Jittor MNIST 分类教程
完整代码:https://github.com/Jittor/mnistclassification-jittor
MNIST介绍 :
MNIST 数据集可在 http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ 下载, 它是一个对0到9十个数字进行分类的数据集。它包含了四个部分:
训练图像: train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz (9.9 MB, 解压后 47 MB, 包含 60,000 个样本)
训练标签: train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz (29 KB, 解压后 60 KB, 包含 60,000 个标签)
测试图像: t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz (1.6 MB, 解压后 7.8 MB, 包含 10,000 个样本)
测试标签: t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz (5KB, 解压后 10 KB, 包含 10,000 个标签)
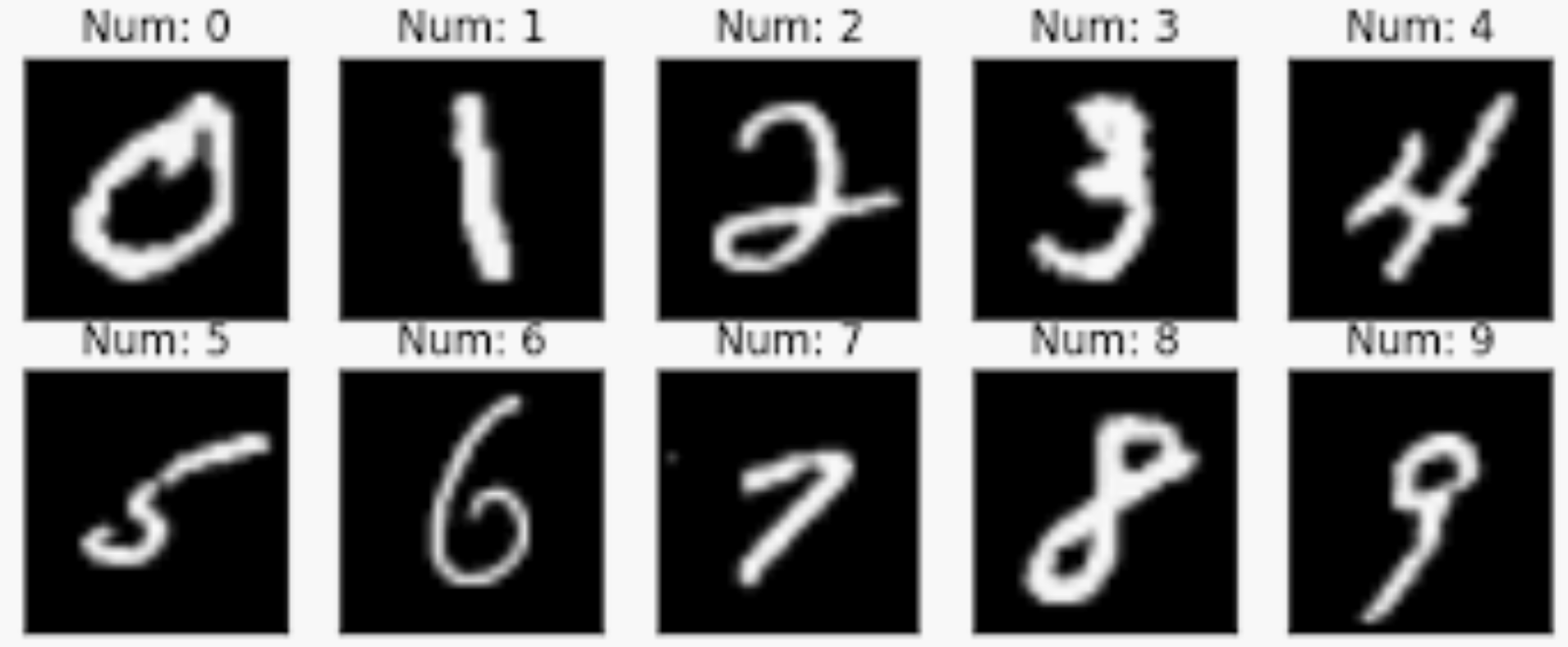
MNIST 数据集如下图所示
使用 Jittor 对 MNIST 进行分类
1.首先第一步,需要引入相关的依赖,如下所示。
# classification mnist example
import jittor as jt # 将 jittor 引入
from jittor import nn, Module # 引入相关的模块
import numpy as np
import sys, os
import random
import math
from jittor import init
if jt.has_cuda:
jt.flags.use_cuda = 1 # jt.flags.use_cuda 表示是否使用 gpu 训练。
# 如果 jt.flags.use_cuda=1,表示使用GPU训练 如果 jt.flags.use_cuda = 0 表示使用 CPU
from jittor.dataset.mnist import MNIST
#由于 MNIST 是一个常见的数据集,其数据载入已经被封装进 jittor 所以可以直接调用。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab as pl # 用于绘制 Loss 曲线 和 MNIST 数据
2.加载 MNIST 数据集,需要继承 Dataset 类,需要实现类中的 __init__() 和 __getitem__() 函数,对于MNIST,实现如下所示.
