally different approach, where semantic
segmentation is achieved along with labeling. To cope with substantial shape variation for objects
in the same category, we first segment point clouds into surface patches and use unsupervised clustering to
group patches in the training set into clusters, providing an intermediate representation for effectively
learning patch relationships. During testing, we propose a novel patch segmentation and classification
framework with multiscale processing, where the local segmentation level is automatically determined by
exploiting the learned cluster based contextual information. Our method thus produces robust patch
segmentation and semantic labeling results, avoiding parameter sensitivity. We further learn object-cluster
relationships from the training set, and produce semantically meaningful object level segmentation.
Our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods on several representative point cloud datasets,
including S3DIS, SceneNN, Cornell RGB-D and ETH.
ClusterVO: Clustering Moving Instances and Estimating Visual Odometry for Self and Surroundings
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020, 2168-2177.

Jiahui Huang, Sheng Yang, Tai-Jiang Mu and Shi-Min Hu
We present ClusterVO, a stereo Visual Odometry which simultaneously clusters and
estimates the motion of both ego and surrounding rigid clusters/objects.
Unlike previous solutions relying on batch input or imposing priors on scene
structure or dynamic object models, ClusterVO is online, general and thus can be
used in various scenarios including indoor scene understanding and autonomous driving.
At the core of our system lies a multi-level probabilistic association mechanism and a
heterogeneous Conditional Random Field (CRF) clustering approach combining semantic,
spatial and motion information to jointly infer cluster segmentations online for every frame.
The poses of camera and dynamic objects are instantly solved through a sliding-window optimization.
Our system is evaluated on Oxford Multimotion and KITTI dataset both quantitatively and qualitatively,
reaching comparable results to state-of-the-art solutions on both odometry and dynamic trajectory recovery.
Unpaired Portrait Drawing Generation via Asymmetric Cycle Mapping
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020, 8217-8225.

Ran Yi, Yong-Jin Liu, Yu-Kun Lai, Paul L. Rosin
Portrait drawing is a common form of art with high abstraction and expressiveness.
Due to its unique characteristics, existing methods achieve decent results only with paired training data,
which is costly and time-consuming to obtain. In this paper,
we address the problem of automatic transfer from face photos to portrait drawings with unpaired training data.
We observe that due to the signi?cant imbalance of information richness between photos and drawings,
existing unpaired transfer methods such as CycleGAN tend to embed invisible reconstruction
information indiscriminately in the whole drawings, leading to important facial features partially
missing in drawings. To address this problem, we propose a novel asymmetric cycle mapping that
enforces the reconstruction information to be visible (by a truncation loss) and only embedded
in selective facial regions (by a relaxed forward cycle-consistency loss). Along with localized
discriminators for the eyes, nose and lips, our method well preserves all important facial features
in the generated portrait drawings. By introducing a style classifier and taking the style vector into account,
our method can learn to generate portrait drawings in multiple styles using a single network.
Extensive experiments show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods
Towards Better Generalization: Joint Depth-Pose Learning without PoseNet
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020, 9151-9161.

Wang Zhao, Shaohui Liu, Yezhi Shu Yong-Jin Liu
In this work, we tackle the essential problem of scale inconsistency for self-supervised
joint depth-pose learning. Most existing methods assume that a consistent scale of depth and pose can
be learned across all input samples, which makes the learning problem harder, resulting in degraded
performance and limited generalization in indoor environments and long-sequence visual odometry
application. To address this issue, we propose a novel system that explicitly disentangles
scale from the network estimation. Instead of relying on PoseNet architecture, our method
recovers relative pose by directly solving fundamental matrix from dense optical ?ow
correspondence and makes use of a two-view triangulation module to recover an up-to-scale
3D structure. Then, we align the scale of the depth prediction with the triangulated point
cloud and use the transformed depth map for depth error computation and dense reprojection
check. Our whole system can be jointly trained end-to-end. Extensive experiments show that
our system not only reaches state-of-the-art performance on KITTI depth and flow estimation,
but also significantly improves the generalization ability of existing self-supervised
depth-pose learning methods under a variety of challenging scenarios, and achieves
state-of-the-art results among self-supervised learning-based methods on KITTI Odometry and NYUv2 dataset.
Furthermore, we present some interesting ?ndings on the limitation of PoseNet-based relative pose estimation
methods in terms of generalization ability. Code is available at https://github.com/B1ueber2y/TrianFlow.
A Metric for Video Blending Quality Assessment
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, Vol. 29, 3014-3022.

Zhe Zhu, Hantao Liu, Jiaming Lu and Shi-Min Hu
We propose an objective approach to assess the quality of video blending. Blending
is a fundamental operation in video editing, which can smooth the intensity changes
of relevant regions. However blending also generates artefacts such as bleeding and
ghosting. To assess the quality of the blended videos, our approach considers the
illuminance consistency as a positive aspect while regard the artefacts as a negative aspect.
Temporal coherence between frames is also considered. We evaluate our metric on a video
blending dataset where the results of subjective evaluation are available.
Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our proposed metric, and shows that
this metric gives superior performance over existing video quality metrics.
Deep Portrait Image Completion and Extrapolation
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, Vol. 29, 2344-2355.

Xian Wu, Rui-Long Li, Fang-Lue Zhang, Jian-Cheng Liu, Jue Wang, Ariel Shamir and Shi-Min Hu
General image completion and extrapolation methods often fail on portrait images where parts of
the human body need to be recovered - a task that requires accurate human body structure and
appearance synthesis. We present a twostage deep learning framework for tackling this problem.
In the first stage, given a portrait image with an incomplete human body, we extract a complete,
coherent human body structure through a human parsing network, which focuses on structure recovery
inside the unknown region with the help of full-body pose estimation. In the second stage, we
use an image completion network to ?ll the unknown region, guided by the structure map recovered in
the first stage. For realistic synthesis the completion network is trained with both perceptual
loss and conditionaladversarial loss. We furtherpropose a face re?nement network to improve the
fidelity of the synthesized face region. We evaluate our method on publicly-available portrait image
datasets, and show that it outperforms other state-of-the-art general image completion methods.
Our method enables new portrait image editing applications such as occlusion removal and portrait extrapolation.
We further show that the proposed general learning framework can be applied to other types of images,
e.g. animal images.
Poisson Vector Graphics (PVG)
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2020, Vol. 26, No.2, 1361-1371.

Fei Hou, Qian Sun, Zheng Fang, Yong-Jin Liu, Shi-Min Hu, Hong Qin, Aimin Hao, and Ying He
This paper presents Poisson vector graphics (PVG), an extension of the popular diffusion curves (DC), for generating
smooth-shaded images. Armed with two new types of primitives, called Poisson curves and Poisson regions, PVG can easily produce
photorealistic effects such as specular highlights, core shadows, translucency and halos. Within the PVG framework, the users specify
color as the Dirichlet boundary condition of diffusion curves and control tone by offsetting the Laplacian of colors, where both controls
are simply done by mouse click and slider dragging. PVG distinguishes itself from other diffusion based vector graphics for 3 unique
features: 1) explicit separation of colors and tones, which follows the basic drawing principle and eases editing; 2) native support of
seamless cloning in the sense that PCs and PRs can automatically fit into the target background; and 3) allowed intersecting primitives
(except for DC-DC intersection) so that users can create layers. Through extensive experiments and a preliminary user study, we
demonstrate that PVG is a simple yet powerful authoring tool that can produce photo-realistic vector graphics from scratch.
Temporally Coherent Video Harmonization Using Adversarial Networks
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, Vol. 29, 214-224.

Hao-Zhi Huang, Sen-Zhe Xu, Jun-Xiong Cai, Wei Liu, and Shi-Min Hu
Compositing is one of the most important editing operations for images and videos. The process of improving the
realism of composite results is often called harmonization. Previous approaches for harmonization mainly focus on images.
In this paper, we take one step further to attack the problem of video harmonization. Speci?cally, we train a
convolutional neural network in an adversarial way, exploiting a pixel-wise disharmony discriminator to
achieve more realistic harmonized results and introducing a temporal loss to increase temporal consistency
between consecutive harmonized frames. Thanks to the pixel-wise disharmony discriminator, we are also able
to relieve the need of input foreground masks. Since existing video datasets which have ground-truth
foreground masks and optical ?ows are not suf?ciently large, we propose a simple yet ef?cient method to
build up a synthetic dataset supporting supervised training of the proposed adversarial network.
The experiments show that training on our synthetic dataset generalizes well to the real-world composite
dataset. In addition, our method successfully incorporates temporal consistency during training and
achieves more harmonious visual results than previous methods.
Other publications in 2020
1. Ding-Nan Zou, Song-Hai Zhang, Tai-Jiang Mu & Min Zhang,
A new dataset of dog breed images and a benchmark for finegrained classification,
Computational Visual Media, 2021, Vol. 7, No. 4, 477-487.

2. Xin Wen, Miao Wang, Christian Richardt, Ze-Yin Chen, Shi-Min Hu,
Photorealistic Audio-driven Video Portraits,
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2020, Vol. 26, No. 12, 3457-3466.

3. Yuntao Jiang, Chen-Feng Li, Shujie Deng, Shi-Min Hu,
A Divergence-free Mixture Model for Multiphase Fluids,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2020, Vol. 39, No. 8, 69-77.

4. Shi-Sheng Huang, Ze-Yu Ma, Tai-Jiang Mu, Hongbo Fu, Shi-Min Hu,
Lidar-Monocular Visual Odometry using Point and Line Features,
IEEE ICRA, 2020, 1092-1097.

5. Minghua Liu, Lu Sheng, Sheng Yang, Jing Shao, Shi-Min Hu,
Morphing and Sampling Network for Dense Point Cloud Completion,
AAAI, 2020, 11596-11603.

6. Xian Wu, Xiao-Nan Fang, Tao Chen & Fang-Lue Zhang,
JMNet: A joint matting network for automatic human matting,
Computational Visual Media, 2020, Vol. 6, No. 2, 215-224.

7. Song-Hai Zhang1, Zheng-Ping Zhou, Bin Liu, Xi Dong, and Peter Hall,
What and where: A context-based recommendation system for object insertion,
Computational Visual Media, 2020, Vol. 6, No. 1, 79-93.

2019
Write-A-Video: Computational Video Montage from Themed Text
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, Vol. 38, No. 6, Article 177.

 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)
Miao Wang, Guo-Wei Yang, SHi-Min Hu, Shing-Tung Yau, Ariel Shamir,
We present Write-A-Video, a tool for the creation of video montage using mostlytext-editing.
Given an input themed text and a related video repository either from online websites or
personal albums, the tool allows novice users to generate a video montage much more
easily than current video editingtools. The resulting video illustrates the given
narrative, provides diverse visual content, and follows cinematographic guidelines.
The process involves three simple steps:
(1) the user provides input,mostly in the form of editing the text,
(2) the tool automatically searches for semantically matching candidate shots from
the video repository, and
(3) an optimization method assembles the video montage.
Visual-semantic matching between segmented text and shots is performed by cascaded
keyword matching and visual-semantic embedding, that have better accuracy than alternative
solutions. The video assembly is formulated as a hybrid optimization problem over a graph
of shots, considering temporal constraints, cinematography metrics such as camera movement
and tone, and user-specified cinematography idioms. Using our system,
users without video editing experience are able to generate appealing videos.
ClusterSLAM: A SLAM Backend for Simultaneous Rigid Body Clustering and Motion Estimation
IEEE ICCV, 2019, 5875-5884.

Jiahui Huang, Sheng Yang, Zishuo Zhao, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu
We present a practical backend for stereo visual SLAM which can simultaneously discover individual
rigid bodies and compute their motions in dynamic environments.
While recent factor graph based state optimization algorithms have shown their ability
to robustly solve SLAM problems by treating dynamic objects as outliers,
the dynamic motions are rarely considered. In this paper, we exploit the consensus
of 3D motions among the landmarks extracted from the same rigid body for clustering
and estimating static and dynamic objects in a uni?ed manner. Specifically,
our algorithm builds a noise-aware motion af?nity matrix upon landmarks,
and uses agglomerative clustering for distinguishing those rigid bodies.
Accompanied by a decoupled factor graph optimization for revising their shape and trajectory,
we obtain an iterative scheme to update both cluster assignments and motion estimation reciprocally.
Evaluations on both synthetic scenes and KITTI demonstrate the capability of our approach,
and further experiments considering online ef?ciency also show the effectiveness of
our method for simultaneous tracking of egomotion and multiple objects.
Two-Layer QR Codes
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, Vol. 28, No. 9, 4413-4428.
.

Tailing Yuan, Yili Wang, Kun Xu, Ralph R. Martin, Shi-Min Hu
A quick-response code (QR code) is a twodimensional code akin to a barcode which encodes a message
of limited length. In this paper, we present a variant of QR code, a two-layer QR code. Its two-layer structure can display
two alternative messages when scanned from two different directions. We propose a method to generate such two-layer
QR codes encoding two given messages in a few seconds. We also demonstrate the robustness of our method on both synthetic
and fabricated examples. All source code will be made publicly available.
Deep inverse rendering for high-resolution SVBRDF estimation from an arbitrary number of images
ACM Transations on Graphics, Vol. 38, No. 4, article No. 134, (ACM SIGGRAPH 2019).
.

Duan Gao, Xiao Li, Yue Dong, Pieter Peers, Kun Xu, Xin Tong
In this paper we present a unified deep inverse rendering framework for
estimating the spatially-varying appearance properties of a planar exemplar
from an arbitrary number of input photographs, ranging from just a single
photograph to many photographs. The precision of the estimated appearance
scales from plausible when the input photographs fails to capture all the
reflectance information, to accurate for large input sets. A key distinguishing
feature of our framework is that it directly optimizes for the appearance
parameters in a latent embedded space of spatially-varying appearance, such
that no handcrafted heuristics are needed to regularize the optimization.
This latent embedding is learned through a fully convolutional auto-encoder
that has been designed to regularize the optimization. Our framework not
only supports an arbitrary number of input photographs, but also at high
resolution. We demonstrate and evaluate our deep inverse rendering solution
on a wide variety of publicly available datasets.
Deep Online Video Stabilization With Multi-Grid Warping Transformation Learning
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, Vol. 28, No. 5, 2283-2292.

Miao Wang, Guo-Ye Yang, Jin-Kun Lin, Song-Hai Zhang, Ariel Shamir, Shao-Ping Lu, Shi-Min Hu
Video stabilization techniques are essential for most hand-held captured videos due to
high-frequency shakes. Several 2D-, 2.5D-, and 3D-based stabilization techniques have been
presented previously, but to the best of our knowledge, no solutions based on deep neural
networks had been proposed to date. The main reason for this omission is shortage in training data
as well as the challenge of modeling the problem using neural networks. In this paper, we present
a video stabilization technique using a convolutional neural network. Previous works usually
propose an off-line algorithm that smoothes a holistic camera path based on feature matching.
Instead, we focus on low-latency, real-time camera path smoothing that does not explicitly
represent the camera path and does not use future frames. Our neural network model, called StabNet,
learns a set of mesh-grid transformations progressively for each input frame from the previous
set of stabilized camera frames and creates stable corresponding latent camera paths implicitly.
To train the network, we collect a dataset of synchronized steady and unsteady video pairs
via a specially designed hand-held hardware. Experimental results show that our proposed
online method performs comparatively to the traditional off-line video stabilization methods
without using future frames while running about 10 times faster. More importantly, our proposed
StabNet is able to handle low-quality videos, such as night-scene videos, watermarked videos,
blurry videos, and noisy videos, where the existing methods fail in feature extraction or matching.
S4Net: SingleStageSalient-InstanceSegmentation
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019.

Ruochen Fan, Ming-Ming Cheng, Qibin Hou, Tai-Jiang Mu, Jingdong Wang, Shi-Min Hu
We consider an interesting problem - salient instance segmentation in this paper.
Other than producing bounding boxes, our network also outputs high-quality instance-level segments.
Taking into account the category-independent property of each target, we design a single stage salient
instance segmentation framework, with a novel segmentation branch. Our new branch regards not only
local context inside each detection window but also its surrounding context, enabling us to
distinguish the instances in the same scope even with obstruction. Our network is end-toend
trainable and runs at a fast speed (40 fps when processing an image with resolution 320 x 320).
We evaluate our approach on a public available benchmark and show that it outperforms other
alternative solutions. We also provide a thorough analysis of the design choices to help
readers better understand the functions of each part of our network. The source code can
be found at https: //github.com/RuochenFan/S4Net.
APDrawingGAN: Generating Artistic Portrait Drawings from Face Photo swith Hierarchical GANs
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019.
 supplemental:
supplemental:

Ran Yi, Yong-Jin Liu, Yu-Kun Lai, Paul L. Rosin
Significant progress has been made with image stylization using deep learning, especially with generative
adversarial networks (GANs).
However, existing methods fail to produce high quality artistic portrait drawings.
Such drawings have a highly abstract style, containing a sparse set of continuous graphical elements such as lines,
and so small artifacts are more exposed than for painting styles. Moreover, artists tend to use different strategies
to draw different facial features and the lines drawn are only loosely related to obvious image features.
To address these challenges, we propose APDrawingGAN, a novel GAN based architecture that builds upon hierarchical
generators and discriminators combining both a global network (for images as a whole) and local networks
(for individual facial regions). This allows dedicated drawing strategies to be learned for
different facial features. To train APDrawingGAN, we construct an artistic drawing
dataset containing high-resolution portrait photos and corresponding professional artistic drawings.
Pose2Seg: DetectionFreeHumanInstanceSegmentation
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019.

Song-Hai Zhang, Ruilong Li, Xin Dong, Paul Rosin, Zixi Cai, Xi Han, Dingcheng Yang, Haozhi Huang and Shi-Min Hu
In this paper, we present a brand new pose-based instance segmentation
framework for humans which separates instances based on human pose, rather than proposal region detection.
We demonstrate that our pose-based framework can achieve better accuracy than the state-of-art detectionbased
approach on the human instance segmentation problem, and can moreover better handle occlusion.
Furthermore,there are few public datasets containing many heavily occluded humans along with comprehensive annotations,
which makes this a challenging problem seldom noticed by researchers. Therefore, in this paper we introduce a
new benchmark "Occluded Human (OCHuman)", which focusesonoccludedhumanswithcomprehensiveannotations including
bounding-box, human pose and instance masks. This dataset contains 8110 detailed annotated human instances
within 4731 images. With an average 0.67 MaxIoU for each person, OCHuman is the most complex and challenging
dataset related to human instance segmentation. Through this dataset,
we want to emphasize occlusion as a challenging problem for researchers to study.
Example-Guided Style-Consistent Image Synthesis from Semantic Labeling
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019.

Miao Wang, Guo-Ye Yang, Ruilong Li, Run-Ze Liang, Song-Hai Zhang, Peter M. Hall, Shi-Min Hu
Example-guided image synthesis aims to synthesize an image from a semantic label map and an exemplary
image indicating style. We use the term "style" in this problem to refer to implicit characteristics
of images, for example: in portraits "style" includes gender, racial identity, age, hairstyle;
in full body pictures it includes clothing; in street scenes it refers to weather and time of day and such like.
A semantic label map in these cases indicates facial expression, full body pose, or scene segmentation.
We propose a solution to the example-guided image synthesis problem using conditional generative adversarial
networks with style consistency. Our key contributions are(i)anovelstylecon sistency discriminator to
determine whether a pair of images are consistent in style;
(ii) an adaptive semantic consistency loss; and (iii) a training data sampling strategy,
for synthesizing style-consistent results to the exemplar. We demonstrate the efficiency of our method on face,
danceand street view synthesis tasks.
Probabilistic Projective Association and Semantic Guided Relocalization for Dense Reconstruction
International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2019.

Sheng Yang, Zheng-Fei Kuang, Yan-Pei Cao, Yu-Kun Lai, and Shi-Min Hu
We present a real-time dense mapping system which uses the predicted 2D semantic labels for optimizing the
geometric quality of reconstruction. With a combination of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for 2D
labeling and a Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) system for camera trajectory estimation,
recent approaches have succeeded in incrementally fusing and labeling 3D scenes. However,
the geometric quality of the reconstruction can be further improved by incorporating such semantic prediction results,
which is not sufficiently exploited by existing methods. In this paper, we propose to use semantic
information to improve two crucial modules in the reconstruction pipeline, namely tracking and loop detection,
for obtaining mutual benefits in geometric reconstruction and semantic recognition. Specifically for tracking,
we use a novel probabilistic projective association approach to efficiently pick out candidate correspondences,
where the confidence of these correspondences is quantified concerning similarities on all available short-term
invariant features. For the loop detection, we incorporate these semantic labels into the original encoding
through Randomized Ferns to generate a more comprehensive representation for retrieving candidate
loop frames.
LineUp: Computing Chain-Based Physical Transformation
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, Vol. 38, No.1, article No. 11

Minjing Yu, Zipeng Ye, Yong-Jin Liu, Ying He, Charlie Wang
In this article, we introduce a novel method that can generate a sequence of physical
transformations between 3D models with different shape and topology. Feasible
transformations are realized on a chain structure with connected components that are
3D printed. Collision-free motions are computed to transform between different configurations
of the 3D printed chain structure. To realize the transformation between different 3D models,
we first voxelize these input models into a similar number of voxels. The challenging part of
our approach is to generate a simple path¡ªas a chain configuration to connect most voxels. A
layer-based algorithm is developed with theoretical guarantee of the existence and the path
length. We find that collision-free motion sequence can always be generated when using a
straight line as the intermediate configuration of transformation. The effectiveness of
our method is demonstrated by both the simulation and the experimental tests taken on 3D
printed chains.
Other publications in 2019
1. Yili Wang, Yifan Liu, Kun Xu,
An Improved Geometric Approach for Palette©\based Image Decomposition and Recoloring,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2019, Vol. 38, No. 7, 11-22 (PG 2019).

2. Xiao-Nan Fang, Miao Wang, Ariel Shamir, Shi-Min Hu,
Learning Explicit Smoothing Kernels for Joint Image Filtering,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2019, Vol. 38, No. 7, 181-190 (PG 2019).

3. Jiaming Lu, Xiao-Song Chen, Xiao Yan, Chen-Feng Li, Ming Lin, Shi-Min Hu,
A Rigging-Skinning Scheme to Control Fluid Simulation,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2019, Vol. 38, No. 7, 501-512 (PG 2019).

4. Junxiong Cai, Tai-Jiang Mu, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu, Deep point-based scene labeling with depth mapping and geometric patch feature encoding,
Graphical Models, 2019, Vol. 104, 101033.

5. Bing Xu, Junfei Zhang, Rui Wang, Kun Xu, Yong-Liang Yang, Chuan Li, Rui Tang,
Adversarial Monte Carlo denoising with conditioned auxiliary feature modulation,
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, Vol. 38, No.6, article No. 224.

 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)
6. Yifan Liu, Kun Xu, Ling-Qi Yan,
Adaptive BRDF-Aware Multiple Importance Sampling of Many Lights,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2019, Vol. 38, No. 4, 123-133 (EGSR 2019).

7. Tai-Ling Yuan, Zhe Zhu, Kun Xu, Cheng-Jun Li, Tai-Jiang Mu, Shi-Min Hu,
A Large Chinese Text Dataset in the Wild,
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2019, Vol. 34, No. 3, 509-521.

8. Qian Fu, Ying He, Fei Hou, Juyong Zhang, Anxiang Zeng, Yong-Jin Liu,
Vectorization Based Color Transfer for Portrait Images,
Computer-Aided Design, 2019, Vol. 115, 111-121.

9. Zipeng Ye, Yong-Jin Liu, Jianmin Zheng, Kai Hormann, Ying He,
DE-Path: A Differential-Evolution-Based Method for Computing Energy-Minimizing Paths on Surfaces,
Computer-Aided Design, 2019, Vol. 114, 73-81.

10. Chenming Wu, Chengkai Dai, Xiaoxi Gong, Yong-Jin Liu, et al.,
Energy Efficient Coverage Path Planning for General Terrain Surfaces,
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, Vol. 4, No. 3, 2584-2591.

11. Chenming Wu, Rui Zeng, Jia Pan, Charlie C. L. Wang, Yong-Jin Liu, Plant Phenotyping by Deep-Learning-Based Planner for Multi-Robots,
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, Vol. 4, No. 4, 3113-3120

12. Zipeng Ye, Minjing Yu, Yong-Jin Liu, NP-completeness of optimal planning problem for modular robots,
Autonomous Robots, 2019, Vol. 43, No. 8, 2261-2270.

13. Shuyang Zhang, Runze Liang, and Miao Wang,
ShadowGAN: Shadow synthesis for virtual objects with conditional adversarial networks,
Computational Visual Media, 2019, Vol. 5, No. 1, 105-115.

14. Ruochen Fan, Xuanrun Wang, Qibin Hou, Hanchao Liu, and Tai-Jiang Mu
SpinNet: Spinning convolutional network for lane boundary detection,
Computational Visual Media, 2019, Vol. 5, No. 4, 417-428.

2018
BiggerSelfie: Selfie Video Expansion with Hand-held Camera
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, Vol. 27, No. 12, 5854-5865.

Miao Wang, Ariel Shamir,Guo-Ye Yang, Jin-Kun Lin, Guo-Wei Yang, Shao-Ping Lu and Shi-Min Hu
Selfie photography from hand-held camera is becoming a popular media type. Although being convenient and flexible, it suffers from low camera motion stability, small field of view
and limited background content. These limitations can annoy users, especially when touring a place of interest and taking selfie videos. In this paper, we present a novel method to create what we call a BiggerSelfie that deals with these shortcomings.
Using a video of the environment that has partial content overlap with the selfie video, we stitch plausible frames selected from the environment video to the original selfie frames, and stabilize the composed video content with a portrait-preserving constraint.
Using the proposed method, one can easily obtain a stable selfie video with expanded background content by merely capturing some background shots. We show various results and several evaluations to demonstrate the applicability of our method.
Delaunay Mesh Simplification with Differential Evolution
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, Vol. 37, No.6, Article No. 263.

RAN YI, Yong-Jin Liu, Ying He
Delaunay meshes (DM) are a special type of manifold triangle meshes where the local Delaunay condition holds everywhere ¡ª and find important
applications in digital geometry processing. This paper addresses the general DM simplification problem: given an arbitrary manifold triangle mesh
M with n vertices and the user-specified resolution m (< n), compute a Delaunay mesh M* with m vertices that has the least Hausdorf distance
to M. To solve the problem, we abstract the simplification process using a 2D Cartesian grid model, in which each grid point corresponds to triangle
meshes with a certain number of vertices and a simplification process is a monotonic path on the grid.We develop a novel diffierential-evolution-based
method to compute a low-cost path, which leads to a high quality Delaunay mesh. Extensive evaluation shows that our method consistently outperforms
the existing methods in terms of approximation error. In particular, our method is highly effective for small-scale CAD models and man-made
objects with sharp features but less details. Moreover, our method is fully automatic and can preserve sharp features well and deal with models with
multiple components, whereas the existing methods often fail.
Real-time High-accuracy 3D Reconstruction with Consumer RGB-D Cameras
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, Vol. 37, No.5, Article No. 171.

