语义分割是计算机视觉的一项重要任务,本教程使用Jittor框架实现了DeepLabV3+语义分割模型。
DeepLabV3+论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1802.02611.pdf
完整代码:https://github.com/Jittor/deeplab-jittor
1. 数据集
1.1 数据准备
VOC2012数据集是目标检测、语义分割等任务常用的数据集之一,本教程使用VOC数据集的2012 trainaug (train + sbd set)作为训练集,2012 val set作为测试集。
VOC数据集中的物体共包括20个前景类别:'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow', 'diningtable', 'dog', 'horse', 'motorbike', 'person', 'pottedplant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tvmonitor' 和背景类别

最终数据集的文件组织如下。
# 文件组织
根目录
|----voc_aug
| |----datalist
| | |----train.txt
| | |----val.txt
| |----images
| |----annotations
1.2 数据加载
使用jittor.dataset.dataset的基类Dataset可以构造自己的数据集,需要实现__init__、__getitem__、函数。
__init__: 定义数据路径,这里的data_root需设置为之前您设定的voc_aug,split为train val test之一,表示选择训练集、验证集还是测试集。同时需要调用self.set_attrs来指定数据集加载所需的参数batch_size,total_len、shuffle。__getitem__: 返回单个item的数据。
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from jittor.dataset.dataset import Dataset, dataset_root
import jittor as jt
import os
import os.path as osp
from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageFilter
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as sio
import random
def fetch(image_path, label_path):
with open(image_path, 'rb') as fp:
image = Image.open(fp).convert('RGB')
with open(label_path, 'rb') as fp:
label = Image.open(fp).convert('P')
return image, label
def scale(image, label):
SCALES = (0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, 2.0)
ratio = np.random.choice(SCALES)
w,h = image.size
nw = (int)(w*ratio)
nh = (int)(h*ratio)
image = image.resize((nw, nh), Image.BILINEAR)
label = label.resize((nw, nh), Image.NEAREST)
return image, label
def pad(image, label):
w,h = image.size
crop_size = 513
pad_h = max(crop_size - h, 0)
pad_w = max(crop_size - w, 0)
image = ImageOps.expand(image, border=(0, 0, pad_w, pad_h), fill=0)
label = ImageOps.expand(label, border=(0, 0, pad_w, pad_h), fill=255)
return image, label
def crop(image, label):
w, h = image.size
crop_size = 513
x1 = random.randint(0, w - crop_size)
y1 = random.randint(0, h - crop_size)
image = image.crop((x1, y1, x1 + crop_size, y1 + crop_size))
label = label.crop((x1, y1, x1 + crop_size, y1 + crop_size))
return image, label
def normalize(image, label):
mean = (0.485, 0.456, 0.40)
std = (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)
image = np.array(image).astype(np.float32)
label = np.array(label).astype(np.float32)
image /= 255.0
image -= mean
image /= std
return image, label
def flip(image, label):
if random.random() < 0.5:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
label = label.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
return image, label
class BaseDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_root='/voc/', split='train', batch_size=1, shuffle=False):
super().__init__()
''' total_len , batch_size, shuffle must be set '''
self.data_root = data_root
self.split = split
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.image_root = os.path.join(data_root, 'images')
self.label_root = os.path.join(data_root, 'annotations')
self.data_list_path = os.path.join(self.data_root,'datalist/' + self.split + '.txt')
self.image_path = []
self.label_path = []
with open(self.data_list_path, "r") as f:
lines = f.read().splitlines()
for idx, line in enumerate(lines):
_img_path = os.path.join(self.image_root, line + '.jpg')
_label_path = os.path.join(self.label_root, line + '.png')
assert os.path.isfile(_img_path)
assert os.path.isfile(_label_path)
self.image_path.append(_img_path)
self.label_path.append(_label_path)
self.total_len = len(self.image_path)
# set_attrs must be called to set batch size total len and shuffle like __len__ function in pytorch
self.set_attrs(batch_size = self.batch_size, total_len = self.total_len, shuffle = self.shuffle) # bs , total_len, shuffle
def __getitem__(self, image_id):
return NotImplementedError
class TrainDataset(BaseDataset):
