JMedSeg: Jittor医学图像智能分割模型库开源了!
Part 1
医学图像分割旨在从计算机断层扫描 (CT)、磁共振成像 (MRI) 和 X 射线等不同类型的医学图像中分离器官或病变组织。作为医学图像智能分析最底层、最关键的步骤,精确的医学图像分割被广泛认为是医学研究和辅助诊断等领域的最具挑战性的领域之一。
首先,我们很少有完美的像素级数据集用于医学图像分割模型的训练。在医学图像分割领域,由于有经验的医生日常工作非常繁重,难以进行像素级的手工标注,获取医学图像的手工标注非常昂贵且难以实现。
其次,分割器官形态各异,目标器官或病变的大小和形状不仅因人而异,也可能因图像的切片而异。
再者,不同医院使用的不同设备具有不同的设定,获取的数据具有不同的分布,使得医学图像分割模型难以训练,尽管随着深度学习方法和技术的发展,医学图像智能分割的精度有了显著的提高,但我们的实测表明目前发表的各种分割模型稳定性差,难以应用到真实环境。
如何在少量训练数据的支撑下获得具有出色泛化性能的医学图像分割神经网络模型,是当前深度学习应用于医学领域的最基础的挑战。
JMedSeg研发团队对近年来在顶级国际会议和期刊等科研平台发表的典型医学图像分割模型进行了全面探索和基于Jittor的实现,并进行所有模型的训练和对比实验!
在此基础上,JMedSeg研发团队对现有的方法进行取长补短,提出了基于 MoCo 对比学习框架的自监督预训练框架、数据增强方法,以及STN 空间变形网络结合的SAS(Self supervise learning & data Augmentation & Spatial transformer networks) 医学图像分割模型训练框架。
用户可以通过这些方法的组合使用,取得更好的分割和泛化性能,在有限数据的条件下得到高精度、高稳定的分割模型。SAS分割模型训练框架是医学图像智能分割向实际应用迈出的最坚实的一步!