Yan-Pei Cao, Leif Kobbelt, Shi-Min Hu
We present an integrated approach for reconstructing high-fidelity 3D models using consumer RGB-D cameras. RGB-D registration and reconstruction
algorithms are prone to errors from scanning noise, making it hard to perform 3D reconstruction accurately. The key idea of our method is to assign
a probabilistic uncertainty model to each depth measurement, which then guides the scan alignment and depth fusion. This allows us to effectively
handle inherent noise and distortion in depth maps while keeping the overall scan registration procedure under the iterative closest point (ICP) frame-
work for simplicity and efficiency. We further introduce a local-to-global, submap-based, and uncertainty-aware global pose optimization scheme to
improve scalability and guarantee global model consistency. Finally, we have implemented the proposed algorithm on the GPU, achieving real-time
3D scanning frame rates and updating the reconstructed model on-the-fly. Experimental results on simulated and real-world data demonstrate that
the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art systems in terms of the accuracy of both recovered camera trajectories and reconstructed models.
PhotoRecomposer: Interactive Photo Recomposition by Cropping (Spotlight paper)
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2018, Vol. 24, No. 10, 2728-2742.

Yuan Liang, Xiting Wang, Song-Hai Zhang, Shi-Min Hu and Shixia Liu
We present a visual analysis method for interactively recomposing a large number of photos based on example photos with
high-quality composition. The recomposition method is formulated as a matching problem between photos. The key to this formulation is
a new metric for accurately measuring the composition distance between photos. We have also developed an earth-mover-distancebased
online metric learning algorithm to support the interactive adjustment of the composition distance based on user preferences. To
better convey the compositions of a large number of example photos, we have developed a multi-level, example photo layout method to
balance multiple factors such as compactness, aspect ratio, composition distance, stability, and overlaps. By introducing an
EulerSmooth-based straightening method, the composition of each photos is clearly displayed. The effectiveness and usefulness of the
method has been demonstrated by the experimental results, user study, and case studies.
Learning to Reconstruct High-quality 3D Shapes with Cascaded Fully Convolutional Networks
Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018, 616-633.

Yan-Pei Cao, Zheng-Ning Liu, Zheng-Fei Kuang, Leif Kobbelt, Shi-Min Hu
We present a data-driven approach to reconstructing highresolution and detailed volumetric representations of 3D shapes. Although
well studied, algorithms for volumetric fusion from multi-view depth scans are still prone to scanning noise and occlusions, making it
hard to obtain high-fidelity 3D reconstructions. In this paper, inspired by recent advances in efficient 3D deep learning techniques, we introduce
a novel cascaded 3D convolutional network architecture, which learns to reconstruct implicit surface representations from noisy and incomplete
depth maps in a progressive, coarse-to-fine manner. To this end, we also develop an algorithm for end-to-end training of the proposed cascaded
structure. Qualitative and quantitative experimental results on both simulated and real-world datasets demonstrate that the presented approach
outperforms existing state-of-the-art work in terms of quality and fidelity of reconstructed models.
Associating Inter-Image Salient Instances for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018, 367-383.

Ruochen Fan, Qibin Hou, Ming-Ming Cheng, Gang Yu, Ralph R. Martin, and Shi-Min Hu
Effectively bridging between image level keyword annotations and corresponding image pixels is one of the main challenges in weakly supervised
semantic segmentation. In this paper, we use an instance-level salient object detector
to automatically generate salient instances (candidate objects) for training
images. Using similarity features extracted from each salient instance in the
whole training set, we build a similarity graph, then use a graph partitioning algorithm
to separate it into multiple subgraphs, each of which is associated with
a single keyword (tag). Our graph-partitioning-based clustering algorithm allows
us to consider the relationships between all salient instances in the training set
as well as the information within them. We further show that with the help of attention
information, our clustering algorithm is able to correct certain wrong assignments,
leading to more accurate results. The proposed framework is general,
and any state-of-the-art fully-supervised network structure can be incorporated
to learn the segmentation network. When working with DeepLab for semantic
segmentation, our method outperforms state-of-the-art weakly supervised alternatives
by a large margin, achieving 65.6% mIoU on the PASCAL VOC 2012
dataset. We also combine our method with Mask R-CNN for instance segmentation,
and demonstrated for the first time the ability of weakly supervised instance
segmentation using only keyword annotations.
Detecting and Removing Visual Distractors for Video Aesthetic Enhancement
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, Vol. 20, No. 8, 1987-1999.
 demo:
demo:  More examples:
More examples: 
Fang-Lue Zhang, Xian Wu, Rui-Long Li, Jue Wang,Zhao-Heng Zheng and Shi-Min Hu
Personal videos often contain visual distractors, which are objects that are accidentally captured that can distract viewers from focusing
on the main subjects. We propose a method to automatically detect and localize these distractors through learning from a manually labeled
dataset. To achieve spatially and temporally coherent detection, we propose extracting features at the Temporal-Superpixel (TSP) level using a
traditional SVM-based learning framework. We also experiment with end-to-end learning using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which
achieves slightly higher performance than other methods. The classification result is further refined in a post-processing step based on graph-cut
optimization. Experimental results show that our method achieves an accuracy of 81% and a recall of 86%. We demonstrate several ways of
removing the detected distractors to improve the video quality, including video hole filling; video frame replacement; and camera path re-planning.
The user study results show that our method can significantly improve the aesthetic quality of videos.
Real-time High-fidelity Surface Flow Simulation
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2018, Vol. 24, No. 8, 2411-2423.

Bo Ren, Tailing Yuan, Chenfeng Li, Kun Xu, and Shi-Min Hu
Surface flow phenomena, such as rain water flowing down a tree trunk and progressive water front in a shower room,
are common in real life. However, compared with the 3D spatial fluid flow, these surface flow problems have been much less
studied in the graphics community. To tackle this research gap, we present an efficient, robust and high-fidelity simulation
approach based on the shallow-water equations. Specifically, the standard shallow-water flow model is extended to general
triangle meshes with a feature-based bottom friction model, and a series of coherent mathematical formulations are derived to
represent the full range of physical effects that are important for real-world surface flow phenomena. In addition, by achieving
compatibility with existing 3D fluid simulators and by supporting physically realistic interactions with multiple fluids and solid
surfaces, the new model is flexible and readily extensible for coupled phenomena. A wide range of simulation examples are
presented to demonstrate the performance of the new approach.
A Comparative Study of Algorithms for Realtime Panoramic Video Blending
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, Vol. 27, No. 6, 2952-2965.

Zhe Zhu, Jiaming Lu, Minxuan Wang, Songhai Zhang, Ralph R. Martin, Hantao Liu,
and Shi-Min Hu
Unlike image blending algorithms, video blending algorithms have been little studied. In this paper, we investigate 6 popular blending algorithms¡ªfeather blending, multi-band
blending, modified Poisson blending, mean value coordinate blending, multi-spline blending and convolution pyramid blending. We consider their application to blending realtime panoramic
videos, a key problem in various virtual reality tasks. To evaluate the performances and suitabilities of the 6 algorithms for this problem, we have created a video benchmark with several videos
captured under various conditions. We analyze the time and memory needed by the above 6 algorithms, for both CPU and GPU implementations (where readily parallelizable). The visual quality provided by these algorithms is also evaluated both
objectively and subjectively. The video benchmark and algorithm implementations are publicly available.
CartoonGAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Photo Cartoonization
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018, 9465-9474.

Yang Chen, Yu-Kun Lai, Yong-Jin Liu
In this paper, we propose CartoonGAN, a generative adversarial network (GAN) framework
for cartoon stylization. Our method takes unpaired photos and cartoon images for training, which is easy to
use. Two novel losses suitable for cartoonization are proposed:
(1) a semantic content loss, which is formulated as a sparse regularization in the high-level feature maps of
the VGG network to cope with substantial style variation between photos and cartoons, and (2) an edge-promoting
adversarial loss for preserving clear edges. We further introduce an initialization phase, to improve the convergence
of the network to the target manifold. Our method is also much more efficient to train than existing methods. Experimental
results show that our method is able to generate high-quality cartoon images from real-world photos (i.e.,
following specific artists¡¯ styles and with clear edges and smooth shading) and outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Content-Sensitive Supervoxels via Uniform Tessellations on Video Manifolds
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018, 646-655.

Ran Yi, Yong-Jin Liu, Yu-Kun Lai
In this paper, we propose content-sensitive supervoxels (CSS), which are
regularly-shaped 3D primitive volumes that possess the following characteristic: they are typically larger and longer
in content-sparse regions (i.e., with homogeneous appearance and motion), and smaller and shorter in content-dense
regions (i.e., with high variation of appearance and/or motion). To compute CSS, we map a video $\xi$ to a
3-dimensional manifold M embedded in $R^6$, whose volume elements give a good measure of the content density in
We propose an efficient Lloyd-like method with a splitting-merging scheme to compute a uniform tessellation on M,
which induces the CSS in $\xi$. Theoretically our method has a good competitive ratio O(1). We also present a simple
extension of CSS to stream CSS for processing long videos
that cannot be loaded into main memory at once. We evaluate CSS, stream CSS and seven representative supervoxel
methods on four video datasets. The results show that our method outperforms existing supervoxel methods.
Hyper-lapse from Multiple Spatially-overlapping Videos
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, Vol. 27, No. 4, 1735 - 1747.
 demo:
demo:  More examples:
More examples: 
Miao Wang, Jun-Bang Liang, Song-Hai Zhang, Shao-Ping Lu, Ariel Shamir and Shi-Min Hu
Hyper-lapse video with high speed-up rate is an efficient way to overview long videos such as a human activity in first-person view. Existing hyper-lapse video creation methods
produce a fast-forward video effect using only one video source. In this work, we present a novel hyper-lapse video creation approach based on multiple spatially-overlapping videos. We assume the videos share a common view or location, and find
transition points where jumps from one video to another may occur. We represent the collection of videos using a hyper-lapse transition graph; the edges between nodes represent possible hyper-lapse frame transitions. To create a hyper-lapse video, a shortest path search is performed on this digraph to optimize
frame sampling and assembly simultaneously. Finally, we render the hyper-lapse results using video stabilization and appearance smoothing techniques on the selected frames. Our technique can synthesize novel virtual hyper-lapse routes which may not exist
originally. We show various application results on both indoor and outdoor video collections with static scenes, moving objects, and crowds.
Intrinsic Manifold SLIC: A Simple and Efficient Method for Computing Content-Sensitive Superpixels
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, Vol. 40, No. 3, 653 - 666.

Yong-Jin Liu, Minjing Yu, Bing-Jun Li, and Ying He
Superpixels are perceptually meaningful atomic regions that can effectively capture image features. Among various
methods for computing uniform superpixels, simple linear iterative clustering (SLIC) is popular due to its simplicity and high
performance. In this paper, we extend SLIC to compute content-sensitive superpixels, i.e., small superpixels in content-dense regions
with high intensity or colour variation and large superpixels in content-sparse regions. Rather than using the conventional SLIC method
that clusters pixels in R5, we map the input image I to a 2-dimensional manifoldM�R5, whose area elements are a good measure of
the content density in I. We propose a simple method, called intrinsic manifold SLIC (IMSLIC), for computing a geodesic centroidal
Voronoi tessellation (GCVT)¡ªa uniform tessellation¡ªonM, which induces the content-sensitive superpixels in I. In contrast to the
existing algorithms, IMSLIC characterizes the content sensitivity by measuring areas of Voronoi cells onM. Using a simple and fast
approximation to a closed-form solution, the method can compute the GCVT at a very low cost and guarantees that all Voronoi cells are
simply connected. We thoroughly evaluate IMSLIC and compare it with eleven representative methods on the BSDS500 dataset and
seven representative methods on the NYUV2 dataset. Computational results show that IMSLIC outperforms existing methods in terms
of commonly used quality measures pertaining to superpixels such as compactness, adherence to boundaries, and achievable
segmentation accuracy. We also evaluate IMSLIC and seven representative methods in an image contour closure application, and the
results on two datasets, WHD and WSD, show that IMSLIC achieves the best foreground segmentation performance.
Controllable Dendritic Crystal Simulation Using Orientation Field
Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37, No.2, 485-495, 2018, (Eurographics 2018).
 demo:
demo: 
Bo Ren, Jiahui Huang, Ming C. Lin, and Shi-Min Hu
Real world dendritic growths show charming structures by their exquisite balance between the symmetry and randomness in the crystal formation. Other than the variety in the natural crystals, richer visual appearance of crystals can benefit from artificially
controlling of the crystal growth on its growing directions and shapes. In this paper, by introducing one extra dimension of freedom, i.e. the orientation field, into the simulation, we propose an efficient algorithm for dendritic crystal simulation that is
able to reproduce arbitrary symmetry patterns with different levels of asymmetry breaking effect on general grids or meshes, including spreading on curved surfaces and growth in 3D. Flexible artistic control is also enabled in a unified manner by
exploiting and guiding the orientation field in the visual simulation. We show the effectiveness of our approach by various demonstrations of simulation results.
Computational Design of Transforming Pop-up Books
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 37, No.1, 2018, Article No. 8.
 demo:
demo: 
Nan Xiao, Zhe Zhu, Ralph Martin, Kun Xu, Jia-Ming Lu and Shi-Min Hu
We present the first computational tool to help ordinary users create transforming pop-up books. In each transforming pop-up, when the user pulls a
tab, an initial flat 2D pattern, i.e. a 2D shape with a superimposed picture, such as an airplane, turns into a new 2D pattern, such as a robot, standing
up from the page. Given the two 2D patterns, our approach automatically computes a 3D pop-up mechanism that transforms one pattern into the other;
it also outputs a design blueprint, allowing the user to easily make the
final model. We also present a theoretical analysis of basic transformation
mechanisms; combining these basic mechanisms allows more flexibility of
final designs. Using our approach, inexperienced users can create models in
a short time; previously, even experienced artists often took weeks to manually
create them. We demonstrate our method on a variety of real world examples.
Other publications in 2018
1. Xiao Yan, Cheng-Feng Li, Xiao-Song Chen, Shi-Min Hu,
MPM simulation of interacting fluids and solids,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2018, Vol. 37, No. 8, 183-193.

2. Yu Fang, Yuanming Hu, Shi-Min Hu, Chenfanfu Jiang,
A Temporally Adaptive Material Point Method with Regional Time Stepping,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2018, Vol. 37, No. 8, 195-204.

3. Sen-Zhe Xu, Jun Hu, Miao Wang, Tai-Jiang Mu, Shi-Min Hu, Deep Video Stabilization Using Adversarial Networks,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2018, Vol. 37, No. 7, 267-276.

4. Yuan Liang, Fei Xu, Song-Hai Zhang, Yu-Kun Lai, and Taijiang Mu£¬
Knowledge graph construction with structure and parameter learning for indoor scene design,
Computational Visual Media, 2018, Vol. 4, No. 2, 123-137.

5. Yifan Lu, Jiaming Lu, Songhai Zhang, and Peter Hall,
Traffic signal detection and classification in street views using an attention model,
Computational Visual Media, 2018, Vol. 4, No. 3, 253-266. (2018 Honorable Mention Award)

6. Jiahui Huang, Jun Gao, Vignesh Ganapathi-Subramanian, Hao Su, Yin Liu, Chengcheng Tang, Leonidas J. Guibas,
DeepPrimitive: Image decomposition by layered primitive detection,
Computational Visual Media, 2018, Vol. 4, No. 4, 385-397.

2017
A Unified Particle System Framework for Multi-Phase, Multi-Material Visual Simulations
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 36, No. 6. ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2017, Article No.224.
 demo:
demo: 
Tao Yang, Jian Chang, Ming C. Lin, Ralph R. Martin, Jian J. Zhang, Shi-Min Hu
We introduce a unified particle framework which integrates the phase-field method with multi-material simulation to allow modeling of both liquids
and solids, as well as phase transitions between them. A simple elastoplastic
model is used to capture the behavior of various kinds of solids, including deformable bodies, granular materials, and cohesive soils. States of
matter or phases, particularly liquids and solids, are modeled using the nonconservative
Allen-Cahn equation. In contrast, materials¡ªmade of different substances¡ªare advected by the conservative Cahn-Hilliard equation. The
distributions of phases and materials are represented by a phase variable and a concentration variable, respectively, allowing us to represent commonly
observed fluid-solid interactions. Our multi-phase, multi-material system is governed by a unified Helmholtz free energy density. This framework
provides the first method in computer graphics capable of modeling a continuous
interface between phases. It is versatile and can be readily used in many scenarios that are challenging to simulate. Examples are provided to
demonstrate the capabilities and effectiveness of this approach.
An Optimization Approach for Localization Refinement of Candidate Traffic Signs
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation System, 2017, Vol. 18, No. 11, 3006-3016.

Zhe Zhu, Jiaming Lu, Ralph R. Martin, and Shi-Min Hu
We propose a localization refinement approach for candidate traffic signs. Previous traffic sign localization
approaches, which place a bounding rectangle around the sign, do not always give a compact bounding box, making the subsequent
classification task more difficult. We formulate localization as a segmentation problem, and incorporate prior knowledge
concerning color and shape of traffic signs. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach, we use it as an intermediate step
between a standard traffic sign localizer and a classifier. Our experiments use the well-known German Traffic Sign Detection
Benchmark (GTSDB) as well as our new Chinese Traffic Sign Detection Benchmark. This newly created benchmark is publicly
available,1 and goes beyond previous benchmark data sets: it has over 5000 high-resolution images containing more than
14 000 traffic signs taken in realistic driving conditions. Experimental results show that our localization approach significantly
improves bounding boxes when compared with a standard localizer, thereby allowing a standard traffic sign classifier to
generate more accurate classification results.
Pairwise Force SPH Model for Real-Time Multi-Interaction Applications
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2017, Vol. 23, No. 10, 2235 - 2247.

Tao Yang, Ralph R. Martin, Ming C. Lin, Jian Chang, and Shi-Min Hu
In this paper, we present a novel pairwise-force smoothed particle hydrodynamics (PF-SPH) model to allow modeling of
various interactions at interfaces in real time. Realistic capture of interactions at interfaces is a challenging problem for SPH-based
simulations, especially for scenarios involving multiple interactions at different interfaces. Our PF-SPH model can readily handle multiple
kinds of interactions simultaneously in a single simulation; its basis is to use a larger support radius than that used in standard SPH.
We adopt a novel anisotropic filtering term to further improve the performance of interaction forces. The proposed model is stable;
furthermore, it avoids the particle clustering problem which commonly occurs at the free surface. We show how our model can be used
to capture various interactions. We also consider the close connection between droplets and bubbles, and show how to animate bubbles
rising in liquid as well as bubbles in air. Our method is versatile, physically plausible and easy-to-implement. Examples are provided to
demonstrate the capabilities and effectiveness of our approach.
Extracting Sharp Features from RGB-D Images
Computer Graphics Forum, 2017, Vol.35, No. 8, 138-174.

Yan-Pei Cao, Tao Ju, Jie XU and Shi-Min Hu
Sharp edges are important shape features and their extraction has been extensively studied both on point clouds and surfaces.
We consider the problem of extracting sharp edges from a sparse set of colour-and-depth (RGB-D) images. The noise-ridden
depth measurements are challenging for existing feature extraction methods that work solely in the geometric domain (e.g. points
or meshes). By utilizing both colour and depth information, we propose a novel feature extraction method that produces much
cleaner and more coherent feature lines. We make two technical contributions. First, we show that intensity edges can augment
the depth map to improve normal estimation and feature localization from a single RGB-D image. Second, we designed a novel
algorithm for consolidating feature points obtained from multiple RGB-D images. By utilizing normals and ridge/valley types
associated with the feature points, our algorithm is effective in suppressing noise without smearing nearby features.
Saliency-aware Real-time Volumetric Fusion for Object Reconstruction
Computer Graphics Forum, 2017, Vol.35, No. 7, 167-174. Pacofic Graphics 2017.

Sheng Yang, Kang Chen, Minghua Liu, Hongbo Fu and Shi-Min Hu
We present a real-time approach for acquiring 3D objects with high fidelity using hand-held consumer-level RGB-D scanning
devices. Existing real-time reconstruction methods typically do not take the point of interest into account, and thus might fail
to produce clean reconstruction results of desired objects due to distracting objects or backgrounds. In addition, any changes
in background during scanning, which can often occur in real scenarios, can easily break up the whole reconstruction process.
To address these issues, we incorporate visual saliency into a traditional real-time volumetric fusion pipeline. Salient regions
detected from RGB-D frames suggest user-intended objects, and by understanding user intentions our approach can put more
emphasis on important targets, and meanwhile, eliminate disturbance of non-important objects. Experimental results on realworld
scans demonstrate that our system is capable of effectively acquiring geometric information of salient objects in cluttered
real-world scenes, even if the backgrounds are changing.
Learning to Rank Retargeted Images
IEEE CVPR, 2017: 4743-4751.

Yang Chen, Yong-Jin Liu, Yu-Kun Lai
Image retargeting techniques that adjust images into different sizes have attracted much attention recently.
Existing OQA methods output an absolute score for each retargeted image and use these scores to compare different results.
Observing that it is challenging even for human subjects to give consistent scores for retargeting results of different source images,
in this paper we propose a learning-based OQA method that predicts the ranking of a set of retargeted images with the same source image.
We show that this more manageable task helps achieve more consistent prediction to human preference and is sufficient for
most application scenarios. To compute the ranking, we propose a simple yet efficient machine learning framework that uses
a General Regression Neural Network (GRNN) to model a
combination of seven elaborate OQA metrics. We then propose a simple scheme to transform the relative scores output from GRNN into
a global ranking. We train our GRNN model using human preference data collected in the elaborate RetargetMe benchmark and evaluate
our method based on the subjective study in RetargetMe.
PlenoPatch: Patch-based Plenoptic Image Manipulation
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2017, Vol.23, No. 5, 1561-1573.

Fang-Lue Zhang, Jue Wang, Eli Shechtman, Zi-Ye Zhou, Jia-Xin Shi, and Shi-Min Hu
Patch-based image synthesis methods have been successfully applied for various editing tasks on still images, videos and stereo
pairs. In this work we extend patch-based synthesis to plenoptic images captured by consumer-level lenselet-based devices for interactive,
efficient light field editing. In our method the light field is represented as a set of images captured from different viewpoints. We decompose
the central view into different depth layers, and present it to the user for specifying the editing goals. Given an editing task, our method
performs patch-based image synthesis on all affected layers of the central view, and then propagates the edits to all other views. Interaction
is done through a conventional 2D image editing user interface that is familiar to novice users. Our method correctly handles object boundary
occlusion with semi-transparency, thus can generate more realistic results than previous methods. We demonstrate compelling results on
a wide range of applications such as hole-filling, object reshuffling and resizing, changing object depth, light field upscaling and parallax
magnification.
View suggestion for interactive segmentation of indoor scenes
Computational Visual Media, 2017, Vol. 3, No. 2, 131-146.


Sheng Yang, Jie Xu, Kang Chen, Hongbo Fu
Point cloud segmentation is a fundamental problem. Due to the complexity of real-world scenes and the limitations of 3D scanners, interactive segmentation
is currently the only way to cope with all kinds of point clouds. However, interactively segmenting complex and large-scale scenes is very time-consuming. In this paper, we present a novel interactive system
for segmenting point cloud scenes. Our system automatically suggests a series of camera views, in which users can conveniently specify segmentation guidance. In this way, users may focus on specifying
segmentation hints instead of manually searching for desirable views of unsegmented objects, thus significantly reducing user effort. To achieve this, we introduce a novel view preference model, which is based
on a set of dedicated view attributes, with weights learned from a user study. We also introduce support relations for both graph-cut-based segmentation and finding similar objects. Our experiments show that
our segmentation technique helps users quickly segment various types of scenes, outperforming alternative methods.
Constructing Intrinsic Delaunay Triangulations from the Dual of Geodesic Voronoi Diagrams
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, Vol. 36, No. 2, 15:1-15:15.

Yong-Jin Liu, Dian Fan, Chunxu Xu, Ying He
Intrinsic Delaunay triangulation (IDT) naturally generalizes Delaunay triangulation from $R^2$ to curved surfaces.
Due to many favorable properties, the
IDT whose vertex set includes all mesh vertices is of particular interest in
polygonal mesh processing. To date, the only way for constructing such IDT
is the edge-flipping algorithm, which iteratively flips non-Delaunay edges
to become locally Delaunay. Although this algorithm is conceptually simple
and guarantees to terminate in finite steps, it has no known time complexity
and may also produce triangulations containing faces with only two edges.
This article develops a new method to obtain proper IDTs on manifold triangle
meshes. We first compute a geodesic Voronoi diagram (GVD) by taking
all mesh vertices as generators and then find its dual graph. The sufficient
condition for the dual graph to be a proper triangulation is that all Voronoi
cells satisfy the so-called closed ball property. To guarantee the closed ball
property everywhere, a certain sampling criterion is required. For Voronoi
cells that violate the closed ball property, we fix them by computing topologically
safe regions, in which auxiliary sites can be added without changing the
topology of the Voronoi diagram beyond them. Given a mesh with n vertices,
we prove that by adding at most $O(n)$ auxiliary sites, the computed GVD
satisfies the closed ball property, and hence its dual graph is a proper IDT.
Our method has a theoretical worst-case time complexity $O(n^2 + tn log n)$,
where t is the number of obtuse angles in the mesh. Computational results
show that it empirically runs in linear time on real-world models.
A survey of the state-of-the-art in patch-based synthesis
Computational Visual Media, 2017, Vol. 3, No. 1, 3-20.


Connelly Barnes and Fang-Lue Zhang
This paper surveys the state-of-the-art of research in patch-based synthesis. Patch-based methods synthesize output images by copying small regions from
exemplar imagery. This line of research originated from an area called ¡°texture synthesis¡±, which focused on creating regular or semi-regular textures from small exemplars. However, more recently, much research
has focused on synthesis of larger and more diverse imagery, such as photos, photo collections, videos, and light fields. Additionally, recent research has focused
on customizing the synthesis process for particular problem domains, such as synthesizing artistic or decorative brushes, synthesis of rich materials, and
synthesis for 3D fabrication. This report investigates recent papers that follow these themes, with a particular emphasis on papers published since 2009, when the last survey in this area was published. This
survey can serve as a tutorial for readers who are not yet familiar with these topics, as well as provide comparisons between these papers, and highlight some
open problems in this area.
Other publications in 2017
1. Zhao-Heng Zheng, Hao-Tian Zhang, Fang-Lue Zhang, Tai-Jiang Mu, Image-based clothes changing system,
Computational Visual Media, 2017, Vol. 3, No. 4, 337-347.

2. Han-Chao Liu, Fang-Lue Zhang, David Marshall, Luping Shi, Shi-Min Hu, High-speed video generation with an event camera,
The Visual Computer, 2017, Vol. 33, No. 6-8, 749-759.

3. Ruochen Fan, Fang-Lue Zhang, Min Zhang, Ralph R. Martin, Robust tracking-by-detection using a selection and completion mechanism,
Computational Visual Media, 2017, Vol. 3, No. 3, 285-294.

4. Bin Liu, Kun Xu and Ralph Martin, Static Scene Illumination Estimation from Video with Applications,
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2017, Vol. 32, No. 3, 430-442.

5. Haozhi Huang, Xiaonan Fang, Yufei Ye, Songhai Zhang and Paul L. Rosin, Practical automatic background substitution for live video,
Computational Visual Media, 2017, Vol. 3, No. 3, 273-284.