def __init__(self, data_root='/voc/', split='train', batch_size=1, shuffle=False):
super(TrainDataset, self).__init__(data_root, split, batch_size, shuffle)
def __getitem__(self, image_id):
image_path = self.image_path[image_id]
label_path = self.label_path[image_id]
image, label = fetch(image_path, label_path)
image, label = scale(image, label)
image, label = pad(image, label)
image, label = crop(image, label)
image, label = flip(image, label)
image, label = normalize(image, label)
image = np.array(image).astype(np.float).transpose(2, 0, 1)
image = jt.array(image)
label = jt.array(np.array(label).astype(np.int))
return image, label
class ValDataset(BaseDataset):
def __init__(self, data_root='/voc/', split='train', batch_size=1, shuffle=False):
super(ValDataset, self).__init__(data_root, split, batch_size, shuffle)
def __getitem__(self, image_id):
image_path = self.image_path[image_id]
label_path = self.label_path[image_id]
image, label = fetch(image_path, label_path)
image, label = normalize(image, label)
image = np.array(image).astype(np.float).transpose(2, 0, 1)
image = jt.array(image)
label = jt.array(np.array(label).astype(np.int))
return image, label
2. 模型定义
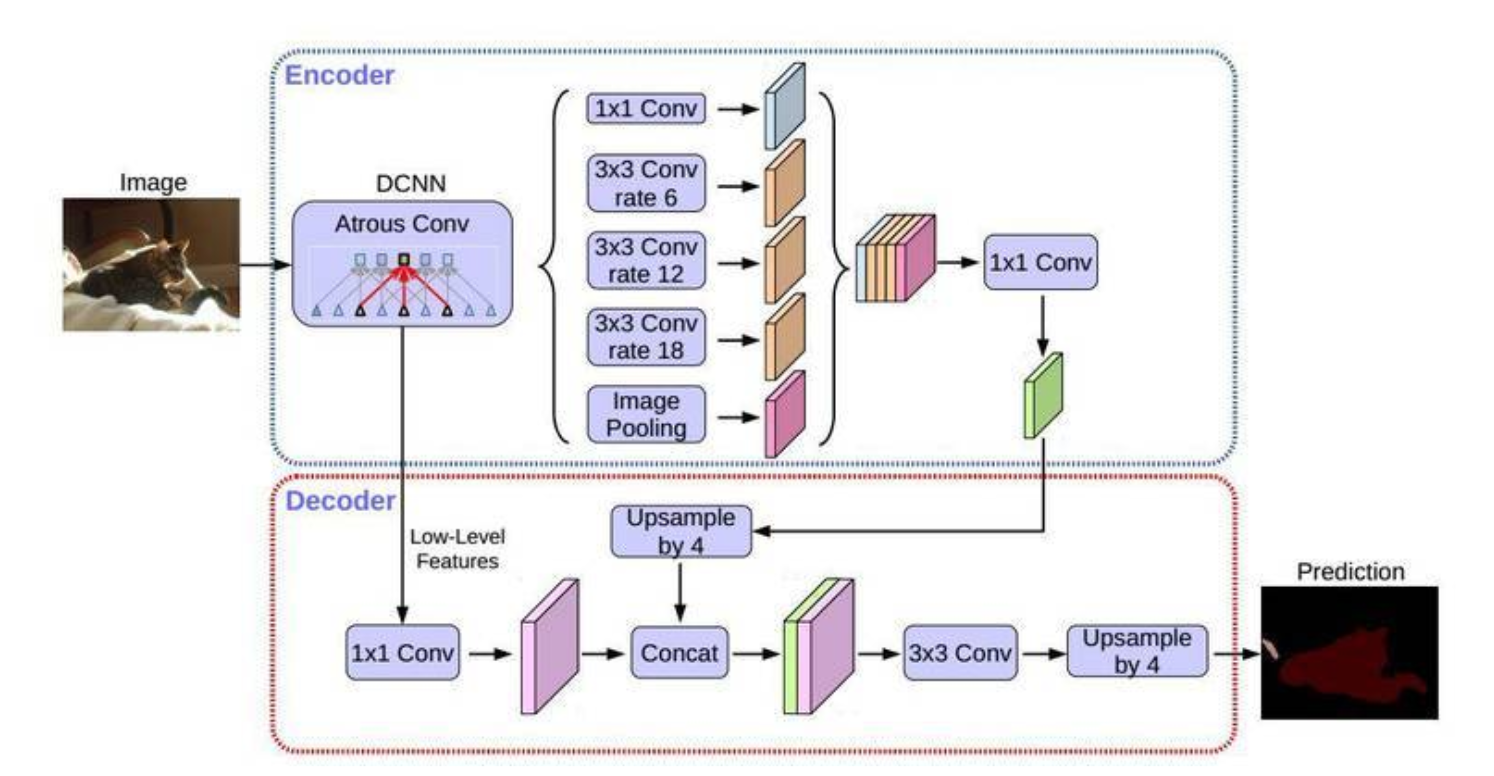
上图为DeepLabV3+论文给出的网络架构图。本教程采用ResNe为backbone。输入图像尺寸为513*513。
整个网络可以分成 backbone aspp decoder 三个部分。
2.1
backbonb这里使用最常见的ResNet作为backbone并且在ResNet的最后两次使用空洞卷积来扩大感受野,其完整定义如下:
import jittor as jt
from jittor import nn
from jittor import Module
from jittor import init
from jittor.contrib import concat, argmax_pool
import time
class Bottleneck(Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, dilation=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm(planes)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
dilation=dilation, padding=dilation, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm(planes)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm(planes * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.dilation = dilation
def execute(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers, output_stride):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 64
blocks = [1, 2, 4]
if output_stride == 16:
strides = [1, 2, 2, 1]
dilations = [1, 1, 1, 2]
elif output_stride == 8:
strides = [1, 2, 1, 1]
dilations = [1, 1, 2, 4]
else:
raise NotImplementedError
# Modules
self.conv1 = nn.Conv(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
# self.maxpool = nn.Pool(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0], stride=strides[0], dilation=dilations[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=strides[1], dilation=dilations[1])
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=strides[2], dilation=dilations[2])
self.layer4 = self._make_MG_unit(block, 512, blocks=blocks, stride=strides[3], dilation=dilations[3])
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilation=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, dilation, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, dilation=dilation))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_MG_unit(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilation=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, dilation=blocks[0]*dilation,
downsample=downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, len(blocks)):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride=1,
dilation=blocks[i]*dilation))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def execute(self, input):
x = self.conv1(input)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = argmax_pool(x, 2, 2)
x = self.layer1(x)
low_level_feat = x
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
return x, low_level_feat
def resnet50(output_stride):
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3,4,6,3], output_stride)
return model
def resnet101(output_stride):
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3,4,23,3], output_stride)
return model
2.2
ASPP即使用不同尺寸的 dilation conv 对 backbone 得到的 feature map 进行卷积,最后 concat 并整合得到新的特征。
import jittor as jt