import gzip
from PIL import Image
from jittor.dataset import Dataset
from jittor_utils.misc import download_url_to_local
class MNIST(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_root="./mnist_data/", train=True ,download=True, batch_size=1, shuffle=False):
# if you want to test resnet etc you should set input_channel = 3, because the net set 3 as the input dimensions
super().__init__()
self.data_root = data_root
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.is_train = train
if download == True:
self.download_url()
filesname = [
"train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz",
"t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz",
"train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz",
"t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz"
]
self.mnist = {}
if self.is_train:
with gzip.open(data_root + filesname[0], 'rb') as f:
self.mnist["images"] = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16).reshape(-1,28, 28)
with gzip.open(data_root + filesname[2], 'rb') as f:
self.mnist["labels"] = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
else:
with gzip.open(data_root + filesname[1], 'rb') as f:
self.mnist["images"] = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16).reshape(-1,28, 28)
with gzip.open(data_root + filesname[3], 'rb') as f:
self.mnist["labels"] = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
assert(self.mnist["images"].shape[0] == self.mnist["labels"].shape[0])
self.total_len = self.mnist["images"].shape[0]
# this function must be called
self.set_attrs(batch_size = self.batch_size, total_len=self.total_len, shuffle= self.shuffle)
def __getitem__(self, index):
img = Image.fromarray (self.mnist['images'][index])
img = np.array (img)
img = img[np.newaxis, :]
return np.array((img / 255.0), dtype = np.float32), self.mnist['labels'][index]
def download_url(self):
resources = [
("http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz", "f68b3c2dcbeaaa9fbdd348bbdeb94873"),
("http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz", "d53e105ee54ea40749a09fcbcd1e9432"),
("http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz", "9fb629c4189551a2d022fa330f9573f3"),
("http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz", "ec29112dd5afa0611ce80d1b7f02629c")
]
for url, md5 in resources:
filename = url.rpartition('/')[2]
download_url_to_local(url, filename, self.data_root, md5)
3.模型的定义:我们定义模型需要继承 jittor 的 Module 类。需要实现 __init__ 函数和 execute 函数。__init__ 用于定义模型由哪些操作组成, execute 函数定义了模型执行的顺序和模型的返回值。
class Model (Module):
def __init__ (self):
super (Model, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv (1, 32, 3, 1) # no padding
self.conv2 = nn.Conv (32, 64, 3, 1)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm(64)
self.max_pool = nn.Pool (2, 2)
self.relu = nn.Relu()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear (64 * 12 * 12, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear (256, 10)
def execute (self, x) :
# it's simliar to forward function in Pytorch
x = self.conv1 (x)
x = self.relu (x)
x = self.conv2 (x)
x = self.bn (x)
x = self.relu (x)
x = self.max_pool (x)
x = jt.reshape (x, [x.shape[0], -1])
x = self.fc1 (x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2 (x)
return x
4.对模型进行训练。对模型训练需要定义训练时的超参数,以及需要定义训练过程。训练函数在 train 函数中定义,测试函数在 val 函数中定义。
def train(model, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, losses, losses_idx):
model.train()
lens = len(train_loader)
for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(train_loader):
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = nn.cross_entropy_loss(outputs, targets)
optimizer.step (loss)
losses.append(loss.numpy()[0])
losses_idx.append(epoch * lens + batch_idx)
if batch_idx % 10 == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx, len(train_loader) ,
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.numpy()[0]))
def val(model, val_loader, epoch):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
total_acc = 0
total_num = 0
for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(val_loader):
batch_size = inputs.shape[0]
outputs = model(inputs)
pred = np.argmax(outputs.numpy(), axis=1)
acc = np.sum(targets.numpy()==pred)
total_acc += acc
total_num += batch_size
acc = acc / batch_size
print(f'Test Epoch: {epoch} [{batch_idx}/{len(val_loader)}]\tAcc: {acc:.6f}')
print('Test Acc =', total_acc / total_num)
batch_size = 64
learning_rate = 0.1
momentum = 0.9
weight_decay = 1e-4
epochs = 1
losses = []
losses_idx = []
train_loader = MNIST(train=True, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
val_loader = MNIST(train=False, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
model = Model ()
optimizer = nn.SGD(model.parameters(), learning_rate, momentum, weight_decay)
for epoch in range(epochs):
train(model, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, losses, losses_idx)
val(model, val_loader, epoch)
5.绘制 Loss 曲线 : 将 Loss 曲线进行可视化。
pl.plot(losses_idx, losses)
pl.xlabel('Iterations')
pl.ylabel('Train_loss')
6.存储模型:模型训练完成需要存储起来,下面代码展示了 Jittor 如何进行存储模型。
model_path = './mnist_model.pkl'
model.save(model_path)
7.加载模型并对模型进行测试,下面展示了 Jittor 如何加载模型,并对模型进行测试。
def vis_img(img):
np_img = img.numpy().reshape([28, 28])
plt.imshow(np_img, cmap='gray')
new_model = Model()
new_model.load_parameters(jt.load(model_path))
data_iter = iter(val_loader)
val_data, val_label = next(data_iter)
print (val_label.shape)
outputs = new_model(val_data)
prediction = np.argmax(outputs.numpy(), axis=1)
print (prediction)
print (val_label)
vis_img(val_data)