2016
Extracting 3D Objects from Photographs Using 3-Sweep
Communication of ACM, 2016, Vol. 59, No. 12, 121-129.(It's invited highlight paper based on a earlier paper in ACM TOG 2013)

Tao Chen, Zhe Zhu, Shi-Min Hu, Daniel Cohen-Or, and Ariel Shamir
We introduce an interactive technique to extract and manipulate simple 3D shapes in a single photograph. Such extraction requires an understanding of the shape¡¯s components, their projections, and their relationships. These cognitive
tasks are simple for humans, but particularly difficult for automatic algorithms. Thus, our approach combines the cognitive abilities of humans with the computational accuracy of the machine to create a simple modeling tool. In
our interface, the human draws three strokes over the photograph to generate a 3D component that snaps to the outline of the shape. Each stroke defines one dimension of the
component. Such human assistance implicitly segments a complex object into its components, and positions them in space. The computer reshapes the component to fit the
image of the object in the photograph as well as to satisfy various inferred geometric constraints between components imposed by a global 3D structure. We show that this
intelligent interactive modeling tool provides the means to create editable 3D parts quickly. Once the 3D object has been extracted, it can be quickly edited and placed back into
photos or 3D scenes, permitting object-driven photo editing tasks which are impossible to perform in image-space.
Robust Background Identification for Dynamic Video Editing
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 35, No. 6. ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2016, Article No. 197.

Fang-Lue Zhang, Xian Wu, Hao-Tian Zhang, Jue Wang, Shi-Min Hu
Extracting background features for estimating the camera path is
a key step in many video editing and enhancement applications.
Existing approaches often fail on highly dynamic videos that are
shot by moving cameras and contain severe foreground occlusion.
Based on existing theories, we present a new, practical method that
can reliably identify background features in complex video, leading
to accurate camera path estimation and background layering.
Our approach contains a local motion analysis step and a global
optimization step. We first divide the input video into overlapping
temporal windows, and extract local motion clusters in each window.
We form a directed graph from these local clusters, and identify
background ones by finding a minimal path through the graph
using optimization. We show that our method significantly outperforms
other alternatives, and can be directly used to improve common
video editing applications such as stabilization, compositing
and background reconstruction.
Manifold Differential Evolution (MDE): A Global Optimization Method
for Geodesic Centroidal Voronoi Tessellations on Meshes
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 35, No. 6. ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2016, Article No. 243.

Yong-Jin Liu, Chun-Xu Xu, Ran Yi, Dian Fan, Ying He
Computing centroidal Voronoi tessellations (CVT) has many applications
in computer graphics. The existing methods, such as
the Lloyd algorithm and the quasi-Newton solver, are efficient and
easy to implement; however, they compute only the local optimal
solutions due to the highly non-linear nature of the CVT energy.
This paper presents a novel method, called manifold differential
evolution (MDE), for computing globally optimal geodesic CVT
energy on triangle meshes. Formulating the mutation operator using
discrete geodesics, MDE naturally extends the powerful differential
evolution framework from Euclidean spaces to manifold
domains. Under mild assumptions, we show that MDE has a provable
probabilistic convergence to the global optimum. Experiments
on a wide range of 3D models show that MDE consistently outperforms
the existing methods by producing results with lower energy.
Thanks to its intrinsic and global nature, MDE is insensitive
to initialization and mesh tessellation. Moreover, it is able to handle
multiply-connected Voronoi cells, which are challenging to the
existing geodesic CVT methods.
A Robust Divide and Conquer Algorithm for Progressive Medial Axes of Planar Shapes
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2016, Vol.22, No.12, 2522-2536.

Yong-Jin Liu, Cheng-Chi Yu, Min-Jing Yu, Kai Tang, and Deok-Soo Kim
The medial axis is an important shape representation that finds a wide range of applications in shape analysis. For largescale
shapes of high resolution, a progressive medial axis representation that starts with the lowest resolution and gradually adds more
details is desired. In this paper, we propose a fast and robust geometric algorithm that computes progressive medial axes of a largescale
planar shape. The key ingredient of our method is a novel structural analysis of merging medial axes of two planar shapes along a
shared boundary. Our method is robust by separating the analysis of topological structure from numerical computation. Our method is
also fast and we show that the time complexity of merging two medial axes is $O(n log n_v)$, where $n$ is the number of total boundary
generators, $n_v$ is strictly smaller than n and behaves as a small constant in all our experiments. Experiments on large-scale polygonal
data and comparison with state-of-the-art methods show the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed method.
HFS: Hierarchical Feature Selection for Efficient Image Segmentation
European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2016, 867-882.


Ming-Ming Cheng, Yun Liu, Qibin Hou, Jiawang Bian, Philip Torr, Shi-Min Hu, and Zhuowen Tu
In this paper, we propose a real-time system, Hierarchical Feature Selection (HFS), that performs image segmentation at a speed of
50 frames-per-second. We make an attempt to improve the performance
of previous image segmentation systems by focusing on two aspects: (1)
a careful system implementation on modern GPUs for efficient feature
computation; and (2) an effective hierarchical feature selection and fusion
strategy with learning. Compared with classic segmentation algorithms,
our system demonstrates its particular advantage in speed, with comparable
results in segmentation quality. Adopting HFS in applications
like salient object detection and object proposal generation results in a
significant performance boost. Our proposed HFS system (will be opensourced)
can be used in a variety computer vision tasks that are built on
top of image segmentation and superpixel extraction.
Appearance Harmonization for Single Image Shadow Removal
Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 35, No.7, 189-197, PG 2016.

Liqian Ma, Jue Wang, Eli Shechtman, Kalyan Sunkavalli and Shi-min Hu
Shadow removal is a challenging problem and previous approaches often produce de-shadowed regions that are visually inconsistent
with the rest of the image.We propose an automatic shadow region harmonization approach that makes the appearance of
a de-shadowed region (produced using any previous technique) compatible with the rest of the image. We use a shadow-guided
patch-based image synthesis approach that reconstructs the shadow region using patches sampled from non-shadowed regions.
This result is then refined based on the reconstruction confidence to handle unique textures. Qualitative comparisons over a
wide range of images, and a quantitative evaluation on a benchmark dataset show that our technique significantly improves
upon the state-of-the-art.
Multiphase SPH Simulation for Interactive Fluids and Solids
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 35, No. 4. ACM SIGGRAPH 2016


Xiao Yan, Yun-Tao Jiang, Chen-Feng Li, Ralph R. Martin, and Shi-Min Hu
This work extends existing multiphase-fluid SPH frameworks to cover solid phases, including deformable bodies and granular materials.
In our extended multiphase SPH framework, the distribution and shapes of all phases, both fluids and solids, are uniformly represented
by their volume fraction functions. The dynamics of the multiphase system is governed by conservation of mass and momentum
within different phases. The behavior of individual phases and the interactions between them are represented by corresponding
constitutive laws, which are functions of the volume fraction fields and the velocity fields. Our generalized multiphase SPH framework
does not require separate equations for specific phases or tedious interface tracking. As the distribution, shape and motion of each
phase is represented and resolved in the same way, the proposed approach is robust, efficient and easy to implement. Various simulation
results are presented to demonstrate the capabilities of our new multiphase SPH framework, including deformable bodies, granular
materials, interaction between multiple fluids and deformable solids, flow in porous media, and dissolution of deformable solids.
Versatile Interactions at Interfaces for SPH-Based Simulations
Eurographics/ ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation,2016


Tao Yang, Ming C. Lin, Ralph R. Martin, Jian Chang, and Shi-Min Hu
The realistic capture of various interactions at interfaces is a challenging problem for SPH-based simulation. Previous works
have mainly considered a single type of interaction, while real-world phenomena typically exhibit multiple interactions at
different interfaces. For instance, when cracking an egg, there are simultaneous interactions between air, egg white, egg yolk,
and the shell. To conveniently handle all interactions simultaneously in a single simulation, a versatile approach is critical. In
this paper, we present a new approach to the surface tension model based on pairwise interaction forces; its basis is to use
a larger number of neighboring particles. Our model is stable, conserves momentum, and furthermore, prevents the particle
clustering problem which commonly occurs at the free surface. It can be applied to simultaneous interactions at multiple
interfaces (e.g. fluid-solid and fluid-fluid). Our method is versatile, physically plausible and easy-to-implement.We also consider
the close connection between droplets and bubbles, and show how to animate bubbles in air as droplets, with the help of a new
surface particle detection method. Examples are provided to demonstrate the capabilities and effectiveness of our approach.
Traffic-Sign Detection and Classification in the Wild
IEEE CVPR, 2016. 2110-2118


Zhe Zhu, Dun Liang, Song-Hai Zhang, Xiaolei Huang, Baoli Li and Shi-Min Hu
Although promising results have been achieved in the areas of traffic-sign detection and classification, few works
have provided simultaneous solutions to these two tasks for realistic real world images. We make two contributions to
this problem. Firstly, we have created a large traffic-sign benchmark from 100000 Tencent Street View panoramas,
going beyond previous benchmarks. It provides 100000 images containing 30000 traffic-sign instances. These images
cover large variations in illuminance and weather conditions. Each traffic-sign in the benchmark is annotated with
a class label, its bounding box and pixel mask. We call this benchmark Tsinghua-Tencent 100K. Secondly, we demon-
strate how a robust end-to-end convolutional neural network (CNN) can simultaneously detect and classify traffic-
signs. Most previous CNN image processing solutions target objects that occupy a large proportion of an image, and
such networks do not work well for target objects occupying only a small fraction of an image like the traffic-signs
here. Experimental results show the robustness of our network and its superiority to alternatives. The benchmark,
source code and the CNN model introduced in this paper is publicly available.
Manifold SLIC: A Fast Method to Compute Content-Sensitive Superpixels
IEEE CVPR, 2016. 2110-2118


Yong-Jin Liu, Cheng-Chi Yu, Min-Jing Yu, Ying He
Superpixels are perceptually meaningful atomic regions that can effectively capture image features. Among various
methods for computing uniform superpixels, simple linear iterative clustering (SLIC) is popular due to its simplicity
and high performance. In this paper, we extend SLIC
to compute content-sensitive superpixels, i.e., small superpixels
in content-dense regions (e.g., with high intensity or
color variation) and large superpixels in content-sparse regions.
Rather than the conventional SLIC method that clusters
pixels in $R^5$, we map the image $I$ to a 2-dimensional
manifold $M \ inR^5$, whose area elements are a good measure
of the content density in $I$. We propose an efficient
method to compute restricted centroidal Voronoi tessellation
(RCVT) ¡ª a uniform tessellation ¡ª on $M$, which induces
the content-sensitive superpixels in $I$. Unlike other
algorithms that characterize content-sensitivity by geodesic
distances, manifold SLIC tackles the problem by measuring
areas of Voronoi cells on $M$, which can be computed at a
very low cost. As a result, it runs 10 times faster than the
state-of-the-art content-sensitive superpixels algorithm. We
evaluate manifold SLIC and seven representative methods
on the BSDS500 benchmark and observe that our method
outperforms the existing methods.
Faithful Completion of Images of Scenic Landmarks using Internet Images
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2016, Vol.22, No. 8, 1945-1958.

Zhe Zhu, Hao-Zhi Huang, Zhi-Peng Tan, Kun Xu, and Shi-Min Hu
Previous works on image completion typically aim to produce visually plausible results rather than factually correct ones. In
this paper, we propose an approach to faithfully complete the missing regions of an image. We assume that the input image is taken at a
well-known landmark, so similar images taken at the same location can be easily found on the Internet. We first download thousands of
images from the Internet using a text label provided by the user. Next, we apply two-step filtering to reduce them to a small set of candidate
images for use as source images for completion. For each candidate image, a co-matching algorithm is used to find correspondences of
both points and lines between the candidate image and the input image. These are used to find an optimal warp relating the two images.
A completion result is obtained by blending the warped candidate image into the missing region of the input image. The completion results
are ranked according to combination score, which considers both warping and blending energy, and the highest ranked ones are shown to
the user. Experiments and results demonstrate that our method can faithfully complete images.
Support Substructures: Support-Induced Part-Level Structural Representation
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2016, Vol.22, No. 8, 2024-2036.

Shi-sheng Huang, Hongbo Fu, Lingyu Wei, Shi-Min Hu
In this work we explore a support-induced structural organization of object parts. We introduce the concept of support substructures,
which are special subsets of object parts with support and stability. A bottom-up approach is proposed to identify such
substructures in a support relation graph. We apply the derived high-level substructures to part-based shape reshuffling between
models, resulting in nontrivial functionally plausible model variations that are difficult to achieve with symmetry-induced
substructures by the state-of-the-art methods. We also show how to automatically or interactively turn a single input model
to new functionally plausible shapes by structure rearrangement and synthesis, enabled by support substructures.
To the best of our knowledge no single existing method has been designed for all these applications.
Efficient, Edge-Aware, Combined Color Quantization and Dithering
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, Vol. 26, No. 3, 1152 - 1162.

Hao-Zhi Huang, Kun Xu, Ralph R. Martin, Fei-Yue Huang, and Shi-Min Hu
In this paper we present a novel algorithm to
simultaneously accomplish color quantization and dithering of
images. This is achieved by minimizing a perception-based cost
function which considers pixel-wise differences between filtered
versions of the quantized image and the input image. We use
edge aware filters in defining the cost function to avoid mixing
colors on opposite sides of an edge. The importance of each pixel
is weighted according to its saliency. To rapidly minimize the
cost function, we use a modified multi-scale iterative conditional
mode (ICM) algorithm which updates one pixel a time while
keeping other pixels unchanged. As ICM is a local method,
careful initialization is required to prevent termination at a local
minimum far from the global one. To address this problem, we
initialize ICM with a palette generated by a modified mediancut
method. Compared to previous approaches, our method can
produce high quality results with fewer visual artifacts but also
requires significantly less computational effort.
Comfort-driven disparity adjustment for stereoscopic video
Computational Visual Media, 2016, Vol.2, No. 1, 3-17

Miao Wang, Xi-Jin Zhang, Jun-Bang Liang, Song-Hai Zhang, and Ralph R. Martin
Pixel disparity¡ªthe offset of corresponding pixels between left and right views¡ªis a crucial
parameter in stereoscopic three-dimensional (S3D) video, as it determines the depth perceived by the
human visual system (HVS). Unsuitable pixel disparity distribution throughout an S3D video may lead to
visual discomfort. We present a unified and extensible stereoscopic video disparity adjustment framework
which improves the viewing experience for an S3D video by keeping the perceived 3D appearance as
unchanged as possible while minimizing discomfort. We first analyse disparity and motion attributes of S3D
video in general, then derive a wide-ranging visual discomfort metric from existing perceptual comfort
models. An objective function based on this metric is used as the basis of a hierarchical optimisation method
to find a disparity mapping function for each input video frame. Warping-based disparity manipulation
is then applied to the input video to generate the output video, using the desired disparity mappings as
constraints. Our comfort metric takes into account disparity range, motion, and stereoscopic window
violation; the framework could easily be extended to use further visual comfort models. We demonstrate the
power of our approach using both animated cartoons and real S3D videos.
2015
3D indoor scene modeling from RGB-D data: a survey
Computational Visual Media, Vol. 1, No. 4, 267-278

Kang Chen, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu
3D scene modeling has long been a fundamental problem in computer graphics and
computer vision. With the popularity of consumer-level RGB-D cameras, there is a growing interest in digitizing
real-world indoor 3D scenes. However, modeling indoor 3D scenes remains a challenging problem because of the
complex structure of interior objects and poor quality of RGB-D data acquired by consumer-level sensors.
Various methods have been proposed to tackle these challenges. In this survey, we provide an overview of
recent advances in indoor scene modeling techniques, as well as public datasets and code libraries which can
facilitate experiments and evaluation.
Simultaneous Camera Path Optimization and Distraction Removal for Improving Amateur Video
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, Vol.24, No.12, 5982 - 5994.


Fang-Lue Zhang, Jue Wang, Han Zhao, Ralph R. Martin, Shi-Min Hu
A major difference between amateur and professional video lies in the quality of camera paths. Previous work on video stabilization has
considered how to improve amateur video by smoothing the camera path. In this paper, we show that additional changes to the camera path can
further improve video aesthetics. Our new optimization method achieves multiple simultaneous goals: (i) stabilizing video content over short time
scales, (ii) ensuring simple and consistent camera paths over longer time scales, and (iii) improving scene composition by automatically removing
distractions, a common occurrence in amateur video. Our approach uses an L1 camera path optimization framework, extended to handle multiple
constraints. Two-passes of optimization are used to address both low-level and high-level constraints on the camera path. Experimental and user
study results show that our approach outputs video which is perceptually better than the input, or the results of using stabilization only.
Magic Decorator: Automatic Material Suggestion for Indoor Digital Scenes
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 34, No. 6, Article No. 232, SIGGRAPH ASIA 2015.


Kang Chen, Kun Xu, Yizhou Yu, Tian-Yi Wang, Shi-Min Hu
Assigning textures and materials within 3D scenes is a tedious and
labor-intensive task. In this paper, we present Magic Decorator,
a system that automatically generates material suggestions for 3D
indoor scenes. To achieve this goal, we introduce local material
rules, which describe typical material patterns for a small group of
objects or parts, and global aesthetic rules, which account for the
harmony among the entire set of colors in a specific scene. Both
rules are obtained from collections of indoor scene images. We cast
the problem of material suggestion as a combinatorial optimization
considering both local material and global aesthetic rules. We have
tested our system on various complex indoor scenes. A user study
indicates that our system can automatically and efficiently produce
a series of visually plausible material suggestions which are comparable
to those produced by artists.
Fast Multiple-fluid Simulation Using Helmholtz Free Energy
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 34, No. 6, Article No. 201, SIGGRAPH ASIA 2015.


Tao Yang, Jian Chang, Bo Ren, Ming C. Lin, Jian Jun Zhang, and Shi-Min Hu
Multiple-fluid interaction is an interesting and common visual phenomenon
we often observe. In this paper we present an energybased
Lagrangian method that expands the capability of existing
multiple-fluid methods to handle various phenomena, including
extraction, partial dissolution, etc. Based on our user-adjusted
Helmholtz free energy functions, the simulated fluid evolves from
high-energy states to low-energy states, allowing flexible capture of
various mixing and unmixing processes. We also extend the original
Cahn-Hilliard equation to gain abilities of simulating complex
fluid-fluid interaction and rich visual phenomena such as motionrelated
mixing and position based pattern. Our approach is easy to
be integrated with existing state-of-the-art smooth particle hydrodynamic
(SPH) solvers and can be further implemented on top of the
position based dynamics (PBD) method, improving the stability and
incompressibility of the fluid during Lagrangian simulation under
large time steps. Performance analysis shows that our method is at
least 4 times faster than the state-of-the-art multiple-fluid method.
Examples are provided to demonstrate the new capability and effectiveness
of our approach.
Efficient Construction and Simplification of Delaunay Meshes
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 34, No.6, Article No.174, SIGGRAPH ASIA 2015.


Yong-Jin Liu, Chun-Xu Xu, Dian Fan, Ying He
Delaunay meshes (DM) are a special type of triangle mesh where
the local Delaunay condition holds everywhere. We present an
efficient algorithm to convert an arbitrary manifold triangle mesh
M into a Delaunay mesh. We show that the constructed DM has
O(Kn) vertices, where n is the number of vertices in M and K
is a model-dependent constant. We also develop a novel algorithm
to simplify Delaunay meshes, allowing a smooth choice of detail
levels. Our methods are conceptually simple, theoretically sound
and easy to implement. The DM construction algorithm also scales
well due to its O(nK logK) time complexity.
Delaunay meshes have many favorable geometric and numerical
properties. For example, a DM has exactly the same geometry
as the input mesh, and it can be encoded by any mesh data structure.
Moreover, the empty geodesic circumcircle property implies
that the commonly used cotangent Laplace-Beltrami operator has
non-negative weights. Therefore, the existing digital geometry processing
algorithms can benefit the numerical stability of DM without
changing any codes. We observe that DMs can improve the
accuracy of the heat method for computing geodesic distances.
Also, popular parameterization techniques, such as discrete harmonic
mapping, produce more stable results on the DMs than on
the input meshes.
Active Exploration of Large 3D Model Repositories
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 21, No.12, 1390-1402.

Lin Gao, Yan-Pei Cao, Yu-Kun Lai, Hao-Zhi Huang, Leif Kobbelt, Shi-Min Hu
With broader availability of large-scale 3D model repositories, the need for efficient and effective
exploration becomes more and more urgent. Existing model retrieval techniques do not scale well with
the size of the database since often a large number of very similar objects are returned for a query,
and the possibilities to refine the search are quite limited. We propose an interactive approach where the
user feeds an active learning procedure by labeling either entire models or parts of them as ¡°like¡±
or ¡°dislike¡± such that the system can automatically update an active set of recommended models.
To provide an intuitive user interface, candidate models are presented based on their estimated relevance
for the current query. From the methodological point of view, our main contribution is to exploit
not only the similarity between a query and the database models but also the similarities among the
database models themselves. We achieve this by an offline pre-processing stage, where global and local
shape descriptors are computed for each model and a sparse distance metric is derived that can be
evaluated efficiently even for very large databases. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method
by interactively exploring a repository containing over 100K models.
Anisotropic density estimation for photon mapping
Computational Visual Media, Vol. 1, No. 3, 221-228

Fu-Jun Luan, Li-Fan Wu, Kun Xu
Photon mapping is a widely used technique for global illumination rendering. In the density
estimation step of photon mapping, the indirect radiance at a shading point is estimated through
a ltering process using nearby stored photons; an isotropic ltering kernel is usually used. However,
using an isotropic kernel is not always the optimal choice, especially for cases when eye paths intersect
with surfaces with anisotropic BRDFs. In this paper, we propose an anisotropic ltering kernel for density
estimation to handle such anisotropic eye paths. The anisotropic ltering kernel is derived from the
recently introduced anisotropic spherical Gaussian representation of BRDFs. Compared to conventional
photon mapping, our method is able to reduce rendering errors with negligible additional cost when
rendering scenes containing anisotropic BRDFs.
Semi-Continuity of Skeletons in 2-Manifold and Discrete Voronoi Approximation
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 37, No. 9, 1938 - 1944.

Yong-Jin Liu
The skeleton of a 2D shape is an important geometric structure in pattern analysis and computer vision. In this paper
we study the skeleton of a 2D shape in a 2-manifold $\mathcal{M}$, based on a geodesic metric. We present a formal
definition of the skeleton $S(\Omega)$ for a shape $\Omega$ in $\mathcal{M}$ and show several properties that
make $S(\Omega)$ distinct from its Euclidean counterpart in $\mathbb{R}^2$. We further prove that for a shape
sequence $\{\Omega_i\}$ that converge to a shape $\Omega$ in $\mathcal{M}$, the mapping $\Omega\rightarrow\overline{S}(\Omega)$
is lower semi-continuous. A direct application of this result is that we can use a set $P$ of sample points to
approximate the boundary of a 2D shape $\Omega$ in $\mathcal{M}$, and the Voronoi diagram
of $P$ inside $\Omega\subset\mathcal{M}$ gives a good approximation to the skeleton $S(\Omega)$.
Examples of skeleton computation in topography and brain morphometry are illustrated.
A simple approach for bubble modelling from multiphase fluid simulation
Computational Visual Media, Vol. 1, No. 2, 171-181

Bo Ren, Yuntao Jiang, Chenfeng Li, Ming C. Lin
This article presents a novel and flexible bubble modelling technique for multi-fluid
simulations using a volume fraction representation. By combining the volume fraction data obtained from a
primary multi-fluid simulation with simple and efficient secondary bubble simulation, a range of real-world
bubble phenomena are captured with a high degree of physical realism, including large bubble deformation,
sub-cell bubble motion, bubble stacking over the liquid surface, bubble volume change, dissolving of bubbles,
etc. Without any change in the primary multi-fluid simulator, our bubble modelling approach is applicable
to any multi-fluid simulator based on the volume fraction representation.
PatchTable: Efficient Patch Queries for Large Datasets and Applications
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 34, No. 4, Article No. 97, SIGGRAPH 2015.


Connelly Barnes, Fang-Lue Zhang, Liming Lou, Xian Wu, Shi-Min Hu
This paper presents a data structure that reduces approximate nearest
neighbor query times for image patches in large datasets. Previous
work in texture synthesis has demonstrated real-time synthesis
from small exemplar textures. However, high performance
has proved elusive for modern patch-based optimization techniques
which frequently use many exemplar images in the tens of megapixels
or above. Our new algorithm, PatchTable, offloads as much
of the computation as possible to a pre-computation stage that
takes modest time, so patch queries can be as efficient as possible.
There are three key insights behind our algorithm: (1) a lookup
table similar to locality sensitive hashing can be precomputed, and
used to seed sufficiently good initial patch correspondences during
querying, (2) missing entries in the table can be filled during precomputation
with our fast Voronoi transform, and (3) the initially
seeded correspondences can be improved with a precomputed knearest
neighbors mapping. We show experimentally that this accelerates
the patch query operation by up to 9� over k-coherence,
up to 12� over TreeCANN, and up to 200� over PatchMatch. Our
fast algorithm allows us to explore efficient and practical imaging
and computational photography applications. We show results
for artistic video stylization, light field super-resolution, and multiimage
editing.
Panorama completion for street views
Computational Visual Media, Vol. 1, No. 1, 49-57

Zhe Zhu, Ralph R. Martin, Shi-Min Hu
This paper considers panorama images used for street views. Their viewing angle of
360 degree causes pixels at the top and bottom to appear stretched and warped.
Although current image completion algorithms work well, they cannot be directly
used in the presence of such distortions found in panoramas of street views.
We thus propose a novel approach to complete such 360 degree panoramas using optimization-based
projection to deal with distortions. Experimental results show that our approach
is efficient and provides an improvement over standard image completion algorithms.
Fast Wavefront Propagation (FWP)for Computing Exact Geodesic Distances on Meshes
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2015, Vol 21, No. 7, 822-834.

Chunxu Xu, Tuanfeng Y. Wang, Yong-Jin Liu, Ligang Liu, Ying He
Computing geodesic distances on triangle meshes is a fundamental problem in computational geometry and computer
graphics. To date, two notable classes of algorithms, the Mitchell-Mount-Papadimitriou (MMP) algorithm and the Chen-Han (CH)
algorithm, have been proposed. Although these algorithms can compute exact geodesic distances if numerical computation is exact,
they are computationally expensive, which diminishes their usefulness for large-scale models and/or time-critical applications. In this
paper, we propose the fast wavefront propagation (FWP) framework for improving the performance of both the MMP and CH
algorithms. Unlike the original algorithms that propagate only a single window (a data structure locally encodes geodesic information) at
each iteration, our method organizes windows with a bucket data structure so that it can process a large number of windows
simultaneously without compromising wavefront quality. Thanks to its macro nature, the FWP method is less sensitive to mesh
triangulation than the MMP and CH algorithms. We evaluate our FWP-based MMP and CH algorithms on a wide range of large-scale
real-world models. Computational results show that our method can improve the speed by a factor of 3-10.
A Response Time Model for Abrupt Changes in Binocular Disparity
The Visual Computer, 2015, Vol. 31, N0. 5, 675-687.

Tai-Jiang Mu, Jia-Jia Sun, Ralph Martin, Shi-Min Hu
We propose a novel depth perception model
to determine the time taken by the human visual system (HVS) to adapt to an abrupt change in
stereoscopic disparity, such as can occur in a scene cut. A series
of carefully designed perceptual experiments on successive disparity contrast were used to build our model.
Factors such as disparity, changes in disparity, and the spatial frequency of luminance contrast were taken into
account. We further give a computational method to predict the response time during scene cuts in
stereoscopic cinematography, which has been validated in user studies. We also consider various applications of our
model.
Global Contrast based Salient Region Detection
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015,Vol. 37, No. 3, 569 - 582.