from jittor import nn
from jittor import Module
from jittor import init
from jittor.contrib import concat
class Single_ASPPModule(Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, kernel_size, padding, dilation):
super(Single_ASPPModule, self).__init__()
self.atrous_conv = nn.Conv(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=1, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def execute(self, x):
x = self.atrous_conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class ASPP(Module):
def __init__(self, output_stride):
super(ASPP, self).__init__()
inplanes = 2048
if output_stride == 16:
dilations = [1, 6, 12, 18]
elif output_stride == 8:
dilations = [1, 12, 24, 36]
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self.aspp1 = Single_ASPPModule(inplanes, 256, 1, padding=0, dilation=dilations[0])
self.aspp2 = Single_ASPPModule(inplanes, 256, 3, padding=dilations[1], dilation=dilations[1])
self.aspp3 = Single_ASPPModule(inplanes, 256, 3, padding=dilations[2], dilation=dilations[2])
self.aspp4 = Single_ASPPModule(inplanes, 256, 3, padding=dilations[3], dilation=dilations[3])
self.global_avg_pool = nn.Sequential(GlobalPooling(),
nn.Conv(inplanes, 256, 1, stride=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm(256),
nn.ReLU())
self.conv1 = nn.Conv(1280, 256, 1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm(256)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def execute(self, x):
x1 = self.aspp1(x)
x2 = self.aspp2(x)
x3 = self.aspp3(x)
x4 = self.aspp4(x)
x5 = self.global_avg_pool(x)
x5 = x5.broadcast((1,1,x4.shape[2],x4.shape[3]))
x = concat((x1, x2, x3, x4, x5), dim=1)
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
return x
class GlobalPooling (Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GlobalPooling, self).__init__()
def execute (self, x):
return jt.mean(x, dims=[2,3], keepdims=1)
2.3 Decoder: Decoder 将 ASPP 的特征放大后与 ResNet 的中间特征一起 concat 得到最后分割所用的特征。
import jittor as jt
from jittor import nn
from jittor import Module
from jittor import init
from jittor.contrib import concat
import time
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
low_level_inplanes = 256
self.conv1 = nn.Conv(low_level_inplanes, 48, 1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm(48)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.last_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv(304, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Conv(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.1),
nn.Conv(256, num_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=True))
def execute(self, x, low_level_feat):
low_level_feat = self.conv1(low_level_feat)
low_level_feat = self.bn1(low_level_feat)
low_level_feat = self.relu(low_level_feat)
x_inter = nn.resize(x, size=(low_level_feat.shape[2], low_level_feat.shape[3]) , mode='bilinear')
x_concat = concat((x_inter, low_level_feat), dim=1)
x = self.last_conv(x_concat)
return x
2.4 完整的模型整合如下: 即将以上部分通过一个类连接起来。
import jittor as jt
from jittor import nn
from jittor import Module
from jittor import init
from jittor.contrib import concat
from decoder import Decoder
from aspp import ASPP
from backbone import resnet50, resnet101
class DeepLab(Module):
def __init__(self, output_stride=16, num_classes=21):
super(DeepLab, self).__init__()
self.backbone = resnet101(output_stride=output_stride)
self.aspp = ASPP(output_stride)
self.decoder = Decoder(num_classes)
def execute(self, input):
x, low_level_feat = self.backbone(input)
x = self.aspp(x)
x = self.decoder(x, low_level_feat)
x = nn.resize(x, size=(input.shape[2], input.shape[3]), mode='bilinear')
return x
3. 模型训练
3.1 模型训练参数设定如下:
# Learning parameters
batch_size = 8
learning_rate = 0.005
momentum = 0.9
weight_decay = 1e-4
epochs = 50
3.2 定义模型、优化器、数据加载器。
model = DeepLab(output_stride=16, num_classes=21)
optimizer = nn.SGD(model.parameters(),
lr,
momentum=momentum,
weight_decay=weight_decay)
train_loader = TrainDataset(data_root='/vocdata/',
split='train',