图1给出医学图像分割模型泛化性能实验。图中的Original是《模式识别》课上同学用自己的手机从普通计算机屏幕上拍摄的医学图像,用于测试分割模型的泛化性能。所有被测试的模型都用医学图像原始数据训练。Ours是SAS训练框架训练UNet的分割结果。UNet是直接使用数据训练的分割结果、Color Aug、STN、SSL分别对应于不同训练方法得到的UNet分割结果。
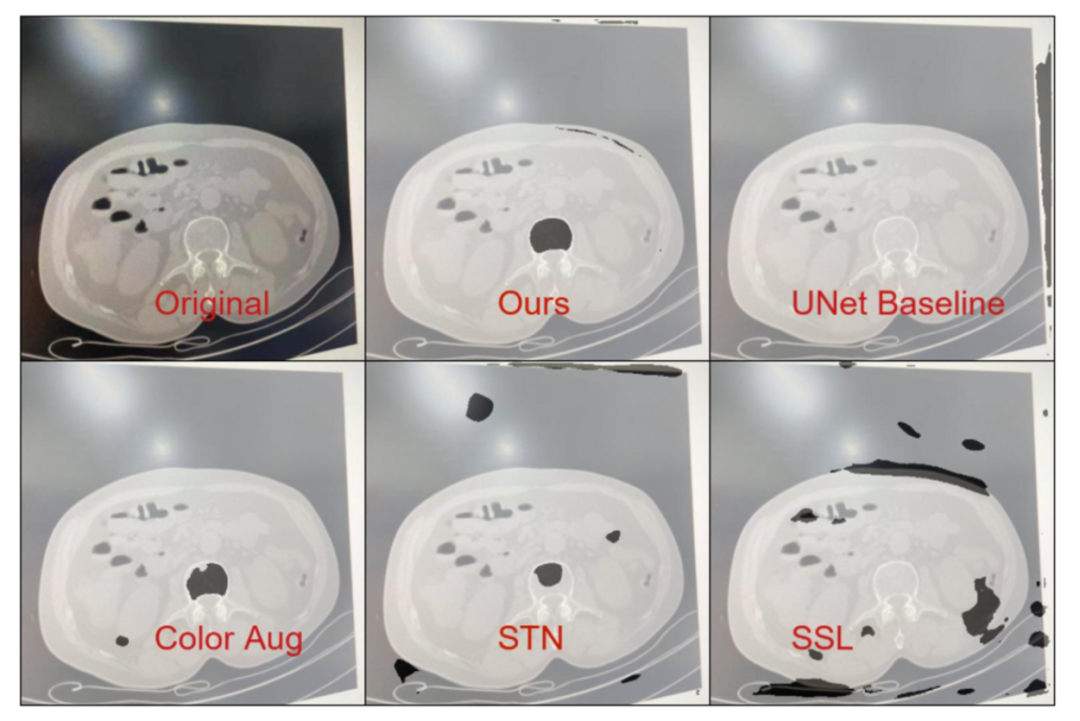
图1 医学图像分割模型泛化性能实验
本次发布的JMedSeg医学图像智能分割模型库包括UNet及其10余个变种网络,以及近年来发布的用于自然图像的分割模型(DANet、OCRNet、SETR 等)共计20余种神经网络模型,以及JMedSeg团队提出的高精度强泛化医学图像分割模型的SAS训练框架。用户既可以基于这些模型进行进一步的探索,也可以根据自己的数据和任务进行迁移学习而得到高精度、高泛化性能的分割模型,为后续的医学研究和诊断奠定坚实的基础。
Part 2
JMedSeg支持UNet及其众多变种。从Attention UNet[2]到Attention R2UNet[3],从发表于IEEE TMI的UNet++[4] 到UNet+++[5],有结合ResNet和UNet的MultiResUNet和ResUNet[6],有结合VGGNet和UNet的TernausUNet[7],也有结合DenseNet和UNet的DenseUNet和Hardnet[8],以及SESCUNet[9],CSNet[10],CENet[11]和U2Net[12]也有支持。
除UNet家族外,JMedSeg还支持了部分用于自然图像分割的著名神经网络模型,例如:
以及发表于CVPR2021的 SETR[22]。
目前 JMedSeg 仅支持单张图片分割模型,其余连续帧分割模型如 3DUNet[30] 及其变种,以及我们在 ICIP2021 最新工作MEPDNet[32] 模型以及训练框架等将在后续版本中进行发布。