Ming-Ming Cheng, Niloy J. Mitra, Xiaolei Huang, Philip H. S. Torr, and Shi-Min Hu
(Earlier version was presented in IEEE CVPR 2011)
Automatic estimation of salient object regions across images, without any prior assumption or knowledge of the contents
of the corresponding scenes, enhances many computer vision and computer graphics applications. We introduce a regional contrast
based salient object detection algorithm, which simultaneously evaluates global contrast differences and spatial weighted coherence
scores. The proposed algorithm is simple, efficient, naturally multi-scale, and produces full-resolution, high-quality saliency maps.
These saliency maps are further used to initialize a novel iterative version of GrabCut, namely SaliencyCut, for high quality unsupervised
salient object segmentation. We extensively evaluated our algorithm using traditional salient object detection datasets, as well as a
more challenging Internet image dataset. Our experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm consistently outperforms 15 existing
salient object detection and segmentation methods, yielding higher precision and better recall rates. We also show that our algorithm
can be used to efficiently extract salient object masks from Internet images, enabling effective sketch-based image retrieval (SBIR) via
simple shape comparisons. Despite such noisy internet images, where the saliency regions are ambiguous, our saliency guided image
retrieval achieves a superior retrieval rate compared with state-of-the-art SBIR methods, and additionally provides important target
object region information.
2014
BiggerPicture: Data-Driven Image Extrapolation Using Graph Matching
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 6, Article No. 173 (ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2014).

Miao Wang, Yu-Kun Lai, Yuan Liang, Ralph R. Martin, Shi-Min Hu
Filling a small hole in an image with plausible content is well
studied. Extrapolating an image to give a distinctly larger one is
much more challenging¡ªa significant amount of additional content
is needed which matches the original image, especially near
its boundaries. We propose a data-driven approach to this problem.
Given a source image, and the amount and direction(s) in which it is
to be extrapolated, our system determines visually consistent content
for the extrapolated regions using library images. As well as
considering low-level matching, we achieve consistency at a higher
level by using graph proxies for regions of source and library images.
Treating images as graphs allows us to find candidates for
image extrapolation in a feasible time. Consistency of subgraphs
in source and library images is used to find good candidates for the
additional content; these are then further filtered. Region boundary
curves are aligned to ensure consistency where image parts are
joined using a photomontage method. We demonstrate the power
of our method in image editing applications.
Improving Visual Quality of View Transitions in Automultiscopic Displays
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 6, Article No. 192(ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2014).

Song-Pei Du, Piotr Didyk, Fredo Durand, Shi-Min Hu, Wojciech Matusik
Automultiscopic screens present different images depending on the
viewing direction. This enables glasses-free 3D and provides motion parallax effect. However, due to the limited angular resolution
of such displays, they suffer from hot-spotting, i. e., image quality is highly affected by the viewing position. In this paper, we
analyze light fields produced by lenticular and parallax-barrier displays, and show that, unlike in real world, the light fields produced
by such screens have a repetitive structure. This induces visual artifacts in the form of view discontinuities, depth reversals,
and excessive disparities when viewing position is not optimal. Although the
problem has been always considered as inherent to the technology,
we demonstrate that light fields reproduced on automultiscopic displays have enough degrees of freedom to improve the visual
quality. We propose a new technique that modifies light fields using
global and local shears followed by stitching to improve their continuity when displayed on a screen. We show that this
enhances visual quality significantly, which is demonstrated in a series of user
experiments with an automultiscopic display as well as lenticular prints.
Automatic Semantic Modeling of Indoor Scenes from Low-quality RGB-D Data using Contextual Information
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 6, Article 208(ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2014).

Kang Chen, Yu-Kun Lai, Yu-Xin Wu, Ralph Martin, Shi-Min Hu
We present a novel solution to automatic semantic modeling of indoor
scenes from a sparse set of low-quality RGB-D images. Such
data presents challenges due to noise, low resolution, occlusion and
missing depth information. We exploit the knowledge in a scene
database containing 100s of indoor scenes with over 10,000 manually
segmented and labeled mesh models of objects. In seconds,
we output a visually plausible 3D scene, adapting these models and
their parts to fit the input scans. Contextual relationships learned
from the database are used to constrain reconstruction, ensuring semantic
compatibility between both object models and parts. Small
objects and objects with incomplete depth information which are
difficult to recover reliably are processed with a two-stage approach.
Major objects are recognized first, providing a known scene
structure. 2D contour-based model retrieval is then used to recover
smaller objects. Evaluations using our own data and two public
datasets show that our approach can model typical real-world indoor
scenes efficiently and robustly.
Multiple-fluid SPH Simulation Using a Mixture Model
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 5, article 171.

Bo Ren, Chen-Feng Li, Xiao Yan, Ming C. Lin, Javier Bonet, and Shi-Min Hu
This paper presents a versatile and robust SPH simulation approach for
multiple-fluid flows. The spatial distribution of different phases or components
is modeled using the volume fraction representation, the dynamics
of multiple-fluid flows is captured by using an improved mixture model,
and a stable and accurate SPH formulation is rigorously derived to resolve
the complex transport and transformation processes encountered in
multiple-fluid flows. The new approach can capture a wide range of realworld
multiple-fluid phenomena, including mixing/unmixing of miscible
and immiscible fluids, diffusion effect and chemical reaction etc. Moreover,
the new multiple-fluid SPH scheme can be readily integrated into existing
state-of-the-art SPH simulators, and the multiple-fluid simulation is easy to
set up. Various examples are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of
our approach.
Interactive Image-Guided Modeling of Extruded Shapes
Computer Graphics Forum, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 7, 101-110 (Pacific Graphics 2014).

Yan-Pei Cao, Tao Ju, Zhao Fu, Shi-Min Hu
(This paper is one of the two Best student papers in Pacific Graphics 2014)
A recent trend in interactive modeling of 3D shapes from a single image is designing minimal interfaces, and
accompanying algorithms, for modeling a specific class of objects. Expanding upon the range of shapes that
existing minimal interfaces can model, we present an interactive image-guided tool for modeling shapes made up
of extruded parts. An extruded part is represented by extruding a closed planar curve, called base, in the direction
orthogonal to the base. To model each extruded part, the user only needs to sketch the projected base shape in the
image. The main technical contribution is a novel optimization-based approach for recovering the 3D normal of
the base of an extruded object by exploring both geometric regularity of the sketched curve and image contents.
We developed a convenient interface for modeling multi-part shapes and a method for optimizing the relative
placement of the parts. Our tool is validated using synthetic data and tested on real-world images.
Learning Natural Colors for Image Recoloring
Computer Graphics Forum, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 7, 299-308 (Pacific Graphics 2014).

Hao-Zhi Huang, Song-Hai Zhang, Ralph R. Martin, Shi-Min Hu
We present a data-driven method for automatically recoloring a photo to enhance its appearance or change a
viewer¡¯s emotional response to it. A compact representation called a RegionNet summarizes color and geometric
features of image regions, and geometric relationships between them. Correlations between color property distributions
and geometric features of regions are learned from a database of well-colored photos. A probabilistic
factor graph model is used to summarize distributions of color properties and generate an overall probability distribution
for color suggestions. Given a new input image, we can generate multiple recolored results which unlike
previous automatic results, are both natural and artistic, and compatible with their spatial arrangements.
Polyline-sourced geodesic Voronoi diagrams on triangle meshes
Computer Graphics Forum, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 7, 161-170 (Pacific Graphics 2014).

Chunxu Xu, Yong-Jin Liu, Qian Sun, Jinyan Li and Ying He
This paper studies the Voronoi diagrams on 2-manifold meshes based on geodesic metric (a.k.a. geodesic Voronoi
diagrams or GVDs), which have polyline generators. We show that our general setting leads to situations more
complicated than conventional 2D Euclidean Voronoi diagrams as well as point-source based GVDs, since a
typical bisector contains line segments, hyperbolic segments and parabolic segments. To tackle this challenge,
we introduce a new concept, called local Voronoi diagram (LVD), which is a combination of additively weighted
Voronoi diagram and line-segment Voronoi diagram on a mesh triangle. We show that when restricting on a single
mesh triangle, the GVD is a subset of the LVD and only two types of mesh triangles can contain GVD edges.
Based on these results, we propose an efficient algorithm for constructing the GVD with polyline generators.
Our algorithm runs in O(nNlogN) time and takes O(nN) space on an n-face mesh with m generators, where
N = max{m;n}. Computational results on real-world models demonstrate the efficiency of our algorithm.
Parametric meta-filter modeling from a single example pair
The Visual Computer, 2014, Vol. 30, No.6-8, 673-684.

Shi-Sheng Huang, Guo-Xin Zhang, Yu-Kun Lai, Johannes Kopf, Daniel Cohen-Or, Shi-Min Hu
We present a method for learning a meta-filter
from an example pair comprising an original image A and its
filtered version A' using an unknown image filter. A metafilter
is a parametric model, consisting of a spatially varying
linear combination of simple basis filters. We introduce
a technique for learning the parameters of the meta-filter f
such that it approximates the effects of the unknownfilter, i.e.,
f(A) approximates A'. The meta-filter can be transferred to
novel input images, and its parametric representation enables
intuitive tuning of its parameters to achieve controlled variations.
We show that our technique successfully learns and
models meta-filters that approximate a large variety of common
image filters with high accuracy both visually and quantitatively.
SalientShape: group saliency in image collections
The Visual Computer, 2014, Vol. 30, No.4, 443-453.

Ming-Ming Cheng, Niloy J. Mitra,Xiaolei Huang, Shi-Min Hu
Efficiently identifying salient objects in large image collections is essential for
many applications including image retrieval, surveillance, image annotation, and
object recognition. We propose a simple, fast, and effective algorithm for locating
and segmenting salient objects by analysing image collections. As a key novelty,
we introduce group saliency to achieve superior unsupervised salient object segmentation
by extracting salient objects (in collections of pre-filtered images) that maximize
between-image similarities and within-image distinctness. To evaluate our method,
we construct a large benchmark dataset consisting of 15 K images across multiple
categories with 6000+ pixel-accurate ground truth annotations for salient object
regions where applicable. In all our tests, group saliency consistently outperforms
state-of-the-art single-image saliency algorithms, resulting in both higher precision
and better recall. Our algorithm successfully handles image collections, of an order
larger than any existing benchmark datasets, consisting of diverse and heterogeneous
images from various internet sources.
A practical algorithm for rendering interreflections with all-frequency BRDFs
ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, Vol. 33, No.1, Article No. 10.

Kun Xu, Yan-Pei Cao, Li-Qian Ma,Zhao Dong, Rui Wang, Shi-Min Hu
Algorithms for rendering interreflection (or indirect illumination) effects often
make assumptions about the frequency range of the materials' reflectance properties.
For example, methods based on Virtual Point Lights (VPLs) perform well for diffuse
and semi-glossy materials but not so for highly glossy or specular materials;
the situation is reversed for methods based on ray tracing. In this article,
we present a practical algorithm for rendering interreflection effects with
all-frequency BRDFs. Our method builds upon a spherical Gaussian representation
of the BRDF, based on which a novel mathematical development of the interreflection
equation is made. This allows us to efficiently compute one-bounce interreflection
from a triangle to a shading point, by using an analytic formula combined with a
piecewise linear approximation. We show through evaluation that this method is
accurate for a wide range of BRDFs. We further introduce a hierarchical integration
method to handle complex scenes (i.e., many triangles) with bounded errors.
Finally, we have implemented the present algorithm on the GPU, achieving rendering
performance ranging from near interactive to a few seconds per frame for various
scenes with different complexity.
A Sketch-Based Approach for Interactive Organization of Video Clips
ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2014, Vol. 11, No.1, Article No. 2.

Yong-Jin Liu, Cui-Xia Ma, Qiufang Fu, Xiaolan Fu, Sheng-Feng Qin, and Lexing Xie
With the rapid growth of video resources, techniques for efficient organization of video clips are becoming
appealing in the multimedia domain. In this article, a sketch-based approach is proposed to intuitively
organize video clips by: (1) enhancing their narrations using sketch annotations and (2) structurizing the organization
process by gesture-based free-form sketching on touch devices. There are two main contributions
of this work. The first is a sketch graph, a novel representation for the narrative structure of video clips to
facilitate content organization. The second is a method to perform context-aware sketch recommendation
scalable to large video collections, enabling common users to easily organize sketch annotations. A prototype
system integrating the proposed approach was evaluated on the basis of five different aspects concerning
its performance and usability. Two sketch searching experiments showed that the proposed context-aware
sketch recommendation outperforms, in terms of accuracy and scalability, two state-of-the-art sketch searching
methods. Moreover, a user study showed that the sketch graph is consistently preferred over traditional
representations such as keywords and keyframes. The second user study showed that the proposed approach
is applicable in those scenarios where the video annotator and organizer were the same person. The third
user study showed that, for video content organization, using sketch graph users took on average 1/3 less
time than using a mass-market tool MovieMaker and took on average 1/4 less time than using a state-of-theart
sketch alternative. These results demonstrated that the proposed sketch graph approach is a promising
video organization tool.
Other publications in 2014
1. Bin Liu, Ralph Martin, Ji-Wu Huang, Shi-Min Hu, Structure Aware Visual Cryptography,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2014, Vol. 33, No. 7, 141-150 (Pacific Graphics 2014).

2. Cheng-Chi Yu, Yong-Jin Liu, Tianfu Wu, Kai-Yun Li, Xiaolan Fu, A global energy optimization framework for 2.1D sketch extraction from monocular images,
Graphical Models, 2014, Vol. 76, No.5, 507-521.

3. Tai-Jiang Mu, Ju-Hong Wang, Song-Pei Du, Shi-Min Hu, Stereoscopic image completion and depth recovery,
The Visual Computer, 2014, Vol. 30, No.6-8, 833-843.

4. Long Zeng, Yong-Jin Liu, Jin Wang, Dong-Liang Zhang, Ming-Fai Yuen, Sketch2Jewelry: Semantic feature modeling for sketch-based jewelry design,
Computers & Graphics, 2014, Vol. 38, No.1, 69-77 (Presented in CAD/Graphics 2013).

2013
Recovering a Semantic Editing History from a Before-and-After Image Pair
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 32, No.6, Article No. 194, 2013 (SIGGRAPH ASIA 2013).

Shi-Min Hu, Kun Xu, Li-Qian Ma, Bin Liu, Bi-Ye Jiang and Jue Wang
We study the problem of inverse image editing, which recovers a semantically-meaningful editing history from a source image and
an edited copy. Our approach supports a wide range of commonlyused editing operations such as cropping, object insertion and removal,
linear and non-linear color transformations, and spatiallyvarying
adjustment brushes. Given an input image pair, we first apply
a dense correspondence method between them to match edited
image regions with their sources. For each edited region, we determine
geometric and semantic appearance operations that have
been applied. Finally, we compute an optimal editing path from
the region-level editing operations, based on predefined semantic
constraints. The recovered history can be used in various applications
such as image re-editing, edit transfer, and image revision control.
PatchNet: A Patch-based Image Representation for Interactive Library-driven Image Editing
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 32, No.6, Article No. 196, 2013 (SIGGRAPH ASIA 2013).

Shi-Min Hu, Fang-Lue Zhang, Miao Wang, Ralph R. Martin, Jue Wang
We introduce PatchNets, a compact, hierarchical representation describing
structural and appearance characteristics of image regions,
for use in image editing. In a PatchNet, an image region with
coherent appearance is summarized by a graph node, associated
with a single representative patch, while geometric relationships between
different regions are encoded by labelled graph edges giving
contextual information. The hierarchical structure of a PatchNet
allows a coarse-to-fine description of the image. We show how
this PatchNet representation can be used as a basis for interactive,
library-driven, image editing. The user draws rough sketches to
quickly specify editing constraints for the target image. The system
then automatically queries an image library to find semanticallycompatible
candidate regions to meet the editing goal. Contextual
image matching is performed using the PatchNet representation, allowing
suitable regions to be found and applied in a few seconds,
even from a library containing thousands of images.
3-Sweep: Extracting Editable Objects from a Single Photo
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 32, No.6, Article No. 195, 2013 (SIGGRAPH ASIA 2013).

Tao Chen, Zhe Zhu, Ariel Shamir, Shi-Min Hu, Daniel Cohen-Or
We introduce an interactive technique for manipulating simple 3D
shapes based on extracting them from a single photograph. Such
extraction requires understanding of the components of the shape,
their projections, and relations. These simple cognitive tasks for
humans are particularly difficult for automatic algorithms. Thus,
our approach combines the cognitive abilities of humans with the
computational accuracy of the machine to solve this problem. Our
technique provides the user the means to quickly create editable 3D
parts¡ª human assistance implicitly segments a complex object into
its components, and positions them in space. In our interface,
three strokes are used to generate a 3D component that snaps to the
shape¡¯s outline in the photograph, where each stroke defines one
dimension of the component. The computer reshapes the component
to fit the image of the object in the photograph as well as to
satisfy various inferred geometric constraints imposed by its global
3D structure. We show that with this intelligent interactive modeling
tool, the daunting task of object extraction is made simple.
Once the 3D object has been extracted, it can be quickly edited and
placed back into photos or 3D scenes, permitting object-driven photo
editing tasks which are impossible to perform in image-space.
Anisotropic Spherical Gaussians
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 32, No.6, Article No. 209, 2013 (SIGGRAPH ASIA 2013).


Kun Xu, Wei-Lun Sun, Zhao Dong, Dan-Yong Zhao, Run-Dong Wu, Shi-Min Hu
We present a novel anisotropic Spherical Gaussian (ASG) function,
built upon the Bingham distribution [Bingham 1974], which is
much more effective and efficient in representing anisotropic spherical
functions than Spherical Gaussians (SGs). In addition to retaining
many desired properties of SGs, ASGs are also rotationally
invariant and capable of representing all-frequency signals. To further
strengthen the properties of ASGs, we have derived approximate
closed-form solutions for their integral, product and convolution
operators, whose errors are nearly negligible, as validated by
quantitative analysis. Supported by all these operators, ASGs can
be adapted in existing SG-based applications to enhance their scalability
in handling anisotropic effects. To demonstrate the accuracy
and efficiency of ASGs in practice, we have applied ASGs in two
important SG-based rendering applications and the experimental results
clearly reveal the merits of ASGs.
A Metric of Visual Comfort for Stereoscopic Motion
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 32, No.6, Article No. 222, 2013 (SIGGRAPH ASIA 2013).

Song-Pei Du, Belen Masia, Shi-Min Hu and Diego Gutierrez
We propose a novel metric of visual comfort for stereoscopic motion,
based on a series of systematic perceptual experiments. We
take into account disparity, motion in depth, motion on the screen
plane, and the spatial frequency of luminance contrast. We further
derive a comfort metric to predict the comfort of short stereoscopic
videos. We validate it on both controlled scenes and real videos
available on the internet, and show how all the factors we take into
account, as well as their interactions, affect viewing comfort. Last,
we propose various applications that can benefit from our comfort
measurements and metric.
Change Blindness Images (Spotlight paper)
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 19, No.11, 1808-1819, 2013. 
Li-Qian Ma, Kun Xu, Tien-Tsin Wong, Bi-Ye Jiang and Shi-Min Hu
Change blindness refers to human inability to recognize large visual changes between images. In this paper,
we present the first computational model of change blindness to quantify the degree of blindness between
an image pair. It comprises a novel context-dependent saliency model and a measure of change, the former
dependent on the site of the change, and the latter describing the amount of change. This saliency model
in particular addresses the influence of background complexity, which plays an important role in the
phenomenon of change blindness. Using the proposed computational model, we are able to synthesize changed
images with desired degrees of blindness. User studies and comparisons to state-of-the-art saliency models
demonstrate the effectiveness of our model.
Flow Field Modulation
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 19, No.10, 1708-1719, 2013. 
Bo Ren, Chen-Feng Li, Ming C. Lin, Theodore Kim, and Shi-Min Hu
The nonlinear and non-stationary nature of Navier-Stokes equations produces fluid flows that can be noticeably different in
appearance with subtle changes. In this paper we introduce a method that can analyze the intrinsic multiscale features of flow fields
from a decomposition point of view, by using the Hilbert-Huang transform method on 3D fluid simulation. We show how this method
can provide insights to flow styles and help modulate the fluid simulation with its internal physical information. We provide easy-toimplement
algorithms that can be integrated with standard grid-based fluid simulation methods, and demonstrate how this approach
can modulate the flow field and guide the simulation with different flow styles. The modulation is straightforward and relates directly to
the flow¡¯s visual effect, with moderate computational overhead.
Sketch2Scene: Sketch-based Co-retrieval and Co-placement of 3D Models
ACM Transactions on Graphics,Vol. 32, No. 4, Article No. 123, SIGGRAPH 2013.
 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)
Kun Xu, Kang Chen, Hongbo Fu, Wei-Lun Sun, Shi-Min Hu
This work presents Sketch2Scene, a framework that automatically turns a freehand sketch drawing inferring multiple scene objects
to semantically valid, well arranged scenes of 3D models. Unlike the existing works on sketch-based search and composition of 3D
models, which typically process individual sketched objects one by one, our technique performs co-retrieval and co-placement of 3D
relevant models by jointly processing the sketched objects. This is enabled by summarizing functional and spatial relationships among
models in a large collection of 3D scenes as structural groups. Our technique greatly reduces the amount of user intervention needed
for sketch-based modeling of 3D scenes and fits well into the traditional production pipeline involving concept design followed by 3D
modeling. A pilot study indicates that the 3D scenes automatically synthesized by our technique in seconds are comparable to those
manually created by an artist in hours in terms of visual aesthetics.
Cubic Mean Value Coordinates
ACM Transactions on Graphics,Vol. 32, No. 4, Article No. 126, SIGGRAPH 2013.
 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)
Xian-Ying Li, Tao Ju and Shi-Min Hu
We present a new method for interpolating both boundary values and gradients over a 2D polygonal domain. Despite various previous
efforts, it remains challenging to define a closed-form interpolant that produces natural-looking functions while allowing flexible
control of boundary constraints. Our method builds on an existing transfinite interpolant over a continuous domain, which in turn
extends the classical mean value interpolant. We re-derive the interpolant from the mean value property of biharmonic functions, and
prove that the interpolant indeed matches the gradient constraints when the boundary is piece-wise linear. We then give closed-form
formula (as generalized barycentric coordinates) for boundary constraints represented as polynomials up to degree 3 (for values) and
1 (for normal derivatives) over each polygon edge. We demonstrate the flexibility and efficiency of our coordinates in two novel applications,
smooth image deformation using curved cage networks and adaptive simplification of gradient meshes.
Qualitative Organization of Collections of Shapes via Quartet Analysis
ACM Transactions on Graphics,Vol. 32, No. 4, Article No. 71, SIGGRAPH 2013.
 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)
Shi-Sheng Huang, Ariel Shamir, Chao-Hui Shen, Hao Zhang, Alla Sheffer, Shi-Min Hu, Daniel Cohen-Or
We present a method for organizing a heterogeneous collection of 3D shapes for overview and exploration. Instead of relying on
quantitative distances, which may become unreliable between dissimilar shapes, we introduce a qualitative analysis which utilizes
multiple distance measures but only in cases where the measures can be reliably compared. Our analysis is based on the notion of
quartets, each defined by two pairs of shapes, where the shapes in each pair are close to each other, but far apart from the shapes in the
other pair. Combining the information from many quartets computed across a shape collection using several distance measures,
we create a hierarchical structure we call categorization tree of the shape collection. This tree satisfies the topological (qualitative)
constraints imposed by the quartets creating an effective organization of the shapes. We present categorization trees computed on
various collections of shapes and compare them to ground truth data from human categorization. We further introduce the concept of degree
of separation chart for every shape in the collection and show the effectiveness of using it for interactive shapes exploration.
Manipulating Perspective in Stereoscopic Images
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, Vol. 19, No. 8, 1288-1297. 
Song-Pei Du, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R Martin
Stereoscopic ("3D") devices and content relying on stereopsis are now widely available. However, traditional image
editing techniques cannot be directly used to edit stereoscopic media, as extra constraints are needed to ensure consistent
changes are made to both left and right images. This paper addresses the problem of manipulating perspective in stereoscopic
pairs. We note that a straightforward approach based on depth recovery is unsatisfactory. Instead, our method relies on feature
correspondences between stereoscopic image pairs. Given a new, user-specified perspective, we determine correspondence
constraints under this perspective, and optimize a 2D warp for each image which preserves straight lines, and guarantees proper
stereopsis relative to the new camera. Experiments demonstrate that our method generates new views with suitable stereoscopic
output which correspond well to expected projections, for a wide range of specified perspective. Various advanced camera effects,
such as dolly zoom and wide angle effects, can also be readily generated for stereoscopic image pairs using our method.
Aesthetic Image Enhancement by Dependence-Aware Object Re-Composition
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, Vol. 15, No. 7, 1480-1490, 2013. 
Fang-Lue Zhang, Miao Wang, Shi-Min Hu
This paper proposes an image enhancement method to optimize photo composition, by rearranging foreground objects in
the photo. To adjust objects¡¯ positions while keeping the original scene content, we first perform a novel structure dependence
analysis on the image to obtain the dependencies between all background regions. To determine the optimal positions for
foreground objects, we formulate an optimization problem based on widely used heuristics for aesthetically pleasing pictures.
Semantic relations between foreground objects are also taken into account during optimization. The final output is produced
by moving foreground objects, together with their dependent regions, to optimal positions. The results show that our approach
can effectively optimize photos with single or multiple foreground objects without compromising the original photo content.
Time-Line Editing of Objects in Video
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, Vol. 19, No.7, 1218-1227.