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True)
val_loader = ValDataset(data_root='/vocdata/',
split='val',
batch_size=1,
shuffle=False)
3.3 模型训练与验证
# lr scheduler
def poly_lr_scheduler(opt, init_lr, iter, epoch, max_iter, max_epoch):
new_lr = init_lr * (1 - float(epoch * max_iter + iter) / (max_epoch * max_iter)) ** 0.9
opt.lr = new_lr
# train function
def train(model, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, init_lr):
model.train()
max_iter = len(train_loader)
for idx, (image, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
poly_lr_scheduler(optimizer, init_lr, idx, epoch, max_iter, 50) # using poly_lr_scheduler
image = image.float32()
pred = model(image)
loss = nn.cross_entropy_loss(pred, target, ignore_index=255)
optimizer.step (loss)
print ('Training in epoch {} iteration {} loss = {}'.format(epoch, idx, loss.numpy()[0]))
# val function
# we omit evaluator code and you can
def val (model, val_loader, epoch, evaluator):
model.eval()
evaluator.reset()
for idx, (image, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
image = image.float32()
output = model(image)
pred = output.numpy()
target = target.numpy()
pred = np.argmax(pred, axis=1)
evaluator.add_batch(target, pred)
print ('Test in epoch {} iteration {}'.format(epoch, idx))
Acc = evaluator.Pixel_Accuracy()
Acc_class = evaluator.Pixel_Accuracy_Class()
mIoU = evaluator.Mean_Intersection_over_Union()
FWIoU = evaluator.Frequency_Weighted_Intersection_over_Union()
best_miou = 0.0
if (mIoU > best_miou):
best_miou = mIoU
print ('Testing result of epoch {} miou = {} Acc = {} Acc_class = {} \
FWIoU = {} Best Miou = {}'.format(epoch, mIoU, Acc, Acc_class, FWIoU, best_miou))
3.4 evaluator 写法:使用混淆矩阵计算 Pixel accuracy 和 mIoU。
class Evaluator(object):
def __init__(self, num_class):
self.num_class = num_class
self.confusion_matrix = np.zeros((self.num_class,)*2)
def Pixel_Accuracy(self):
Acc = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix).sum() / self.confusion_matrix.sum()
return Acc
def Pixel_Accuracy_Class(self):
Acc = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / self.confusion_matrix.sum(axis=1)
Acc = np.nanmean(Acc)
return Acc
def Mean_Intersection_over_Union(self):
MIoU = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / (
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) +
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=0)-
np.diag(self.confusion_matrix))
MIoU = np.nanmean(MIoU)
return MIoU
def Frequency_Weighted_Intersection_over_Union(self):
freq = np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) / np.sum(self.confusion_matrix)
iu = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / (
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) + np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=0) -
np.diag(self.confusion_matrix))
FWIoU = (freq[freq > 0] * iu[freq > 0]).sum()
return FWIoU
def _generate_matrix(self, gt_image, pre_image):
mask = (gt_image >= 0) & (gt_image < self.num_class)
label = self.num_class * gt_image[mask].astype('int') + pre_image[mask]
count = np.bincount(label, minlength=self.num_class**2)
confusion_matrix = count.reshape(self.num_class, self.num_class)
return confusion_matrix
def add_batch(self, gt_image, pre_image):
assert gt_image.shape == pre_image.shape
self.confusion_matrix += self._generate_matrix(gt_image, pre_image)
def reset(self):
self.confusion_matrix = np.zeros((self.num_class,) * 2)
3.5 训练入口函数
epochs = 50
evaluator = Evaluator(21)
train_loader = TrainDataset(data_root='/voc/data/path/', split='train', batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
val_loader = ValDataset(data_root='/voc/data/path/', split='val', batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
learning_rate = 0.005
momentum = 0.9
weight_decay = 1e-4
optimizer = nn.SGD(model.parameters(), learning_rate, momentum, weight_decay)
for epoch in range (epochs):
train(model, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, learning_rate)
val(model, val_loader, epoch, evaluator)