损失函数方面,JMedSeg 支持CE Loss,IoU Loss,Dice Loss,以及Focal Loss 主流损失函数用于模型训练。后续将新增Dual-Term Loss[31] 等最新的用于医学图像分割的损失函数支持。模型评价指标目前支持IoU,Dice,Recall,Precision以及Average Surface Distance (ASD)。
图2给出了JMedSeg 支持的部分模型示意图,其中按自左至右、自上而下的顺序分别为:
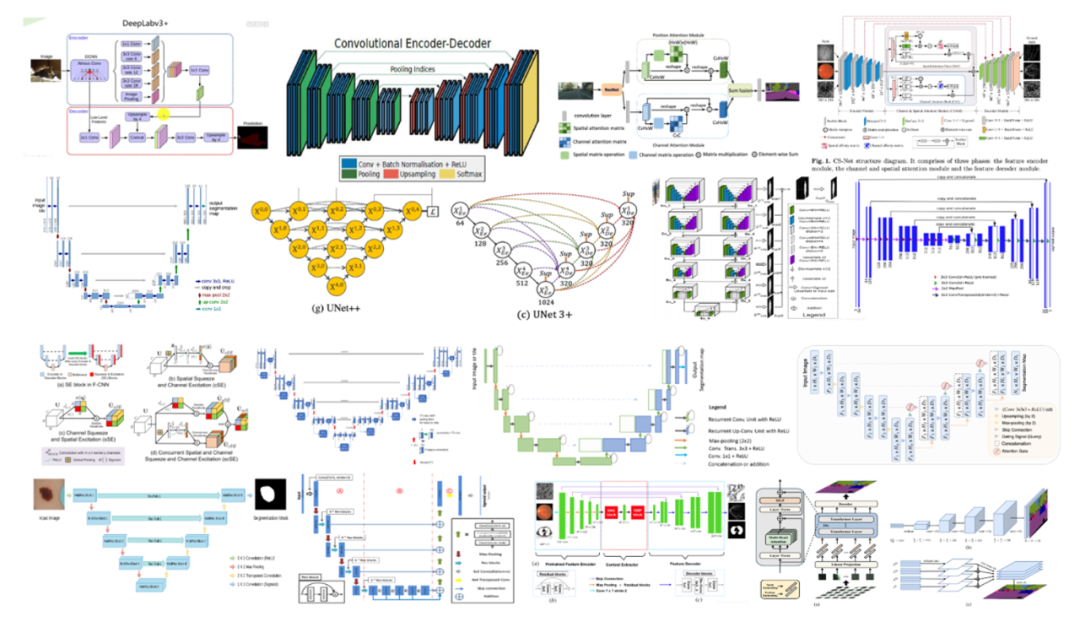
Part 3
在JMedSeg 中,研发团队提出了对于医学图像分割任务的SAS训练框架,它结合自监督预训练、数据增强、以及空间变形网络,助力医学图像分割模型获得出色的泛化性能。
框架简图如下所示:
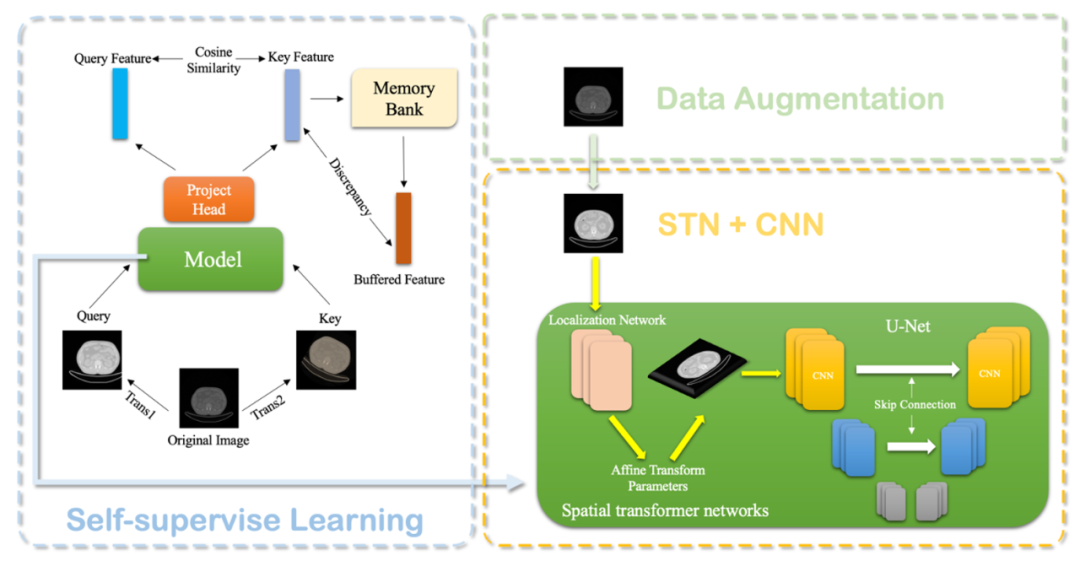
Dan[23]等人证明,通过对图像类数据集的自监督学习,可以提高深度学习模型的稳定性和泛化性能。受到MoCo[24]和SimCLR[25]的启发,JMedSeg研发团队在进行监督学习之前,先对模型进行了MemoryBank对比学习预训练,使用模型提取得到同一个正例样本经过各种图像变换的不同变体的高层语义特征,并同样提取负例的语义特征,通过最大化这两个语义特征之间的差别,得到了可以有效将数据集嵌入到低维空间的特征抽取网络的参数。

同时,[26-28]表明,数据增强,即对于输入数据做如旋转、翻转、亮度调整等变换同样对于深度神经网络的稳定性大有裨益。因此JMedSeg研发团队也进行了数据增强的操作,变相对数据集进行了扩容,以便让JMedSeg中的UNet分割模型接触到更广泛的数据分布。
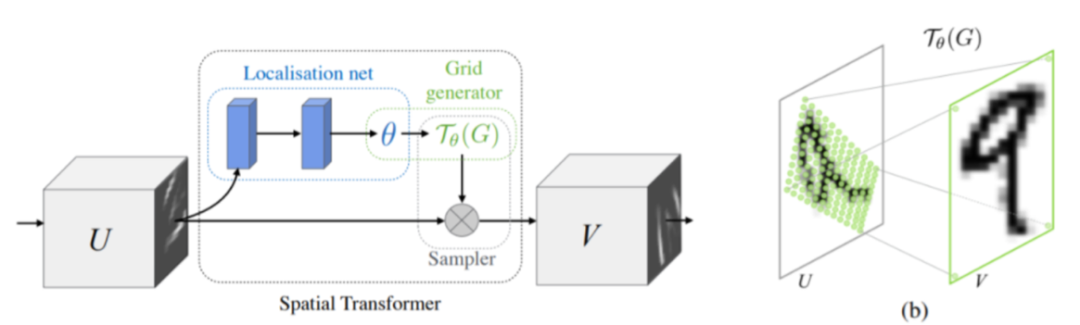
Jaderberg等人[29] 提出了空间变形网络Spatialtransformer networks (STN),通过学习一个自适应的仿射变换,对图像的几何外观进行自动校准。其中,被称为局部化网络的浅层卷积网络得到一组2x3的矩阵,利用如下公式可以得到仿射变换后图像上的像素点对应原图的像素点的位置:

然后利用双线性插值得到具体的像素值。STN可以被嵌入任何利用深度卷积网络进行端到端训练预测的模型中,因此也可以加入UNet等其他网络中。由于腰椎CT片中存在由于仪器位置,病患姿势等造成的图片几何形态不一致,因此利用STN可以增加图像数据集的正则性,实现更精准的分割。
最终仅在85人次的腰椎骨松质训练数据下,基于不同训练方法的UNet对手机拍摄的腰椎CT图像分割结果如图1所示。可见,不使用任何辅助手段得到的UNet具有最差的检测结果,而单独使用SSL,数据增强以及 STN 均不如三者的结合。
Part 4
JMedSeg开源库
在柳瑞阳助教的带领下,选修《模式识别》课程的汪元标,游嘉诚,卢星宇,李胜锐,杨雅儒,黄翰,李响等三十多位同学对现有的医学图像分割方法进行了全面的探索,在Jittor平台上复现了所有的分割模型,并在相同的医学图像数据集上训练和对比测试。
JMedSeg医学图像分割库全部代码已开源在:
https://github.com/THU-CVlab/JMedSeg
本仓库收录了jittor框架实现的如下医学图像分割模型:
UNet
SegNet
DeepLab V2
DANet
EANet
HarDNet 及其改动版本HarDNet_alter
PSPNet
OCNet
OCRNet
DLinkNet
AttentionUNet
UNet++
UNet+++
DenseUNet
TernausNet
CSNet
SCSENet
U2Net series
MultiResUNet
R2UNet
R2Attention UNet
CENet
LRF-EANet
SETR
如果大家在使用过程中发现任何问题,请在github提交issue或者pr。也可以加入Jittor开发者的QQ交流群,交流计图使用中的问题或心得,期待您提出宝贵的意见!