Shao-Ping Lu, Song-Hai Zhang, Jin Wei, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R Martin
We present a video editing technique based on changing the time-lines of individual objects in video, which leaves
them in their original places but puts them at different times. This allows the production of object-level slow motion effects, fast
motion effects, or even time reversal. This is more flexible than simply applying such effects to whole frames, as new relationships
between objects can be created. As we restrict object interactions to the same spatial locations as in the original video, our
approach can produce high-quality results using only coarse matting of video objects. Coarse matting can be done efficiently
using automatic video object segmentation, avoiding tedious manual matting. To design the output, the user interactively indicates
the desired new life-spans of objects, and may also change the overall running time of the video. Our method rearranges the
time-lines of objects in the video whilst applying appropriate object interaction constraints. We demonstrate that, while this editing
technique is somewhat restrictive, it still allows many interesting results.
Motion-Aware Gradient Domain Video Composition
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, Vol. 22, No.7, 2532 - 2544. 
Tao Chen, Jun-Yan Zhu, Ariel Shamir, and Shi-Min Hu
For images, gradient domain composition methods like Poisson blending offer practical solutions for uncertain object
boundaries and differences in illumination conditions. However, adapting Poisson image blending to video faces new challenges
due to the added temporal dimension. In video, the human eye is sensitive to small changes in blending boundaries across
frames, and slight differences in motions of the source patch and target video. We present a novel video blending approach
that tackles these problems by merging the gradient of source and target videos and optimizing a consistent blending boundary
based on a user provided blending trimap for the source video. Our approach extends mean-value coordinates interpolation to
support hybrid blending with a dynamic boundary while maintaining interactive performance. We also provide a user interface
and source object positioning method that can efficiently deal with complex video sequences beyond the capabilities of alpha
blending.
Internet visual media processing: a survey with graphics and vision applications
The Visual Computer, 2013, Vol. 29, No.5, 393-405. 
Shi-Min Hu, Tao Chen, Kun Xu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Ralph R. Martin
In recent years, the computer graphics and computer vision communities have devoted significant attention
to research based on Internet visual media resources. The huge number of images and videos continually being uploaded
by millions of people have stimulated a variety of visual media creation and editing applications, while also
posing serious challenges of retrieval, organization, and utilization.
This article surveys recent research as regards processing of large collections of images and video, including
work on analysis, manipulation, and synthesis. It discusses the problems involved, and suggests possible future directions
in this emerging research area.
Mixed-Domain Edge-Aware Image Manipulation
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, Vol. 22, No. 5, 1915 - 1925. 
Xian-Ying Li, Yan Gu, Shi-Min Hu, and Ralph R. Martin
This paper gives a novel approach to edge-aware image manipulation. Our method processes a Gaussian pyramid from
coarse to fine, and at each level, we apply a nonlinear filter bank to the neighborhood of each pixel. Outputs of these
spatially-varying filters are merged using global optimization, and this optimization problem is solved
using an explicit mixeddomain (real space and DCT transform space) solution, which is efficient, accurate, and
easy-to-implement. We demonstrate applications of our method to a set of problems including detail
and contrast manipulation, HDR compression, non-photorealistic rendering, and haze removal.
PoseShop: A Human Image Database and Personalized Content Synthesis
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, Vol.19, No. 5, 824-837. 
Tao Chen, Ping Tan, Li-Qian Ma, Ming-Ming Cheng, Ariel Shamir and Shi-Min Hu
We present a human image database collected from online images where human figures are segmented out of their background. The
images are organized based on action semantic, clothes attributes and indexed by the shape of their poses. The database is built by downloading,
analyzing, and filtering over 3 million human images from the Internet and can be queried using either silhouette sketch or a skeleton to find a
given pose. We demonstrate the application of this database for multi-frame personalized content synthesis in the form of comic-strips, where the
main character is the user or his/her friends. We address the two challenges of such synthesis, namely personalization and consistency over a
set of frames, by introducing head swapping and clothes swapping techniques. We also demonstrate an action correlation analysis application to
show the usefulness of the database for vision application.
A Data-Driven Approach to Realistic Shape Morphing
Computer Graphics Forum, (Eurographics 2013), Vol. 32, No. 2, 449-457, 2013 
Lin Gao, Yu-Kun Lai, Qixing Huang and Shi-Min Hu
This paper proposes a novel data-driven approach
for shape morphing. Given a database with various models belonging to the same category, we treat them
as data samples in the plausible deformation space. These models are then clustered to form local shape spaces
of plausible deformations. We use a simple metric to reasonably represent the closeness between pairs of models.
Given source and target models, the morphing problem is casted as a global optimization problem of finding a
minimal distance path within the local shape spaces connecting these models. Under the guidance of intermediate
models in the path, an extended as-rigid-as-possible interpolation is used to produce the final morphing. By
exploiting the knowledge of plausible models, our approach produces realistic morphing for challenging cases as
demonstrated by various examples in the paper.
Efficient Synthesis of Gradient Solid Textures
Graphical Models, Vol. 75, No. 3, 104-117, 2013 
(An earlier version has been presented in Computaional Visual Media 2013, Beijing, and received Best paper Award)
Guo-Xin Zhang, Yu-Kun Lai and Shi-Min Hu
Solid textures require large storage and are computationally expensive to synthesize. In this paper, we propose a novel solid
representation called gradient solids to compactly represent solid textures, including a tricubic interpolation scheme of colors
and gradients for smooth variation and a region-based approach for representing sharp boundaries. We further propose a novel
approach based on this to directly synthesize gradient solid textures from exemplars. Compared to existing methods,
our approach avoids the expensive step of synthesizing the complete solid textures at voxel level and produces optimized
solid textures using our representation. This avoids significant amount of unnecessary computation and storage involved
in the voxel-level synthesis while producing solid textures with comparable quality to the state of the art.
The algorithm is much faster than existing approaches for solid texture synthesis and makes it feasible to
synthesize high-resolution solid textures in full. Our compact representation also supports efficient novel applications
such as instant editing propagation on full solids.
Semi-Regular Solid Texturing from 2D Image Exemplars
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, Vol. 19, No. 3, 460-469.

Song-Pei Du, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R.Martin
Solid textures, comprising 3D particles embedded in a matrix in a regular or semi-regular pattern, are common in
natural and man-made materials, such as brickwork, stone walls, plant cells in a leaf, etc. We present a novel technique for
synthesizing such textures, starting from 2D image exemplars which provide cross-sections of the desired volume texture. The
shapes and colors of typical particles embedded in the structure are estimated from their 2D cross-sections. Particle positions
in the texture images are also used to guide spatial placement of the 3D particles during synthesis of the 3D texture. Our
experiments demonstrate that our algorithm can produce higher-quality structures than previous approaches; they are both
compatible with the input images, and have a plausible 3D nature.
Poisson Coordinates
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, Vol.19, No. 2, 344-352. 
Xian-Ying Li and Shi-Min Hu,
Harmonic functions are the critical points of a Dirichlet energy functional, the linear projections of conformal maps. They
play an important role in computer graphics, particularly for gradient-domain image processing and shape-preserving geometric
computation. We propose Poisson coordinates, a novel transfinite interpolation scheme based on the Poisson integral formula, as
a rapid way to estimate a harmonic function on a certain domain with desired boundary values. Poisson coordinates are an extension
of the Mean Value coordinates (MVCs) which inherit their linear precision, smoothness, and kernel positivity. We give explicit formulae
for Poisson coordinates in both continuous and 2D discrete forms. Superior to MVCs, Poisson coordinates are proved to be pseudoharmonic
(i.e., they reproduce harmonic functions on n-dimensional balls). Our experimental results show that Poisson coordinates
have lower Dirichlet energies than MVCs on a number of typical 2D domains (particularly convex domains). As well as presenting a
formula, our approach provides useful insights for further studies on coordinates-based interpolation and fast estimation of harmonic
functions.
View-Dependent Multiscale Fluid Simulation
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, Vol. 19, No. 2, 178-188. 
Yue Gao, Chen-Feng Li, Bo Ren and Shi-Min Hu
Fluid motions are highly nonlinear and non-stationary, with turbulence occurring and developing at different length and time
scales. In real-life observations, the multiscale flow generates different visual impacts depending on the distance to the viewer. We
propose a new fluid simulation framework that adaptively allocates computational resources according to the human visual perception.
First, a 3D empirical model decomposition scheme is developed to obtain the velocity spectrum of the turbulent flow. Then, depending
on the distance to the viewer, the fluid domain is divided into a sequence of nested simulation partitions. Finally, the multiscale fluid
motions revealed in the velocity spectrum are distributed non-uniformly to these view-dependent partitions, and the mixed velocity
fields defined on different partitions are solved separately using different grid sizes and time steps. The fluid flow is solved at different
spatial-temporal resolutions, such that higher-frequency motions closer to the viewer are solved at higher resolutions and vice versa.
The new simulator better utilizes the computing power, producing visually plausible results with realistic fine-scale details in a more
efficient way. It is particularly suitable for large scenes with the viewer inside the fluid domain. Also, as high-frequency fluid motions are
distinguished from low-frequency motions in the simulation, the numerical dissipation is effectively reduced.
2012
Structure Recovery by Part Assembly
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 31, No. 6, Article No. 180, ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2012.
 (click for project webpage, data set is available)
(click for project webpage, data set is available)
Chao-Hui Shen, Hongbo Fu, Kang Chen and Shi-Min Hu
This work presents a technique that allows quick conversion of acquired low-quality data from consumer-level scanning devices to
high-quality 3D models with labeled semantic parts and meanwhile their assembly reasonably close to the underlying geometry. This
is achieved by a novel structure recovery approach that is essentially local to global and bottom up, enabling the creation
of new structures by assembling existing labeled parts with respect to the acquired data. We demonstrate that using only a
small-scale shape repository, our part assembly approach is able to faithfully recover a variety of high-level structures from
only a single-view scan of man-made objects acquired by the Kinect system, containing a highly noisy, incomplete 3D point cloud
and a corresponding RGB image.
An Optimization Approach for Extracting and Encoding Consistent Maps in a
Shape Collection
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 31, No. 6, Article No. 167, ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2012.

Qi-xing Huang, Guoxin Zhang, Lin Gao, Shi-Min Hu, Adrian Butscher and Leonidas Guibas
We introduce a novel diffusion-based approach for computing high quality point-to-point maps among a collection of shapes so that
several desirable properties are satisfied. The proposed approach takes as input a sparse set of initial maps between pairs of shapes
(sufficient to connect the model graph) and implicitly builds a new set of pointwise maps between all pairs of shapes which aim to (1)
align with the initial maps, (2) map neighboring points to neighboring points, and (3) provide cycle-consistency, so that map compositions
along cycles approximate the identity map. Maps among subsets of the shapes that admit nearly perfect loop closure are
highly redundant and can be compactly represented by maps from a single base shape to other shapes. Our algorithm extracts such a
set of base shapes so that every other shape is ¡°covered¡± by at least one of the base shapes.
ImageAdmixture: Putting Together Dissimilar Objects from Groups
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2012, Vol. 18, No.11, 1849-1857.

Fang-Lue Zhang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jiaya Jia, Shi-Min Hu
We present a semi-automatic image editing framework dedicated to individual structured object replacement from groups. The
major technical difficulty is element separation with irregular spatial distribution, hampering previous texture and image synthesis methods
from easily producing visually compelling results. Our method uses the object-level operations and finds grouped elements based on
appearance similarity and curvilinear features. This framework enables a number of image editing applications, including natural image
mixing, structure preserving appearance transfer, and texture mixing.
Fisheye Video Correction
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2012, Vol. 18, No.10, 1771-1783.

Jin Wei, Chen-Feng Li, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph Martin, and Chiew-Lan Tai
Various types of video are captured with fisheye lenses, particularly surveillance video, due to their ability to capture a wide
field of view. However, distortion changes as objects in the scene move, making fisheye video difficult to interpret and uncomfortable
to watch. Current still fisheye image correction methods are either limited to small angles of view, or are strongly content-dependent,
and therefore not suitable for processing video streams. We present a novel scheme for fisheye video correction, which minimizes
time-varying distortions and preserves salient content features in a coherent manner. Our optimization process is controlled by user
annotation, and includes a comprehensive set of measures addressing different aspects of natural scene appearance. These terms
are all formulated in quadratic form, leading to a quadratic programming problem which can be solved in a closed form using a sparse
linear system. We illustrate our method with a range of examples, demonstrating coherent natural-looking video output in which the
visual quality of individual frames is comparable to state-of-the-art methods for still fisheye photograph correction.
Interactive Images: Proxy-based Scene Understanding for Smart Manipulation
ACM Transactions on Graphics (ACM SIGGRAPH),2012,Vol. 31, No. 4, article number 99,

Youyi Zheng, Xiang Chen, Ming-Ming Cheng, Kun Zhou, Shi-Min Hu, Niloy J. Mitra
Images are static and lack important depth information of underlying 3D scenes.
We introduce interactive images in the context of man-made environments wherein objects
are simple, regular, share various non-local relations (e.g., coplanarity, repetitions, etc.),
and are often repeated. We present an interactive framework to create a partial scene
reconstruction based on cuboid-proxies using minimal user interaction. This enables a
range of intuitive image edits mimicking real-world behavior, which are otherwise difficult
to achieve. Effectively, the user simply provides high-level semantic hints, while our
system ensures plausible operations by conforming to the extracted non-local relations.
We demonstrate our system on a range of real-world images and validate the plausibility
of the results using a user study.
Other publications in 2012
1. Li-Qian Ma and Kun XU, Efficient antialiased edit propagation for images and videos,
Computer & Graphics, Vol. 36, No. 8, 1005-1012.

2. Yong-Liang Yang and Chao-Hui Shen, Multi-Scale Salient Features for Analyzing 3D Shapes,
Journal of Computer Science and technology, Vol. 27, No. 6, 1092-1099, 2012.

3. Long Zeng, Yong-Jin Liu, Sang-Hun Lee, Ming-Fai Yuen, Q-Complex: efficient non-manifold boundary representation with inclusion topology,
Computer-Aided Design, Vol. 44, No. 11, 1115-1126, 2012.

4. Ling-Qi Yan, Yahan Zhou, Kun Xu and Rui Wang,Accurate Translucent Material Rendering under Spherical Gaussian Lights,
Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 31, No. 7, 2267-2276, 2012.

5. Long Zeng, Yong-Jin Liu, Ming Chen, Ming-Fai Yuen, Least squares quasi-developable mesh approximation,
Computer Aided Geometric Design, Vol. 29, No. 7, 565-578, 2012.

6. Chen Goldberg, Tao Chen, Fang-Lue Zhang, Ariel Shamir, Shi-Min Hu, Data-Driven Object Manipulation in Images,
Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 31, No. 2, 265-274, 2012 (Eurographics 2012).

7. Tao Chen, Aidong Lu and Shi-Min Hu, Visual storylines: Semantic visualization of movie sequence,
Computer & Graphics, Vol. 36, No. 4, 241-249, 2012.

8. Cui-Xia Ma, Yong-Jin Liu, Hong-An Wang, Dong-Xing Teng, Guo-Zhong Dai, Sketch-based Annotation and Visualization in Video Authoring,
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, Vol. 14, No. 4, 1153-1165, 2012.

9. Yong-Jin Liu, Yi-Fu Zheng, Lu Lv, Yu-Ming Xuan, Xiao-Lan Fu, 3D Model Retrieval based on Color+Geometry Signatures,
The Visual Computer, Vol. 28, No. 1, 75-86, 2012.

2011
Interactive Hair Rendering and Appearance Editing under Environment Lighting
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 30, No. 6, ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2011.

Kun Xu, Li-Qian Ma, Bo Ren, Rui Wang, Shi-Min Hu
We present an interactive algorithm for hair rendering and appearance editing under complex environment
lighting represented as spherical radial basis functions (SRBFs). Our main contribution is to derive a
compact 1D circular Gaussian representation that can accurately model the hair scattering function introduced
by [Marschner et al. 2003]. The primary benefit of this representation is that it enables us to evaluate,
at run-time, closed-form integrals of the scattering function with each SRBF light, resulting
in efficient computation of both single and multiple scatterings. In
contrast to previous work, our algorithm computes the rendering integrals entirely on the fly and does not
depend on expensive precomputation. Thus we allow the user to dynamically change the
hair scattering parameters, which can vary spatially. Analyses show that our 1D circular
Gaussian representation is both accurate and concise. In addition, our algorithm incorporates the eccentricity of
the hair. We implement our algorithm on the GPU, achieving interactive hair rendering and simultaneous
appearance editing under complex environment maps for the first time.
Adaptive Partitioning of Urban Facades
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 30, No. 6, ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2011.

Chao-Hui Shen, Shi-Sheng Huang, Hongbo Fu, Shi-Min Hu
Automatically discovering high-level facade structures in unorganized
3D point clouds of urban scenes is crucial for applications
like digitalization of real cities. However, this problem is challenging
due to poor-quality input data, contaminated with severe
missing areas, noise and outliers. This work introduces the concept
of adaptive partitioning to automatically derive a flexible and
hierarchical representation of 3D urban facades. Our key observation
is that urban facades are largely governed by concatenated
and/or interlaced grids. Hence, unlike previous automatic facade
analysis works which are typically restricted to globally rectilinear
grids, we propose to automatically partition the facade in an
adaptive manner, in which the splitting direction, the number and
location of splitting planes are all adaptively determined. Such an
adaptive partition operation is performed recursively to generate a
hierarchical representation of the facade. We show that the concept
of adaptive partitioning is also applicable to flexible and robust
analysis of image facades. We evaluate our method on a dozen
of LiDAR scans of various complexity and styles, and the image
facades from the eTRIMS database and the Ecole Centrale Paris
database. A series of applications that benefit from our approach
are also demonstrated.
Online Video Stream Abstraction and Stylization
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, vol.13, no.6, pp.1286-1294, Dec. 2011


Song-Hai Zhang, Xian-Ying Li, Shi-Min Hu, and Ralph R. Martin
This paper gives an automatic method for online
video stream abstraction, producing a temporally coherent output
video stream, in the style with large regions of constant color
and highlighted bold edges. Our system includes two novel components.
Firstly, to provide coherent and simplified output, we
segment frames, and use optical flow to propagate segmentation
information from frame to frame; an error control strategy is
used to help ensure that the propagated information is reliable.
Secondly, to achieve coherent and attractive coloring of the
output, we use a color scheme replacement algorithm specifically
designed for an online video stream. We demonstrate real-time
performance for CIF videos, allowing our approach to be used for
live communication and other related applications.
Index Terms¡ªAbstraction, color scheme replacement, optical
flow, segmentation, temporal coherence, video stream.
A Geometric Study of V-style Pop-ups: Theories and Algorithms
ACM Transactions on Graphics 2011, Vol. 30, No. 4, ACM SIGGRAPH 2011


Xian-Ying Li, Tao Ju, Yan Gu, Shi-Min Hu
Pop-up books are a fascinating form of paper art with intriguing geometric
properties. In this paper, we present a systematic study of
a simple but common class of pop-ups consisting of patches falling
into four parallel groups, which we call v-style pop-ups. We give
sufficient conditions for a v-style paper structure to be pop-uppable.
That is, it can be closed flat while maintaining the rigidity of the
patches, the closing and opening do not need extra force besides
holding two patches and are free of intersections, and the closed
paper is contained within the page border. These conditions allow
us to identify novel mechanisms for making pop-ups. Based
on the theory and mechanisms, we developed an interactive tool
for designing v-style pop-ups and an automated construction algorithm
from a given geometry, both of which guaranteeing the popuppability
of the results.
Global Contrast based Salient Region Detection
IEEE CVPR, p. 409-416, 2011,

Ming-Ming Cheng, Guo-Xin Zhang, Niloy J. Mitra, Xiaolei Huang, Shi-Min Hu
Reliable estimation of visual saliency allows appropriate processing of images without prior
knowledge of their content, and thus remains an important step in many computer vision
tasks including image segmentation, object recognition, and adaptive compression.
We propose a regional contrast based saliency extraction algorithm, which simultaneously
evaluates global contrast differences and spatial coherence. The proposed algorithm is simple,
efficient, and yields full resolution saliency maps. Our algorithm consistently outperformed existing saliency detection methods, yielding higher precision and better recall rates, when evaluated using one of the largest publicly available data sets. We also demonstrate how the extracted saliency map can be used to create high quality segmentation masks for subsequent image processing.
Construction of Iso-contours, Bisectors and Voronoi Diagrams on Triangulated Surfaces
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 33, No. 8, 1502-1517, 2011

Yong-Jin Liu, Zhan-Qing Chen, Kai Tang
In the research of computer vision and machine perception, three-dimensional objects are usually
represented by 2-manifold triangular meshes M. In this paper,
we present practical and efficient algorithms to construct iso-contours, bisectors and Voronoi
diagrams of point sites onM, based on an exact geodesic metric. Compared to Euclidean metric spaces,
the Voronoi diagrams on M exhibit many special properties that fail all the existing Euclidean Voronoi algorithms.
To provide practical algorithms for constructing geodesic-metric-based Voronoi diagrams on M,
this paper studies the analytic structure of iso-contours, bisectors and Voronoi diagrams on M.
After a necessary preprocessing of model M, practical algorithms are proposed for quickly obtaining full
information about iso-contours, bisectors and Voronoi diagrams on M. The complexity of the construction
algorithms is also analyzed. Finally three interesting applications, surface sampling and reconstruction,
3D skeleton extraction and point pattern analysis are presented that show the potential power of the
proposed algorithms in pattern analysis.
Image Retargeting Quality Assessment
Computer Graphics Forum, 2011, Vol. 30, No. 2, Eurographics 2011, 
Yong-Jin Liu, Xi Luo, Yu-Ming Xuan, Wen-Feng Chen, Xiao-Lan Fu
Content-aware image retargeting is a technique that can flexibly display images
with different aspect ratios and simultaneously preserve salient regions in images. Recently many image
retargeting techniques have been proposed. To compare image quality by different retargeting methods fast and
reliably, an objective metric simulating the human vision system (HVS) is presented in this paper.
Different from traditional objective assessment methods that work in bottom-up manner (i.e.,
assembling pixel-level features in a local-to-global way), in this paper we propose to use a
reverse order (top-down manner) that organizes image features from global to local viewpoints,
leading to a new objective assessment metric for retargeted images. A scale-space matching
method is designed to facilitate extraction of global geometric structures from retargeted images.
By traversing the scale space from coarse to fine levels, local pixel correspondence is also established.
The objective assessment metric is then based on both global geometric structures and local pixel correspondence.
To evaluate color images, CIE Lab color space is utilized. Experimental results are obtained to
measure the performance of objective assessments with the proposed metric. The results show good
consistency between the proposed objective metric and subjective assessment by human observers.
Connectedness of Random Walk Segmentation
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011. 33(1): p. 200 -202..
Ming-Ming Cheng, Guo-Xin Zhang
Connectedness of random walk segmentation is examined, and novel properties are discovered, by considering electrical circuits equivalent to random walks. A theoretical analysis shows that earlier conclusions concerning connectedness of random walk segmentation results are incorrect, and counterexamples are demonstrated.
Other publications in 2011
1. Wen-Qi Zhang, Yong-Jin Liu, Approximating the Longest Paths in Grid Graphs,
Theoretical Computer Science, 2011, Vol. 412, No. 39, 5340-5350.

2. Yong-Jin Liu, Kai Tang, Wen-Yong Gong, Tie-Ru Wu, Industrial Design using Interpolatory Discrete Developable Surfaces,
Computer-Aided Design, 2011, Vol. 43, No. 9, 1089-1098, 2011.

3. Guo-Xin Zhang, Song-Pei Du, Yu-Kun Lai, Tianyun Ni, Shi-Min Hu, Sketch Guided Solid Texturing,
Graphics Models, 2011, Vol. 73, No.3, 59-73.

4. Cui-Xia Ma, Yong-Jin Liu, Hai-Yan Yang, Dong-Xing Teng, Hong-An Wang, Guo-Zhong Dai, KnitSketch: A Sketch Pad for Conceptual Design of 2D Garment Patterns,
IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2011, Vol. 8, No. 2,

5. Zhe Bian, Shi-Min Hu, Preserving detailed features in digital bas-relief making,
Computer Aided Geometric Design, Vol. 28, No. 4, 245-256, 2011.

6. Yong-Jin Liu, Cui-Xia Ma, Dong-Liang Zhang, Easytoy: a plush toy design system using editable sketch curves,
IEEE Computer Graphics & Applications, 2011, Vol. 31, No. 2,

7. Shao-Ping Lu and Song-Hai Zhang, Saliency-Based Fidelity Adaptation Preprocessing for Video Coding,
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2011, Vol. 26, No. 1, 195-202

2010
Instant Propagation of Sparse Edits on Images and Videos
Computer Graphics Forum, Special issue of Pacific Graphics 2010, Vol. 29, No. 7, 2049-2054
Yong Li, Tao Ju, Shi-Min Hu
The ability to quickly and intuitively edit digital contents has become increasingly important in our everyday life.
We propose a novel method for propagating a sparse set of user edits (e.g., changes in color, brightness, contrast,
etc.) expressed as casual strokes to nearby regions in an image or video with similar appearances. Existing
methods for edit propagation are typically based on optimization, whose computational cost can be prohibitive
for large inputs. We re-formulate propagation as a function interpolation problem in a high-dimensional space,
which we solve very efficiently using radial basis functions. While simple to implement, our method significantly
improves the speed and space cost of existing methods, and provides instant feedback of propagation results even
on large images and videos.
Popup: Automatic Paper Architectures from 3D Models
ACM Transactions on Graphics 2010, Vol. 29, No. 4, ACM SIGGRAPH 2010
Xian-Ying Li, Chao-Hui Shen, Shi-Sheng Huang, Tao Ju, Shi-Min Hu
Paper architectures are 3D paper buildings created by folding and cutting. The creation process of
paper architecture is often labor intensive and highly skill-demanding, even with the aid of
existing computer-aided design tools. We propose an automatic algorithm for generating paper
architectures given a user-specified 3D model. The algorithm is grounded on geometric formulation
of planar layout for paper architectures that can be popped-up in a rigid and stable manner, and
sufficient conditions for a 3D surface to be popped up from such a planar layout. Based on these
conditions, our algorithm computes a class of paper architectures containing two sets of parallel
patches that approximate the input geometry while guaranteed to be physically realizable. The method
is demonstrated on a number of architectural examples, and physically engineered results are presented.
RepFinder: Finding Approximately Repeated Scene Elements for Image Editing
ACM Transactions on Graphics 2010, Vol. 29, No. 4, ACM SIGGRAPH 2010

Ming-Ming Cheng, Fang-Lue Zhang, Niloy J. Mitra, Xiaolei Huang, Shi-Min Hu
Repeated elements are ubiquitous and abundant in both manmade and natural scenes. Editing such
images while preserving the repetitions and their relations is nontrivial due to overlap,
missing parts, deformation between instances, illumination variation, etc. Manually enforcing
such relations is laborious and error prone. We propose a novel framework where simple user
input in the form of scribbles are used to guide detection and extraction of such repeated elements.
Our detection process is based on a novel boundary band method, and robustly extracts the repetitions
along with their mutual depth relations. We then use topological sorting to establish a partial depth
ordering of overlapping repeated instances. Missing parts on occluded instances are completed using
information from other instances. The extracted repeated instances can then be seamlessly edited
and manipulated for a variety of high level tasks that are otherwise difficult to perform.
We demonstrate the versatility of our framework on a large set of inputs of varying complexity,
showing applications to image rearrangement, edit transfer, deformation propagation, and instance replacement.
Metric-Driven RoSy Fields Design
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2010, Vol. 16, No. 1, 95-108.

Yu-Kun Lai, Miao Jin, Xuexiang Xie, Ying He, Jonathan Palacios, Eugene Zhang, Shi-Min Hu and Xianfeng David Gu
This work introduces a rigorous and practical approach for automatic N-RoSy field design on arbitrary surfaces
with user defined field topologies.
The user has full control of the number, positions and indices of the singularities, the turning numbers of
the loops, and is able to edit the field interactively. We formulate N-RoSy field construction as
designing a Riemannian metric, such that the holonomy along any loop is compatible with the local symmetry
of N-RoSy fields. We prove the compatibility condition using discrete parallel transport. The complexity
of N-RoSy field design is caused by curvatures. In
our work, we propose to simplify the Riemannian metric to make it flat almost everywhere. This approach
greatly simplifies the process and improves the flexibility, such that, it can design N-RoSy fields with
single singularity, and mixed-RoSy fields. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we apply our design
system to pen-and-ink sketching and geometry remeshing.
Other publications in 2010
1. Yong-Jin Liu, Dong-Liang Zhang, Matthew Ming-Fai Yuen, A survey on CAD methods in garment design,
Computers in Industry, 2010, Vol. 61, No. 6, 576-593

2. Yong-Jin Liu, Kam-Lung Lai, Gang Dai, Ming-Fai Yuen, A semantic feature model in concurrent engineering,
IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2010, Vol. 7, No. 3, 659-665

3. Yu-Ping Wang, Shi-Min Hu, Optimization approach for 3D model watermarking by linear binary programming,
Computer Aided Design, 2010, Vol. 27, No. 5, 395-404

4. Yong-Jin Liu, Wen-Qi Zhang, Kai Tang, Some notes on maximal arc intersection of spherical polygons: its NP-hardness and approximation algorithms,
The Visual Computer, 2010, Vol. 26, No. 4, 287-292

5. Chao-Hui Shen, Guo-Xin Zhang, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu, Harmonic Field Based Volume Model Construction from Triangle Soup,
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2010, Vol. 25, No. 3, 562-571

6. Jin Wei and Yu Lou, Feature Preserving Mesh Simplification Using Feature Sensitive Metric,
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2010, Vol. 25, No. 3, 595-605

7. Yu-Kun Lai, Leif Kobbelt and Shi-Min Hu, Feature aligned quad dominant remeshing using iterative local updates,
Computer Aided Design, 2010, Vol. 42, No. 2, 109-117

(An earlier version has been presented in ACM Symosium on Solid and Physical Modeling, June 2-4, 2008)
2009
Sketch2Photo: Internet Image Montage
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 28, No. 5, Article No. 124, ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2009

Tao Chen, Ming-Ming Cheng, Ping Tan, Ariel Shamir, Shi-Min Hu
The paper was selected as one of the top 10 most innovative and promising worldwide initiatives of 2009 by the Netexplorateur jury.
We present a system that composes a realistic picture from a user
provided sketch with text labels. The composed picture is generated
by seamlessly stitching several photographs automatically searched
from internet according to the sketch and its text labels. While on
line image search generates noisy results, our system can automat
ically select suitable photographs to generate a high quality com
position. To achieve this, we first design a filtering scheme to exclude undesirable images from searched results. Then we propose
a novel image blending algorithm for seamless image composition.
Our blending algorithm returns a numeric score for each blending,
which is used to optimize the combination of searched images. Several vivid results are generated in the experiments. We also perform
a user study to demonstrate the advantages of our system.
Efficient Affinity-based Edit Propagation using K-D Tree
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 28, No. 5, Article No. 118, ACM SIGGRAPH ASIA 2009

Kun Xu, Yong Li, Tao Ju, Shi-Min Hu, Tian-Qiang Liu
Image/video editing by strokes has become increasingly popular
due to the ease of interaction. Propagating the user inputs to the rest
of the image/video, however, is often time and memory consuming
especially for large data. We propose here an efficient scheme that
allows affinity-based edit propagation to be computed on data containing
tens of millions of pixels at interactive rate (in matter of seconds).
The key in our scheme is a novel means for approximately
solving the optimization problem involved in edit propagation, using
adaptive clustering in a high-dimensional, affinity space. Our
approximation significantly reduces the cost of existing affinitybased
propagation methods while maintaining visual fidelity, and
enables interactive stroke-based editing even on high resolution images
and long video sequences using commodity computers.
Simulating Gaseous Fluids with Low and High Speeds
Computer Graphics Forum, Special issue of Pacific Graphics 2009, Vol. 28, No. 7, 1845-1852


Yue Gao, Chen-Feng Li, Shi-Min Hu, Brian A. Barsky
Gaseous fluids may move slowly, as smoke does, or at high speed, such as occurs with explosions. High-speed
gas flow is always accompanied by low-speed gas flow, which produces rich visual details in the fluid motion.
Realistic visualization involves a complex dynamic flow field with both low and high speed fluid behavior. In
computer graphics, algorithms to simulate gaseous fluids address either the low speed case or the high speed
case, but no algorithm handles both efficiently. With the aim of providing visually pleasing results, we present a
hybrid algorithm that efficiently captures the essential physics of both low- and high-speed gaseous fluids. We
model the low speed gaseous fluids by a grid approach and use a particle approach for the high speed gaseous
fluids. In addition, we propose a physically sound method to connect the particle model to the grid model. By
exploiting complementary strengths and avoiding weaknesses of the grid and particle approaches, we produce
some animation examples and analyze their computational performance to demonstrate the effectiveness of the
new hybrid method.
Edit Propagation on Bidirectional Texture Functions
Computer Graphics Forum, Special issue of Pacific Graphics 2009, Vol. 28, No. 7, 1871-1877

Kun Xu, Jiaping Wang, Xin Tong, Shi-Min Hu, Baining Guo
We propose an efficient method for editing bidirectional texture functions (BTFs) based on edit propagation
scheme. In our approach, users specify sparse edits on a certain slice of BTF. An edit propagation scheme is
then applied to propagate edits to the whole BTF data. The consistency of the BTF data is maintained by propagating
similar edits to points with similar underlying geometry/reflectance. For this purpose, we propose to use
view independent features including normals and reflectance features reconstructed from each view to guide the
propagation process. We also propose an adaptive sampling scheme for speeding up the propagation process.
Since our method needn't any accurate geometry and reflectance information, it allows users to edit complex
BTFs with interactive feedback.
A Shape-Preserving Approach to Image Resizing
Computer Graphics Forum, Special issue of Pacific Graphics 2009, Vol. 28, No. 7, 1897-1906 

Guo-Xin Zhang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R. Martin
We present a novel image resizing method which attempts to ensure that important local regions undergo a geometric
similarity transformation, and at the same time, to preserve image edge structure. To accomplish this, we
define handles to describe both local regions and image edges, and assign a weight for each handle based on an
importance map for the source image. Inspired by conformal energy, which is widely used in geometry processing,
we construct a novel quadratic distortion energy to measure the shape distortion for each handle. The resizing
result is obtained by minimizing the weighted sum of the quadratic distortion energies of all handles. Compared to
previous methods, our method allows distortion to be diffused better in all directions, and important image edges
are well-preserved. The method is efficient, and offers a closed form solution.
Generalized Discrete Ricci Flow
Computer Graphics Forum, Special issue of Pacific Graphics 2009, Vol. 28, No. 7, 2005-2014

Yong-Liang Yang, Ren Guo, Feng Luo, Shi-Min Hu, Xianfeng Gu
Surface Ricci flow is a powerful tool to design Riemannian metrics by user defined curvatures. Discrete surface
Ricci flow has been broadly applied for surface parameterization, shape analysis, and computational topology.
Conventional discrete Ricci flow has limitations. For meshes with low quality triangulations, if high conformality
is required, the flow may get stuck at the local optimum of the Ricci energy. If convergence to the global optimum
is enforced, the conformality may be sacrificed.
This work introduces a novel method to generalize the traditional discrete Ricci flow. The generalized Ricci flow
is more flexible, more robust and conformal for meshes with low quality triangulations. Conventional method is
based on circle packing, which requires two circles on an edge intersect each other at an acute angle. Generalized
method allows the two circles either intersect or separate from each other. This greatly improves the flexibility and
robustness of the method. Furthermore, the generalized Ricci flow preserves the convexity of the Ricci energy, this
ensures the uniqueness of the global optimum. Therefore the algorithm won't get stuck at the local optimum.
Generalized discrete Ricci flow algorithms are explained in details for triangle meshes with both Euclidean and
hyperbolic background geometries. Its advantages are demonstrated by theoretic proofs and practical applications
in graphics, especially surface parameterization.
Automatic and Topology-Preserving
Gradient Mesh Generation for Image Vectorization
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 28, No. 3, article 85, ACM SIGGRAPH 2009

Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R. Martin
Gradient mesh vector graphics representation, used in commercial
software, is a regular grid with specified position and color,
and their gradients, at each grid point. Gradient meshes can compactly
represent smoothly changing data, and are typically used for
single objects. This paper advances the state of the art for gradient
meshes in several significant ways. Firstly, we introduce a
topology-preserving gradient mesh representation which allows an
arbitrary number of holes. This is important, as objects in images
often have holes, either due to occlusion, or their 3D structure. Secondly,
our algorithm uses the concept of image manifolds, adapting
surface parameterization and fitting techniques to generate the gradient
mesh in a fully automatic manner. Existing gradient-mesh
algorithms require manual interaction to guide grid construction,
and to cut objects with holes into disk-like regions. Our new algorithm
is empirically at least 10 times faster than previous approaches.
Furthermore, image segmentation can be used with our
new algorithm to provide automatic gradient mesh generation for
a whole image. Finally, fitting errors can be simply controlled to
balance quality with storage.
Vectorizing Cartoon Animations
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2009, Vol. 15, No. 4, May/June, 618-629 

Song-hai Zhang, Tao Chen, Yi-Fei Zhang, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R. Martin
We present a system for vectorizing 2D raster format carton animations. The output animations are visually flicker free,
smaller in file size, and easy to edit. We identify decorative lines separately from coloured regions.
We use an accurate and semantically meaningful image decomposition algorithm which supports an arbitrary color
model for each region. To ensure temporal coherence in the output cartoon, we reconstruct a universal background
for all frames, and separately extract foreground regions. Simple user-assistance is required to complete the
background. Each region and decorative line is vectorized and stored together with their motions from frame to frame.
A new watermarking method for 3D model based on integral invariant
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2009, Vol. 15, No. 2, March/April, 285-294 
Yu-Ping Wang and Shi-Min Hu
In this report, we propose a new semi-fragile watermarking algorithm for the authentication of 3D models based on integral invariants. To do so, we embed a watermark image by modifying the integral invariants of some of the vertices. Basically, we shift a vertex and its neighbors in order to change the integral invariants. To extract the watermark, test all the vertices for the embedded information, and combine them to recover the watermark image. How many parts can
the watermark image be recovered would help us to make the authentication decision. Experimental test shows that this method is robust against rigid transform and noise attack, and useful to test purposely attack besides transferring noise and geometrical transforming noise. An additional contribution of this paper is a new algorithm for computing two kinds of integral invariants.
Other publications in 2009
1. Yong-Jin Liu, Yu-Kun Lai and Shi-Min Hu, Stripification of Free-Form Surfaces with Global Error Bounds for Developable Approximation,
IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2009, Vol. 6, No. 4, 700-709

2. Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R. Martin and Paul L. Rosin,apid and Effective Segmentation of 3D Models using Random Walks,
Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2009, Vol. 26, No. 6, 665-679.

(An earlier version has been presented in ACM Symosium on Solid and Physical Modeling, June 2-4, 2008)
3. Song-hai Zhang, Tao Chen, Yi-Fei Zhang, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R. Martin, Video-Based Running Water Animation in Chinese Painting Style,
Science in China Series F: Information Sciences, 2009, Vol. 52, No. 2, 162-171

4. Zhe Bian, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R Martin, Evaluation for Small Visual Difference Between Conforming Meshes on Strain Field,
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2009, Vol. 24, No. 1, 65-75

The preliminary version of this work has been presented on GMP2008.
2008
Optimal Surface Parameterization Using Inverse Curvature Map
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2008, Vol. 14, No. 5, Septmber/Octber, 1054-1066. 
Yong-Liang Yang, Junho Kim, Feng Luo, Shi-Min Hu, and Xianfeng Gu
Mesh parameterization is a fundamental technique in computer graphics. The major goals during mesh parameterization are
to minimize both the angle distortion and the area distortion. Angle distortion can be eliminated by use of conformal mapping,
in principle. Our paper focuses on solving the problem of �nding the best discrete conformal mapping that also minimizes area distortion. Major theoretical results and practical algorithms are presented for optimal parameterization based on the inverse curvature map. Comparisons are conducted with existing methods and using different energies. Novel parameterization applications are also introduced. The theoretical framework of the inverse curvature map can be applied to further study discrete conformal mappings.
Shrinkability Maps for Content-Aware Video Resizing
Computer Graphics Forum, Special issue of Pacific Graphics 2008 , Vol. 27, No. 7, 1797-1804 . 
Yi-Fei Zhang,Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R. Martin
A novel method is given for content-aware video resizing, i.e. targeting video to a new resolution (which may involve aspect ratio change) from the original. We precompute a per-pixel cumulative shrinkability map which takes into account both the importance of each
pixel and the need for continuity in the resized result. (If both x and y resizing are required, two separate shrinkability
maps are used, otherwise one suffices). A random walk model is used for efficient offline computation of the
shrinkability maps. The latter are stored with the video to create a multi-sized video, which permits
arbitrarysized new versions of the video to be later very efficiently created in real-time, e.g. by a
video-on-demand server supplying video streams to multiple devices with different resolutions. These
shrinkability maps are highly compressible, so the resulting multi-sized videos are typically less than
three times the size of the original compressed video. A scaling function operates on the multi-sized video,
to give the new pixel locations in the result, giving a high-quality content-aware resized video.
Shape Deformation using a Skeleton to Drive Simplex Transformations
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2008, Vol. 14, No. 3, May/June, 693-706 
Han-Bing Yan, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R Martin, and Yong-Liang Yang
The preliminary version of this work has been presented on CGI 2006
This paper presents a skeleton-based method for deforming meshes (the skeleton need not be the medial axis). The significant difference from previous skeleton-based methods is that the latter use the skeleton to control movement of vertices whereas we use it to control the simplices defining the model. By doing so, errors that occur near joints in other methods can be spread over the whole mesh, via an optimization process, resulting in smooth transitions near joints of the skeleton. By controlling simplices, our method has the additional advantage that no
vertex weights need be defined on the bones, which is a tedious requirement in previous skeleton-based methods. Furthermore, by incorporating the translation vector in our optimisation, unlike other methods, we do not need to fix an arbitrary vertex, and the deformed mesh moves with the deformed skeleton. Our method can also easily be used to control deformation by moving a few chosen line segments, rather than a skeleton.
Spherical Piecewise Constant Basis Functions for All-Frequency Precomputed Radiance Transfer
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2008, Vol. 14, No. 2, March/April, 454-467 

Kun Xu, Yun-Tao Jia, Hongbo Fu, Shi-Min Hu and Chiew-Lan Tai
This paper presents a novel basis function, called spherical piecewise constant basis function (SPCBF), for precomputed radiance transfer. SPCBFs have several desirable properties: rotatability, ability to represent all-frequency signals, and support for efficient multiple product. By partitioning the illumination sphere into a set of subregions, and associating each subregion with an SPCBF valued 1 inside the region and 0 elsewhere, we precompute the light coefficients using the resulting SPCBFs. We run-time approximate BRDF and visibility coefficients with the same set of SPCBFs through fast lookup of summed-area-table (SAT) and visibility distance table (VDT), respectively. SPCBFs enable new effects such as object rotation in all-frequency rendering of dynamic scenes and onthe-fly BRDF editing under rotating environment lighting. With graphics hardware acceleration, our method achieves real-time frame rates.
Video: Download video here (13.0MB).
Other publications in 2008
1. Yu-Kun Lai, Yong-Jin Liu, Yu Zang and Shi-Min Hu, Fairing Wireframes in Industrial Design,
IEEE International Conference on Shape Modeling and Applications, June 4-6, 2008, 29-35.

2. Yong-Jin Liu, Matthew Ming-Fai Yuen, Geometry-optimized virtual human head and its applications,
Computer & Graphics, 2008, Vol. 32, No. 6, 624-631

2007
Editing The Topology of 3D Models by Sketching
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 26, No. 3, Article 42, ACM SIGGRAPH 2007



Tao Ju, Qian-Yi Zhou and Shi-Min Hu
We present a method for modifying the topology of a 3D model with user control. The heart of our method is a guided
topology editing algorithm. Given a source model and a user-provided target shape, the algorithm modifies the source
so that the resulting model is topologically consistent with the target. Our algorithm permits removing or adding
various topological features (e.g., handles, cavities and islands) in a common framework and ensures that each
topological change is made by minimal modification to the source model. To create the target shape, we have also
designed a convenient 2D sketching interface for drawing 3D line skeletons. As demonstrated in a suite of examples,
the use of sketching allows more accurate removal of topological artifacts than previous methods,
and enables creative designs with specific topological goals.
Video:
Download video here (31.8MB). (Cannot open the video? Cannot hear the audio? Get latest QuickTime player.)
Software: A software MendIT based on this paper will come soon, please refer to webpage: http://graphics.usc.edu/~qianyizh/software.html
Real-time homogeneous translucent material editing
EuroGraphics 2007, Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 26, No. 3, 545–552.


Kun Xu, Yue Gao, Yong Li, Tao Ju and Shi-Min Hu
This paper presents a novel method for real-time homogeneous translucent material editing under fixed illumination. We consider the complete analytic BSSRDF model proposed by Jensen et al.[JMLH01], including both multiple scattering and single scattering. Our method allows the user to adjust the analytic parameters of BSSRDF and provides high-quality, real-time rendering feedback. Inspired by recently developed Precomputed Radiance Transfer (PRT) techniques, we approximate both the multiple scattering diffuse reflectance function and the single scattering exponential attenuation function in the analytic model using basis functions, so that re-computing the outgoing radiance at each vertex as parameters change reduces to simple dot products. In addition, using a non-uniform piecewise polynomial basis, we are able to achieve smaller approximation error than using bases adopted in previous PRT-based works, such as spherical harmonics and wavelets. Using hardware acceleration, we demonstrate that our system generates images comparable to [JMLH01] at real-time frame-rates.
Video: Download video here (17.3MB).
Topology Repair of Solid Models Using Skeletons
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2007, Vol. 13, No. 4, 675-685.


Qian-Yi Zhou, Tao Ju and Shi-Min Hu
We present a method for repairing topological errors on solid models in the form of small surface handles, which often arise from surface reconstruction algorithms. We utilize a skeleton representation that offers a new mechanism for identifying and measuring handles. Our method presents two unique advantages over previous approaches. First, handle removal is guaranteed not to introduce invalid geometry or additional handles. Second, by using an adaptive grid structure, our method is capable of processing huge models efficiently at high resolutions.
Slides: Download slides here (24.8MB). A poster for this paper is also available, download poster here (7.5MB).
Software: A software TopoMender based on this paper is now available, please refer to webpage: http://graphics.usc.edu/~qianyizh/software.html
Robust Feature Classification and Editing
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2007, Vol. 13, No.1, January/Feburary, 34-45.
Yu-Kun Lai, Qian-Yi Zhou, Shi-Min Hu, Johannes Wallner and Helmut Pottmann
Sharp edges, ridges, valleys and prongs are critical for the appearance and an accurate representation of a 3D model. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that deals with the global shape of features in a robust way. Based on a remeshing algorithm which delivers an isotropic mesh in a feature sensitive metric, features are recognized on multiple scales via integral invariants of local neighborhoods. Morphological and smoothing operations are then used for feature region extraction and classification into basic types such as ridges, valleys and prongs. The resulting representation of feature regions is further used for feature-specific editing operations.
Other publications in 2007
1. Jean-Baptiste Debard(Yang Fei), Romain Balp (Bai Luomin) , Raphaelle Chaine, Dynamic Delaunay tetrahedralisation of a deforming surface,
The Visual Computers, 2007, Vol. 23, No. 12, 975 - 986


2. Yong-Jin Liu, Qian-Yi Zhou and Shi-Min Hu, Handling Degenerate Cases in Exact Geodesic Computation on Triangle Meshes,
The Visual Computers, 2007, Vol. 23, No. 9-11, 661-668.

3. Yong-Jin Liu, Kai Tang, Ajay Joneja, Modeling dynamic developable meshes by the Hamilton principle,
Computer-Aided Design, 2007, Vol. 39, No. 9, 719-731.

4. Han-Bing Yan, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R Martin, 3D morphing using strain field interpolation,
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2007, Vol. 22, No. 1, 147-155.

2006
Geometry and Convergence Analysis of Algorithms for Registration of 3D Shapes
Geometry and convergence analysis of algorithms for registration of 3D shapes, International Journal of Computer Vision, 2006, Vol. 67, No. 3, 277-296.
Helmut Pottmann, Qi-Xing Huang, Yong-Liang Yang and Shi-Min Hu
The computation of a rigid body transformation which optimally aligns a set of
measurement points with a surface and related registration problems are studied
from the viewpoint of geometry and optimization.We provide a convergence analysis
for widely used registration algorithms such as ICP, using either closest points (Besl
and McKay [2]) or tangent planes at closest points (Chen and Medioni [4]), and for
a recently developed approach based on quadratic approximants of the squared
distance function [24]. ICP based on closest points exhibits local linear convergence
only. Its counterpart which minimizes squared distances to the tangent planes at
closest points is a Gauss-Newton iteration; it achieves local quadratic convergence
for a zero residual problem and { if enhanced by regularization and step size control
{ comes close to quadratic convergence in many realistic scenarios. Quadratically
convergent algorithms are based on the approach in [24]. The theoretical results are
supported by a number of experiments; there, we also compare the algorithms with
respect to global convergence behavior, stability and running time.
Robust Principal Curvatures on Multiple Scales
Proceedings of 4th Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing (2006). Eurographics Association, 223-226.
Yong-Liang Yang, Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu and Helmut Pottmann
Geometry processing algorithms often require the robust extraction
of curvature information. We
propose to achieve this with principal component analysis (PCA) of
local neighborhoods, defined via spherical kernels centered on the
given surface $\Phi$. Intersection of a kernel ball $B_r$ or its
boundary sphere $S_r$ with the volume bounded by $\Phi$ leads to
the so-called ball and sphere neighborhoods. Information obtained
by PCA of these neighborhoods turns out to be more robust than
PCA of the patch neighborhood $B_r \cap \Phi$ previously used.
The relation of the quantities computed by PCA with the principal
curvatures of $\Phi$ is revealed by an asymptotic analysis as the
kernel radius $r$ tends to zero. This also allows us to define principal
curvatures ''at scale $r$'' in a way which is consistent with the classical
setting. The advantages of the new approach are discussed in a comparison
with results obtained by normal cycles and local fitting; whereas the former
method somewhat lacks in robustness, the latter does not achieve a consistent
behavior at features on coarse scales. As to applications,
we address computing principal curves and feature extraction
on multiple scales.
Other publications in 2006
1. Qi-Xing Huang, Simon Flory, Natasha Gelfand, Michael Hofer and Helmut Pottmann, Reassembling Fractured Objects by Geometric Matching,
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 25, No. 3, 569-578, ACM SIGGRAPH 2006

2. Yang Liu, Helmut Pottmann, Johannes Wallner, Yong-Liang Yang and Wenping Wang, Geometric Modeling with Conical Meshes and Developable Surfaces,
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 25 , No. 3, 681-689, ACM SIGGRAPH 2006

3. Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu and Helmut Pottmann, Surface Fitting Based on a Feature Sensitive Parameterization,
Computer-Aided Design, 2006, Vol. 38, No. 7, 800--807.

4. Li Jin, Donguk Kim, Lisen Mu, Deok-Soo Kim and Shi-Min Hu, A Sweepline Algorithm for Euclidean Voronoi Diagram of Circles,
Computer-Aided Design, 2006, Vol. 38, No. 3, 260-278.
5. Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R. Martin, Surface Mosaics,
The Visual Computer, 2006, Vol. 22, No. 9-10, 604-611 (Pacific Graphics 2006).

6. Jiaping Wang, Kun Xu, Kun Zhou, Stephen Lin, Shi-Min Hu and Baining Guo,
Spherical Harmonics Scaling,
The Visual Computer, 2006, Vol. 22, No. 9-10, 713-720 (Pacific Graphics 2006).

7. Yu-Kun Lai, Qian-Yi Zhou, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R. Martin, Feature Sensitive Mesh Segmentation,
ACM Symp. Solid and Physical Modeling, 7-16, 2006.

8. Xiao-Hua Cai, Yun-Tao Jia, Xi Wang, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R. Martin, Rendering Soft Shadows using Multilayered Shadow Fins,
Computer Graphics Forum, 2006, Vol.25, No.1, 1-14.

2005
Video Completion using Tracking and Fragment Merging
The Visual Computer, 2005, Vol. 21, No. 8-10, 601-601. (Pacific Graphics 2005) 
Yun-Tao Jia, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R. Martin
Video completion is the problem of automatically filling space-time holes in video sequences left by the removal of unwanted
objects in a scene. We solve it using texture synthesis, filling a hole inwards using three steps iteratively:
we select the most promising target pixel at the edge of the hole, we find
the source fragment most similar to the known part of the target neighborhood, and we merge source
and target fragments to complete the target neighborhood, reducing the
size of the hole. Earlier methods were slow, due to searching the whole video data for
source fragments or completing holes pixel by pixel; they also produced
blurred results due to sampling and smoothing. For speed, we track
moving objects, allowing us to use a much smaller search space when
seeking source fragments; we also complete holes fragment by fragment
instead of pixelwise. Fine details are maintained by use of a graph cut
algorithm when merging source and target fragments. Further techniques
ensure temporal consistency of hole filling over successive frames.
Examples demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Other publications in 2005
1. Xu-Ping Zhu, Shi-Min Hu, Chiew-Lan Tai, and Ralph R Martin, A Marching Method for Computing Intersection Curves of Two Subdivision Solids, in Mathematics of Srufaces XI, Eds. R. R. Martin, H. Bez, M. A. Sabin, 458-471, 2005.

2. Johannes Wallner, Hans-Peter Schrocker, Shi-min Hu, Tolerance in geometric constraints solving, Reliable Computing, 2005, Vol. 11, No. 3, 235-251.

3. Yu-Kun Lai, Shi-Min Hu, Xianfeng Gu, Ralph R. Martin, Geometric texture synthesis and transfer via geometry images,
ACM Solid and Physical Modeling, MIT, USA, June 13-15, 2005, 15-26.

4. Shi-min Hu, Johannes Wallner, A second order algorithm for orthogonal projection onto curves and surfaces, Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2004, Vol.22, No. 3, 251-260.

5. Qi-Xing Huang, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph R. Martin, Fast degree elevation and knot insertion for B-spline curves, Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2005, Vol 22, No. 2, 183-197.

2004
Generalized Displacement Maps
Proceedings of Eurographics Symposium on Rendering, 2004
Xi Wang, Xin Tong, Stephen Lin, Shimin Hu, Baining Guo and Heung-Yeung Shum
In this paper, we introduce a real-time algorithm to render the rich visual effects of general non-height-field geometric
details, known as mesostructure. Our method is based on a five-dimensional generalized displacement map
(GDM) that represents the distance of solid mesostructure along any ray cast from any point within a volumetric
sample. With this GDM information, we propose a technique that computes mesostructure visibility jointly in object
space and texture space which enables both control of texture distortion and efficient computation of texture
coordinates and shadowing. GDM can be rendered with either local or global illumination as a per-pixel process
in graphics hardware to achieve real-time rendering of general mesostructure.
Other publications in 2004
1. Han-Bing Yan, Shi-Min Hu, Ralph R. Martin, Morphing Based on Strain Field Interpolation, Journal of Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds (CAVW), 2004, Vol.15, No.3-4, 443-452.

2. Shi-min Hu, Johannes Wallner, Error Propagation through Geometric Transformations, Journal for Geometry and Graphics, 2004, Vol.8, No.2, 171-183.

3. Shi-Min Hu, Chen-feng Li, Hui Zhang, Actual Morphing: A phsical-based approach for blending two 2D/3D shapes, ACM Symposium on Solid Modeling and Applications, Genova, Italy, June 9-11, 2004.