参考文献
Ronneberger O, FischerP, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assistedintervention. Springer, Cham, 2015: 234-241. Oktay O, Schlemper J,Folgoc L L, et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999, 2018. Alom M Z, Hasan M,Yakopcic C, et al. Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Network based onU-Net (R2U-Net) for Medical Image Segmentation[J]. 2018. Zhou Z, Siddiquee M MR, Tajbakhsh N, et al. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 39(6): 1856-1867. Huang H, Lin L, Tong R,et al. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation[C]. ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 2020: 1055-1059. Ibtehaz N, Rahman M S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 121: 74-87. Iglovikov V, Shvets A.Ternausnet: U-net with vgg11 encoder pre-trained on imagenet for image segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.05746, 2018. Chao P, Kao C Y, Ruan YS, et al. Hardnet: A low memory traffic network[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 3552-3561. Roy A G, Navab N,Wachinger C. Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’in fullyconvolutional networks. International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, Cham, 2018: 421-429. Mou L, Zhao Y, Chen L, et al. CS-Net: channel and spatial attention network for curvilinear structuresegmentation[C]. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, Cham, 2019: 721-730. Shao W, Tang S, Pan X, et al. Channel equilibrium networks for learning deep representation[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2020: 8645-8654. Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, et al. U2-Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. PatternRecognition, 2020, 106: 107404. Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R.Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machineintelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. Chen L C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, etal. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J]. arXivpreprint arXiv:1706.05587, 2017. Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, et al. Pyramidscene parsing network[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Visionand Pattern Recognition. 2017: 2881-2890. Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, et al. Dualattention network for scene segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 3146-3154. Zhou L, Zhang C, Wu M. D-linknet:Linknet with pretrained encoder and dilated convolution for high resolutionsatellite imagery road extraction[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference onComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. 2018: 182-186. Huang H, Yang W, Chen X, et al. Eanet: Enhancing alignment for cross-domain person re-identification[J]. arXivpreprint arXiv:1812.11369, 2018. Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, et al. Deephigh-resolution representation learning for human poseestimation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 5693-5703. Yuan Y, Huang L, Guo J, et al. Ocnet: Object context network for scene parsing[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00916,2018. Yuan Y, Chen X, Wang J. Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation[C]. ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Part VI 16. 2020: 173-190. Zheng S, Lu J, Zhao H, et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2021: 6881-6890. Hendrycks D, Mazeika M, Kadavath S, etal. Using self-supervised learning can improve model robustness and uncertainty[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.12340, 2019. He K, Fan H, Wu Y, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]. Proceedings of theIEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020: 9729-9738. Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, et al. Asimple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2020:1597-1607. Eaton-Rosen Z, Bragman F, Ourselin S, etal. Improving data augmentation for medical image segmentation[C]. The 1st Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (MIDL 2018), Amsterdam, 2018:1-3 Shorten C, Khoshgoftaar T M. A survey onimage data augmentation for deep learning[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2019, 6(1):1-48. Khosla C, Saini B S. EnhancingPerformance of Deep Learning Models with different Data AugmentationTechniques: A Survey[C]. International Conference on Intelligent Engineering and Management (ICIEM). IEEE, 2020: 79-85. Jaderberg M, Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Spatial transformer networks[J]. Advances in Nural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 28: 2017-2025. Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp S S, et al. 3D U-Net: learning densevolumetric segmentation from sparse annotation[C]. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention. Springer, 2016: 424-432. Huang Q, Zhou Y, Tao L. Dual-Term Loss Function For Shape-Aware MedicalImage Segmentation[C]. IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). IEEE, 2021: 1798-1802. Dachuan Shi , Ruiyang Liu , Linmi Tao, Zuoxiang He, and Li Huo. Multi-Encoder Parse-Decoder Network for Sequential Medical Image Segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on image processing, ICIP 2021.
您可通过下方二维码,关注清华大学图形学实验室,了解计算机图形学、Jittor深度学习框架、CVMJ期刊和CVM会议的相关资讯。