2003
View-Dependent Displacement Mapping
ACM Transactions on Graphics, Vol. 22, No. 3. 334-339, ACM SIGGRAPH 2003 
Lifeng Wang, Xi Wang, Xin Tong, Steve Lin, Shimin Hu, Baining Guo and Heung-Yeung Shum
Significant visual effects arise from surface mesostructure, such as
fine-scale shadowing, occlusion and silhouettes. To efficiently render
its detailed appearance, we introduce a technique called viewdependent
displacement mapping (VDM) that models surface displacements
along the viewing direction. Unlike traditional displacement
mapping, VDM allows for efficient rendering of selfshadows,
occlusions and silhouettes without increasing the complexity
of the underlying surface mesh. VDM is based on per-pixel
processing, and with hardware acceleration it can render mesostructure
with rich visual appearance in real time.
Other publications in 2003
1. Xu-Ping Zhu, Shi-Min Hu and Martin Ralph, Skeleton-Based Seam Computation for Triangulated Surface Parameterization, In Proceedings of Mathematics in Surfaces X, Sept 2003, Leeds, UK; Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2003.
[PS]
2. Chiew-Lan Tai, Hu Shi-Min and Qixing Huang, Approximate merging of B-Spline curves via knot adjustment and constrained optimization, Computer Aided Design, 2003, Vol. 35, No. 10, 893 - 899.

3. Xi Wang, Lifeng Wang, Ligang Liu, Shi-Min Hu and Baining Guo, Interactive Modeling of Tree Bark,
In: Proceedings of Pacific Graphics 2003, IEEE CS Press, Oct 8-10, 2003

4. Tao Wang, Yong Rui, Shi-Min Hu and Jia-guang Sun, Adaptive tree similarity learning for image retrieval, Multimedia Systems, 2003, Vol. 9, 131-143.

2002
1. Shi-Min Hu, Chiew-Lan Tai, Song-Hai Zhang, An Extension algorithm for B-spline curves by curve unclamping, Computer Aided Design, 2002, Vol. 34, No. 5, 415-4191.

2. Yan-Tao Li, Shi-Min Hu and Jia-Guang Sun, A Constructive Approach to Solving 3-D Geometric Constraint Systems Using Dependence Analysis, Computer Aided Design, 2002, Vol. 34, No. 2, 97-108.

3. Liu Shi-Xia, Hu Shi-Min, Sun Jiaguang, Two accelerating techniques for 3D reconstruction, Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 17(3), 362-368, 2002.

2001
1. Shi-Xia Liu, Shi-Min Hu, Yu-Jian Chen, Jia-Guang Sun, Reconstruction of curved solids from engineering drawings, Computer Aided Design, 2001, Vol. 33, No. 14, 1059-1072.

2. Shi-Min Hu, Youfu Li, Tao JU, Xiang Zhu, Modifying the shape of NURBS surfaces with geometric constraints, Computer Aided Design, 2001, Vol. 33, No. 12, 903-912.

3. Shi-Min, Hu Conversion between triangular and rectangular Bezier patches, Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2001, Vol.18, No. 7, 667-671. (In Special issue of memory of P. Bezier).

4. Shi-Min Hu, Hui Zhang, Chiew-Lan Tai, Jia-Guang Sun, Direct Manipulation of FFD: Efficient Explicit Solutions and Decomposible Multiple Point Constraints, The Visual Computers, 2001, Vol. 17, No. 6, 370-379.

5. Jun-Hai Yong, Shi-Min Hu, Jia-Guang Sun, Degree reduction of B-spline curves, Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2001, Vol. 13, NO. 2, 2001, 117-127.

6. Shi-Min Hu, Ruofeng Tong, Tao JU, Jia-Guang Sun, Approximate merging of a pair of Bezier curves, Computer Aided Design, Vol 33, No. 2, 125-136, 2001.

7. Jun-Hai Yong, Shi-Min Hu, JIa-Guang Sun, CIM Algorithm for Approximating Three Dimensional Polygonal Curves, Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 16(6), 489-497,2001.

8. Tao Wang, Yong Rui and Shi-Min Hu, Optimal Adaptive Learning for Image Retrieval, Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2001), I-1140 to 1147, Kauai, Hawaii, December 11-13, 2001.

9. Yan-Tao Li, Shi-Min Hu, Jia-Guang Sun, On the numerical redundancies of geometric constraint systems, Proceedings of Pacific Graphics 2001, 118-123, IEEE Computre Society Press, 2001, Tokyo.

10. Jian-Hua Wu, Shi-Min Hu, Chiew-Lan Tai and Jia-Guang Sun, An effective feature-preserving mesh simplification scheme based on face constriction, Proceedings of Pacific Graphics 2001, 12-21, IEEE Computre Society Press, 2001, Tokyo.















































































































































































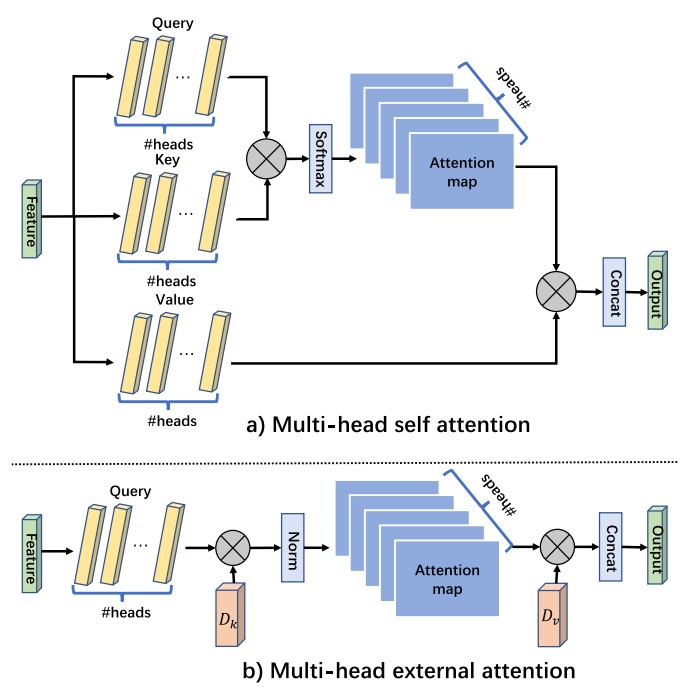























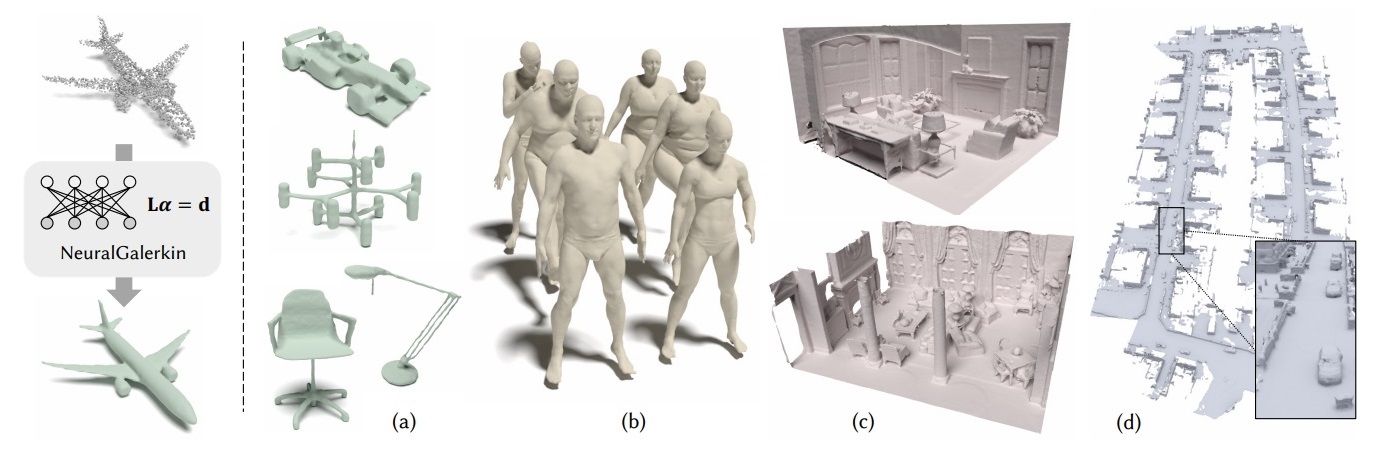



































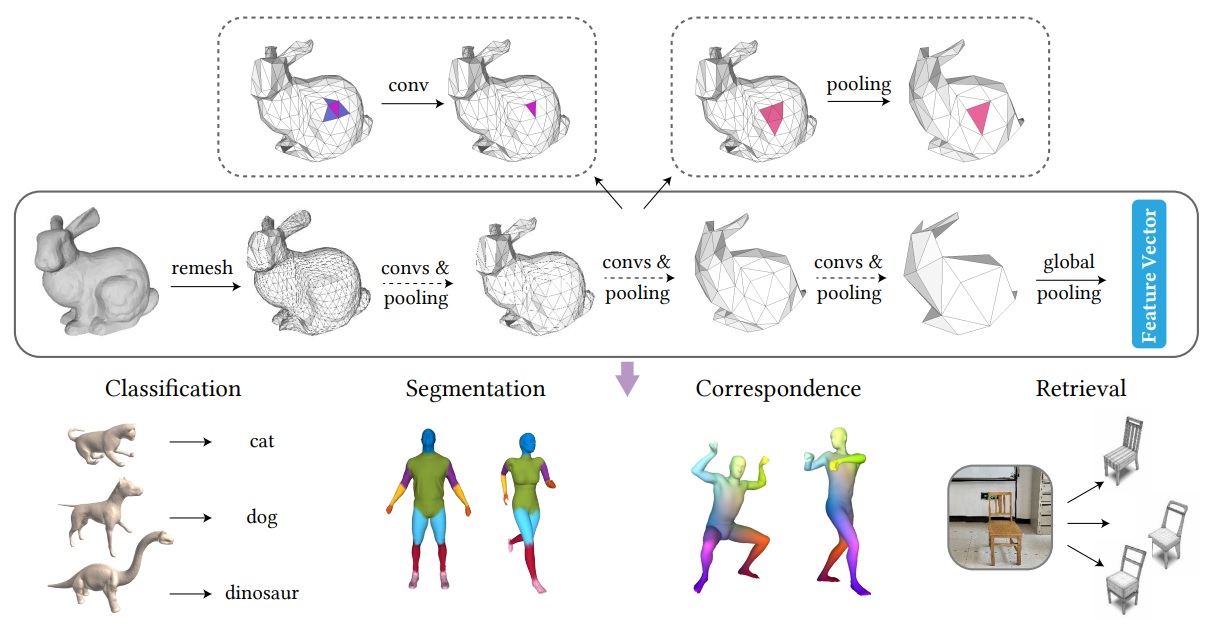











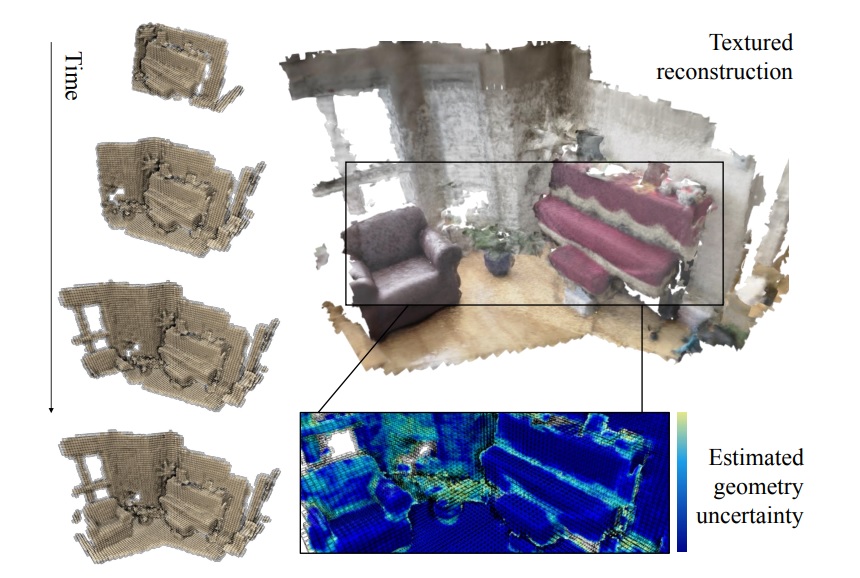





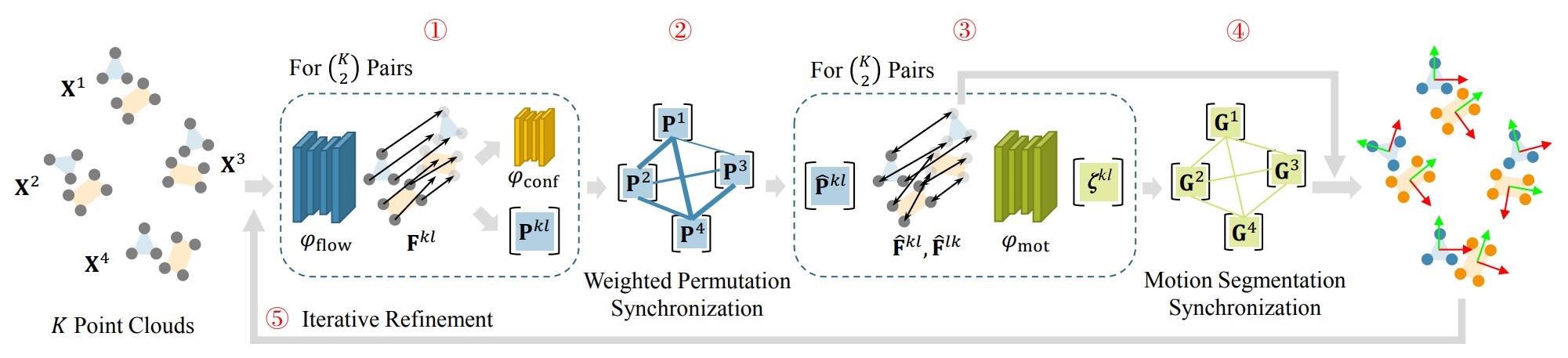





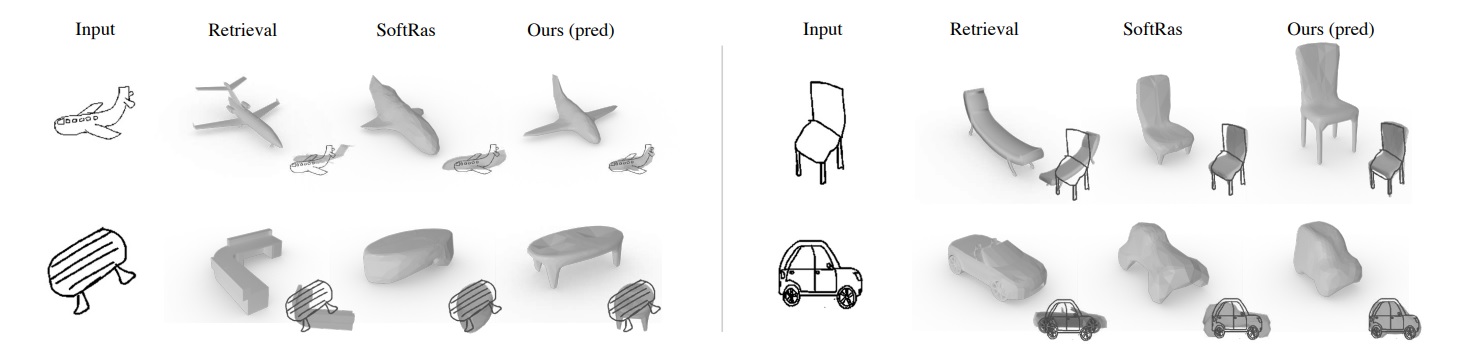











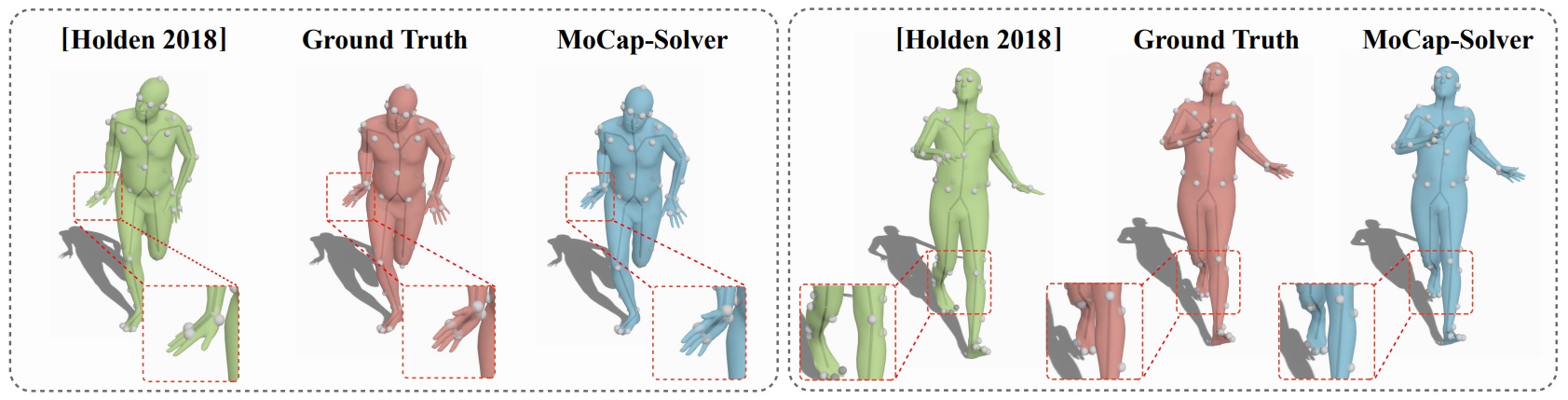





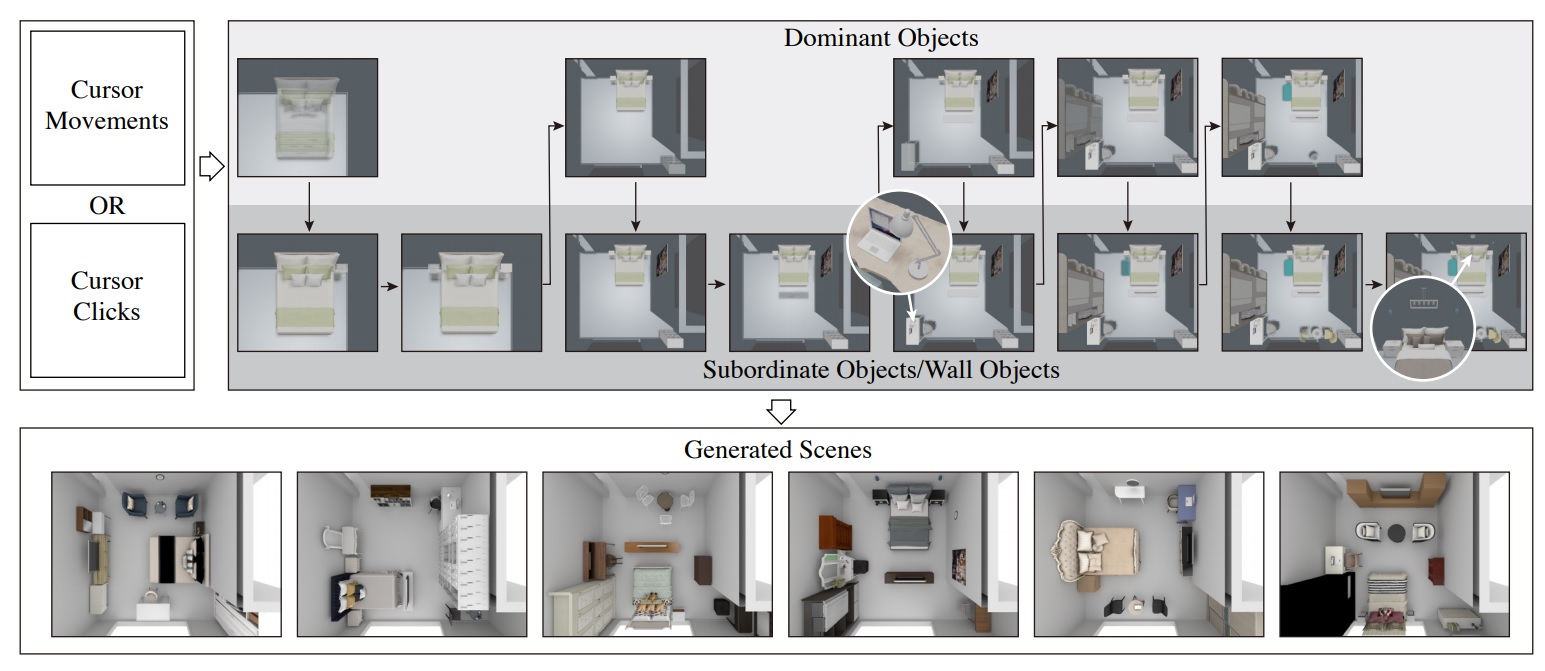



 (click for project webpage in Github)
(click for project webpage in Github)


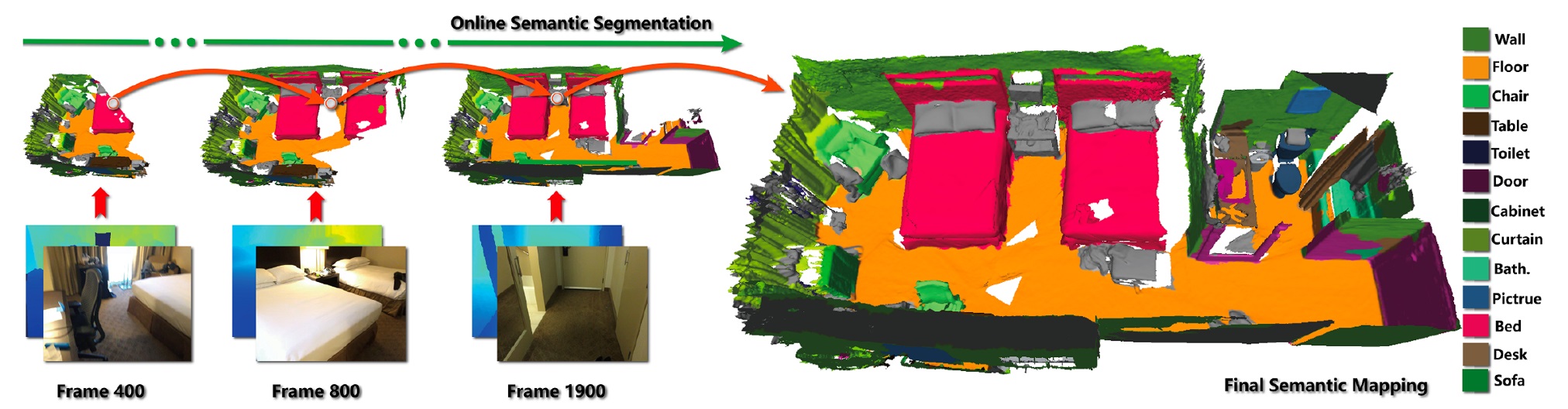





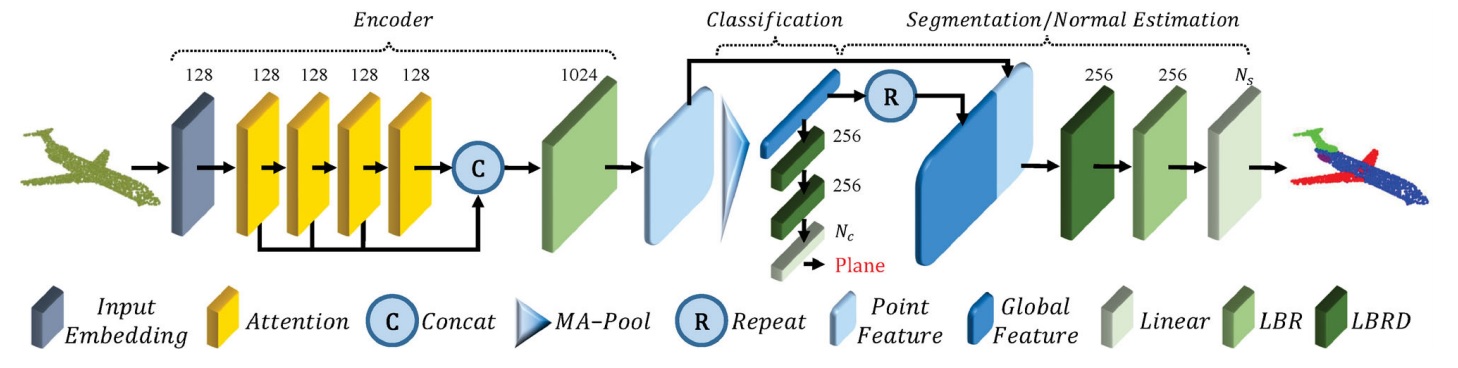





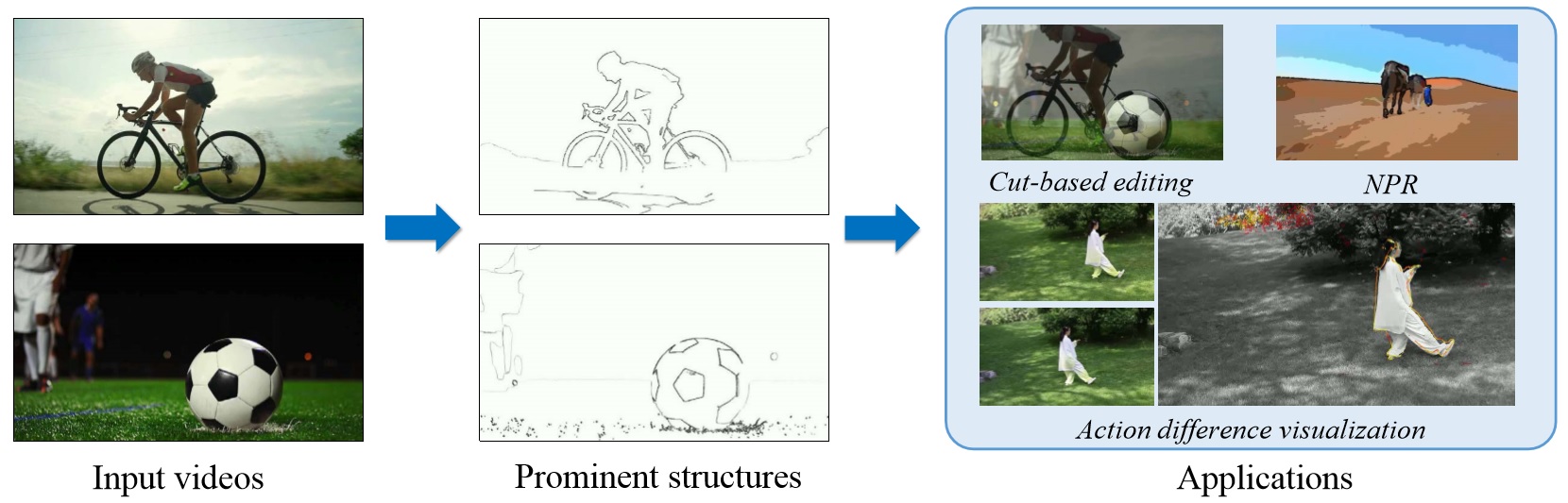





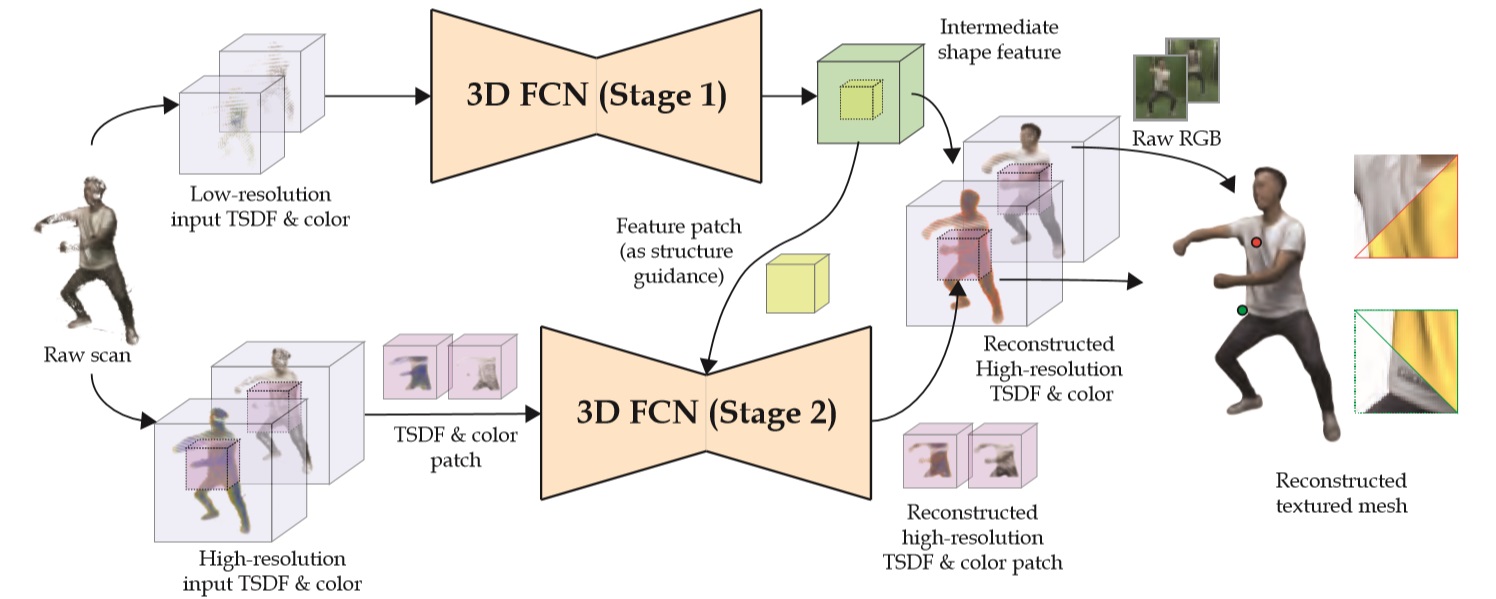
















 (click for project webpage in Github)
(click for project webpage in Github)


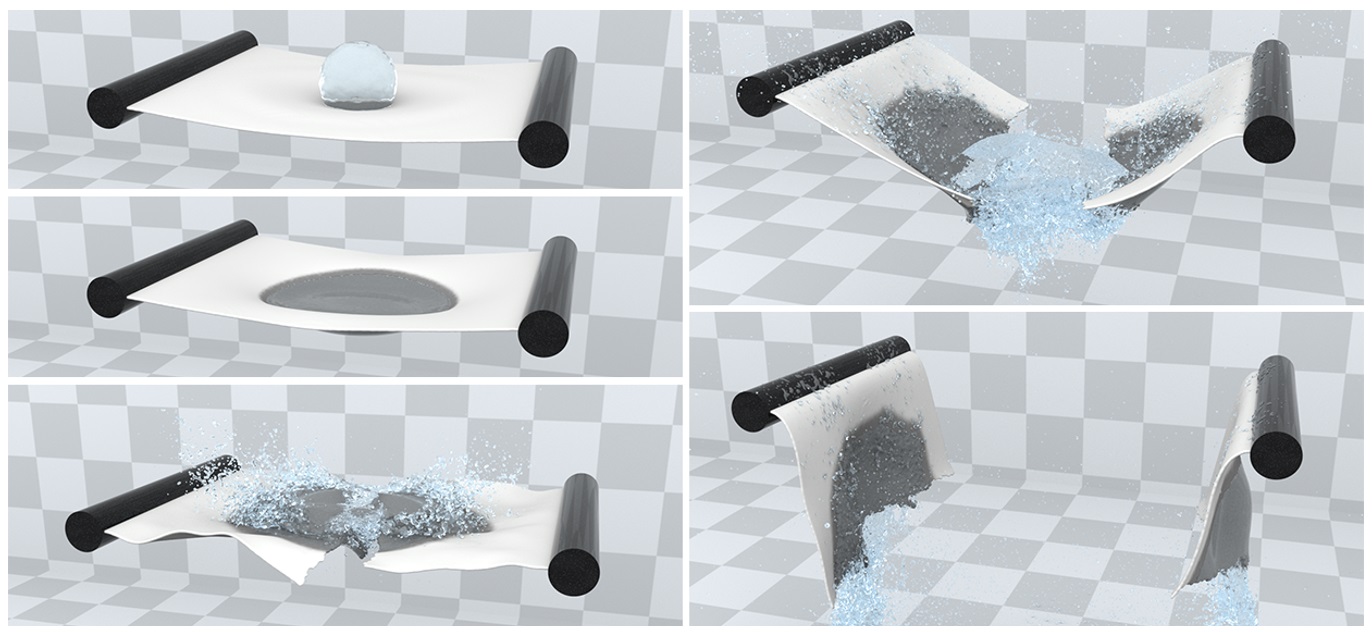











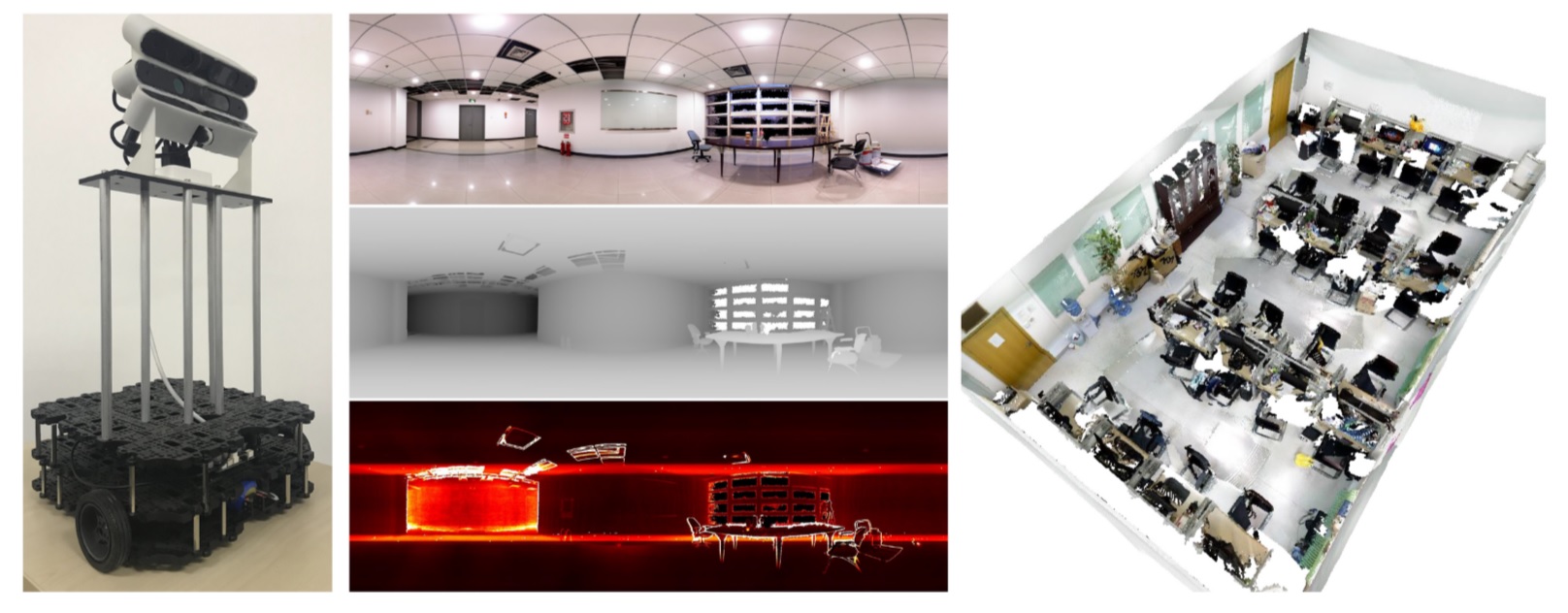





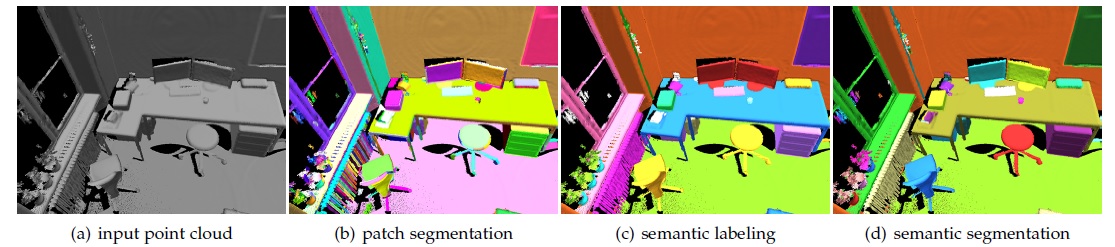





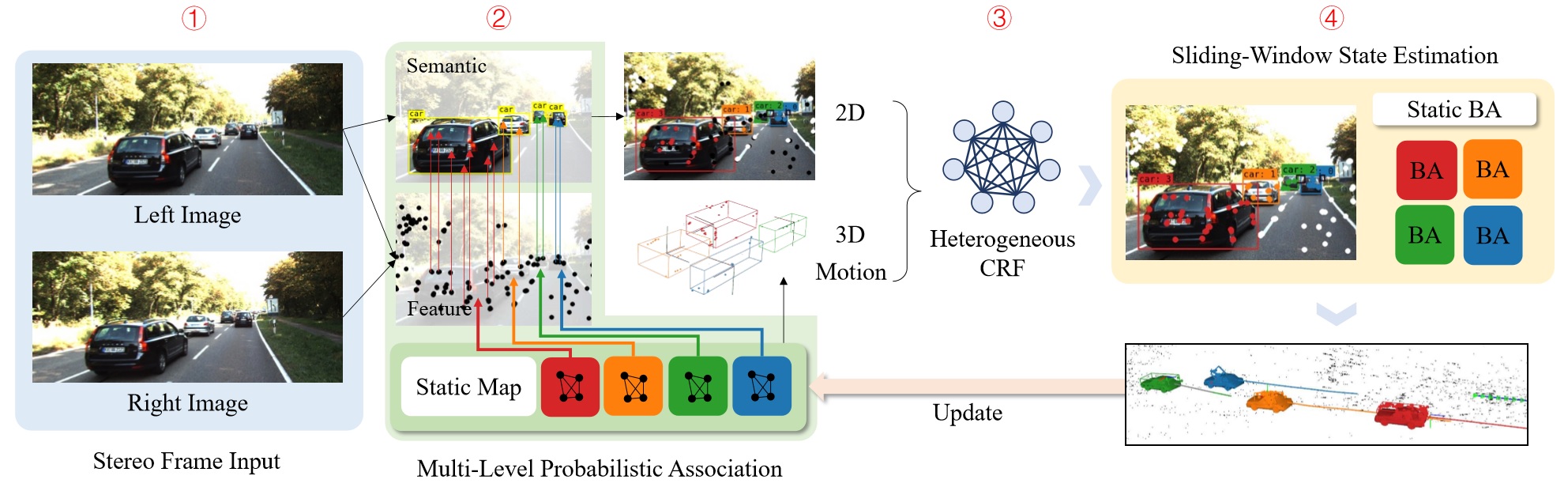





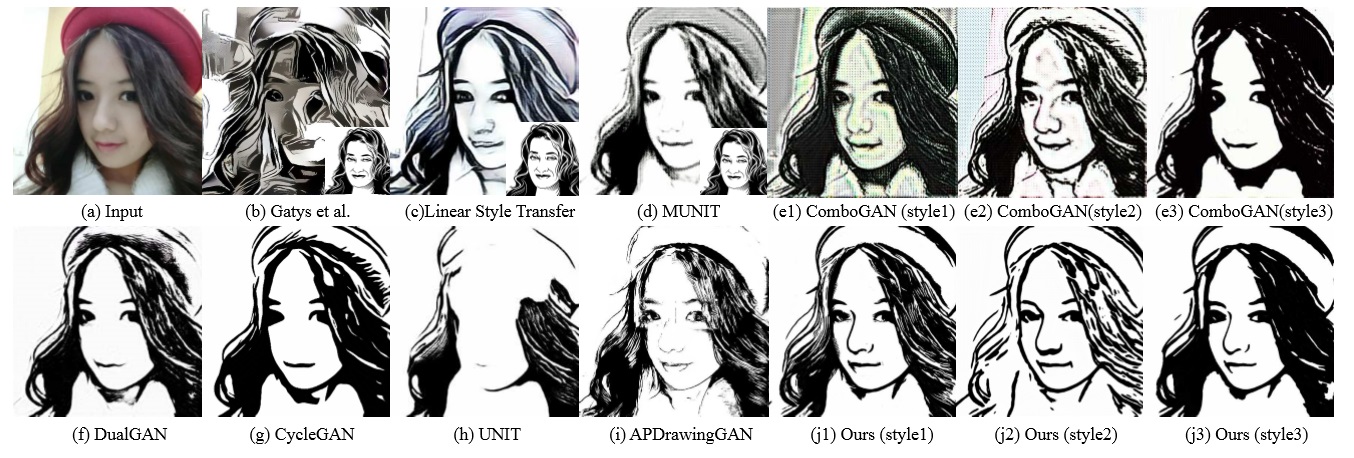










































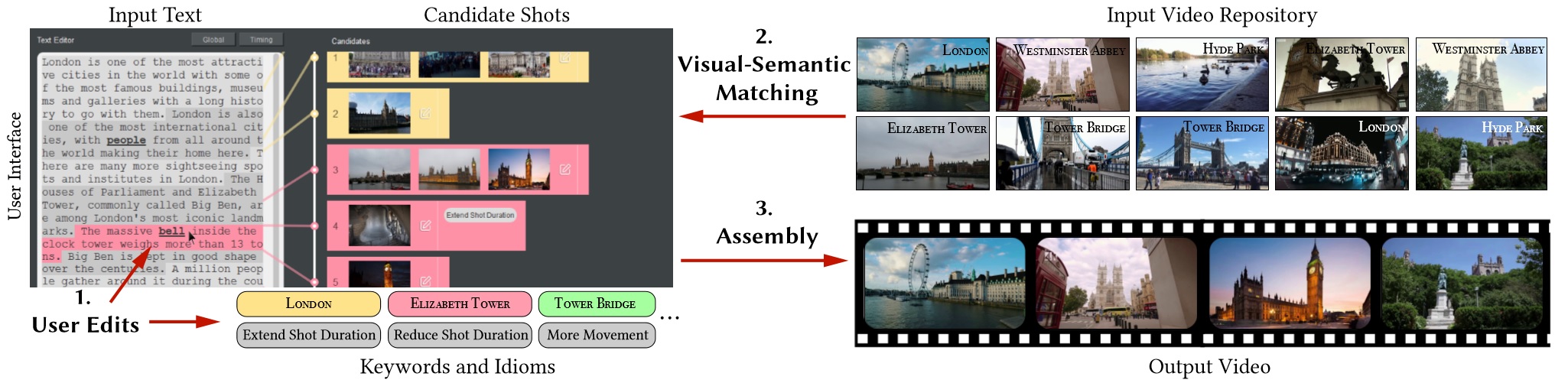



 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)


























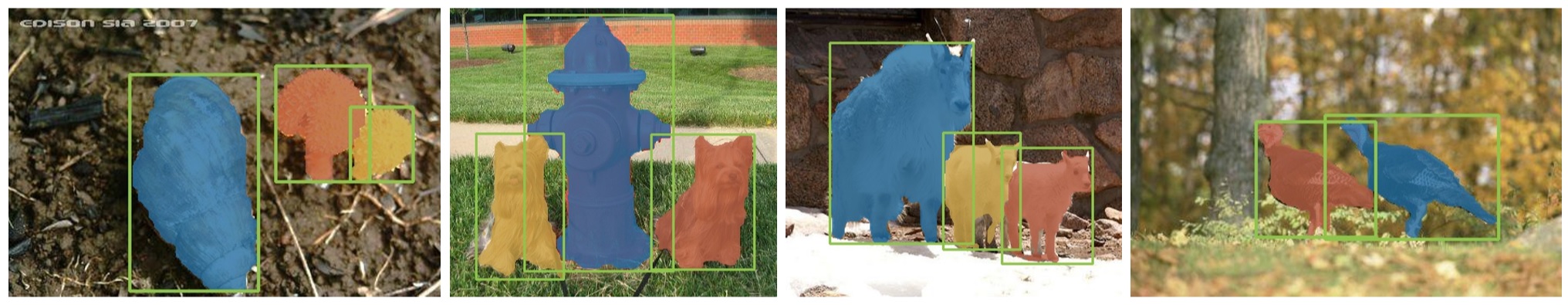








 supplemental:
supplemental:






























 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)











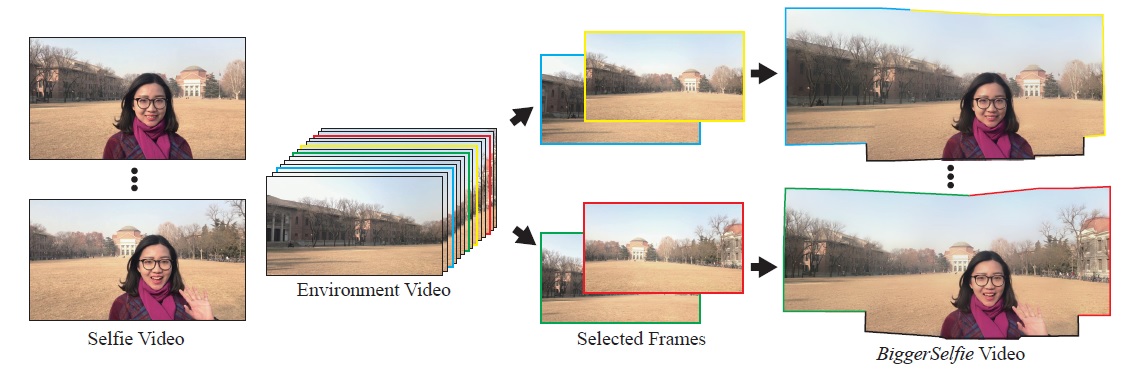





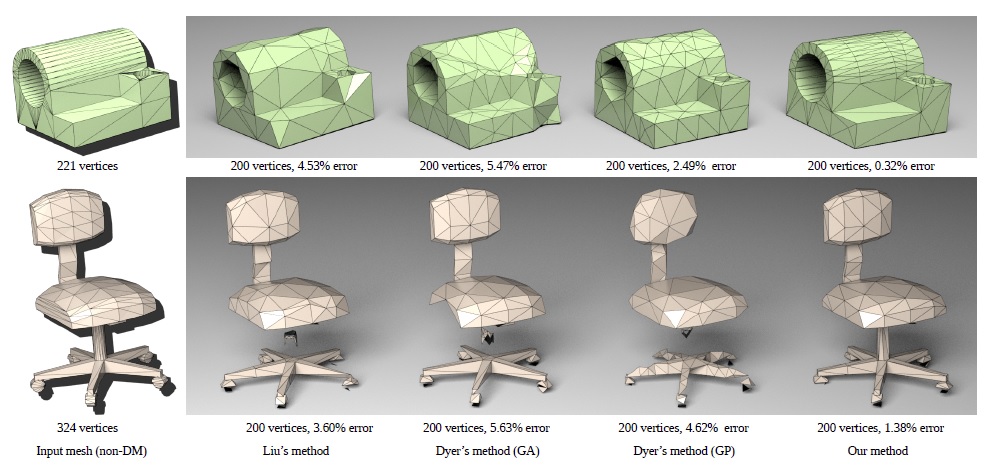




























 demo:
demo:  More examples:
More examples: 



























 demo:
demo:  More examples:
More examples: 










 demo:
demo: 





 demo:
demo: 











 demo:
demo: 



































































































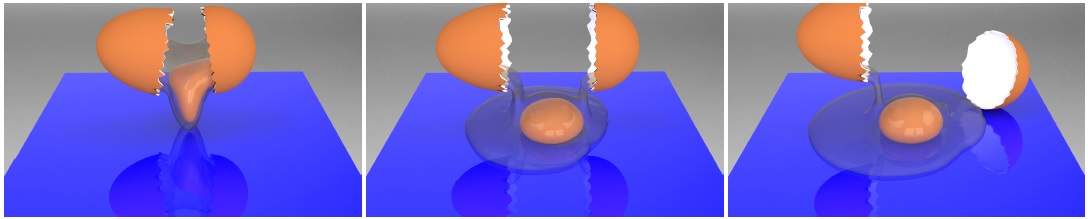





















































































































































































































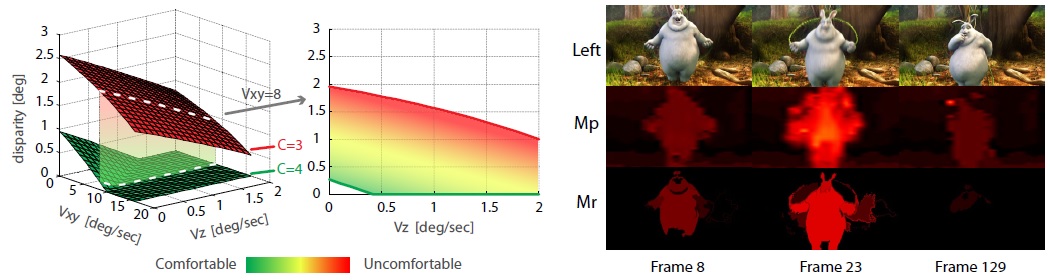




















 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage) 



 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage)



 (click for project webpage)
(click for project webpage) 
















































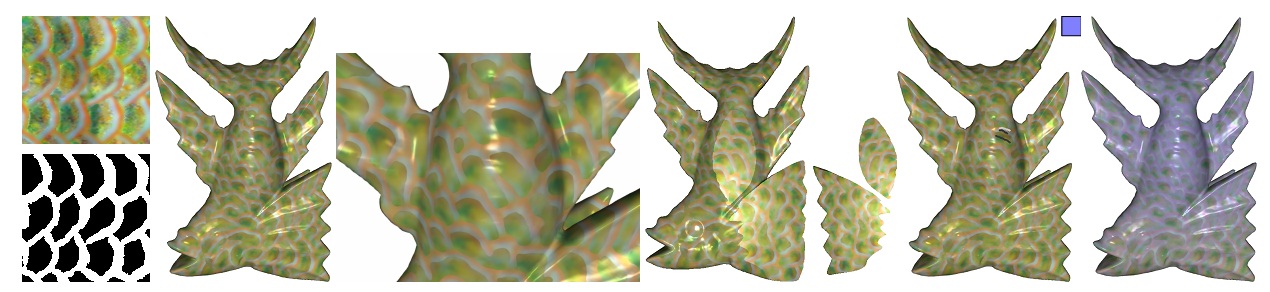





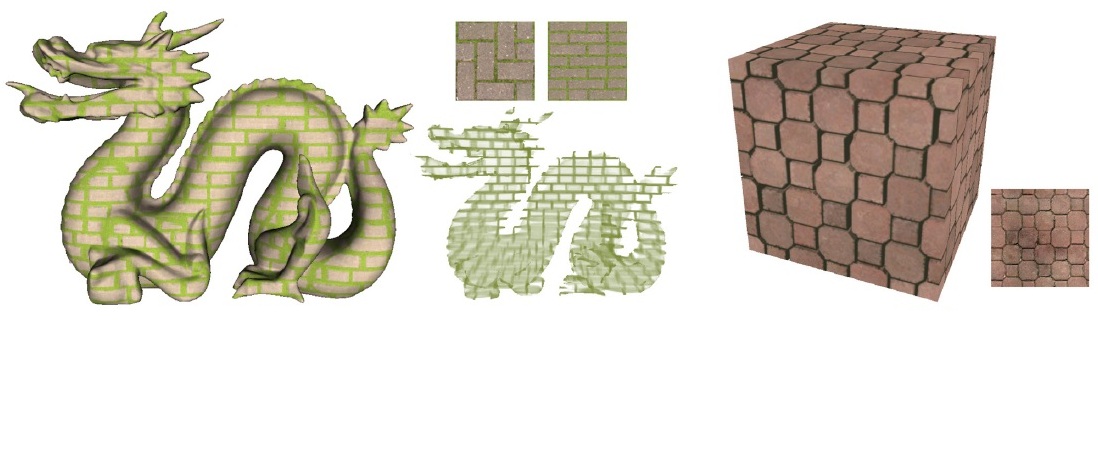





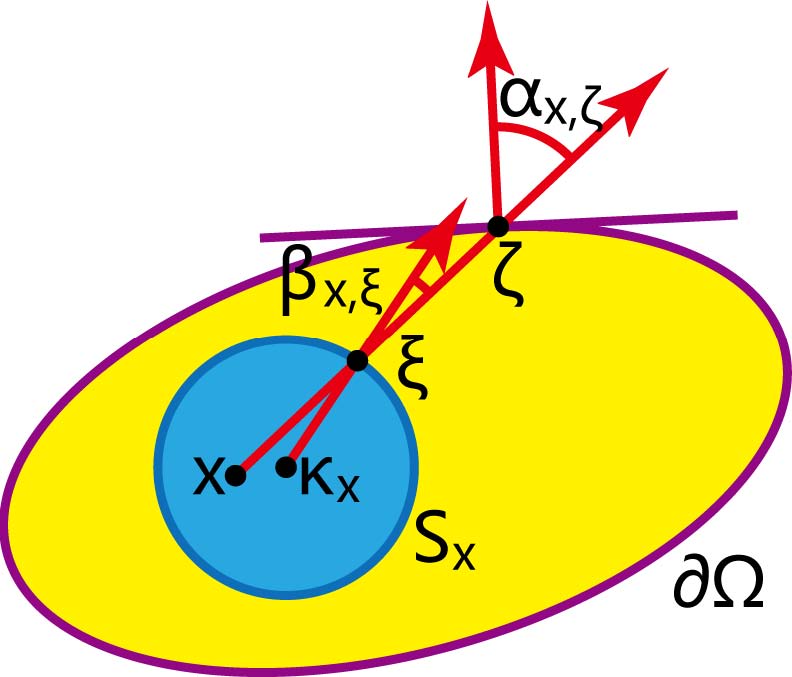





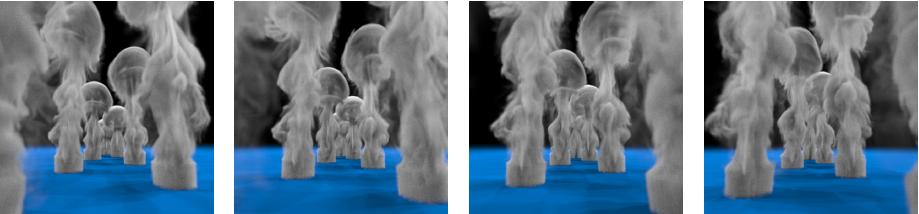








 (click for project webpage, data set is available)
(click for project webpage, data set is available)